Abstract
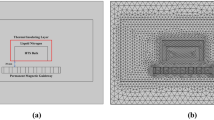
High-temperature superconducting (HTS) maglev is a kind of new maglev structure mode. In actual operation, due to the arrangement and assembly error of the magnet of permanent magnet guideway (PMG) as well as the loss and material stripping during operation, superconductive bulks are always in a state of random fluctuation. In order to study the influence of the irregularity of PMG and bridge deflection on the levitation characteristics of superconductors, the model using the E-J power law model is established in COMSOL Multiphysics 5.6, and the random lateral and vertical irregularity coupled with the bridge deflection is added to PMG for research. The results show that the effects of random excitation and bridge deflection on levitation characteristics are coupled and interact with each other. The vertical excitation and bridge deflection affect the guidance force of dewar while the lateral excitation also affects the levitation force. The levitation characteristics of dewar fluctuate with the fluctuation of random excitation. In the condition without excitation and bridge deflection, the levitation force of the dewar used in this paper is maintained at 3.455kN, the guiding force is − 84.987 N, and the average current density is 1.971MA/m2. The levitation characteristics of dewar will fluctuate with the fluctuation of random excitation. When the bridge deflection is added, the levitation force, guidance force, and average current density of dewar will increase with the increase of bridge deflection. Taking the variation of levitation force as an example, the maximum suspension force is maintained near 5.572kN when the bridge deflection is 2 mm, 8.358kN when the bridge deflection is 4 mm, and 11.858kN when the bridge deflection is 6 mm regardless of random excitation. There is a critical point of levitation force when the dewar is suspended on PMG. If the gap between dewar and PMG exceeds the critical point, the average current density will reverse and the levitation force will be negative. The critical point of the model used in this paper is around 21 mm above the PMG. These results provide a reference for the working condition prediction of the HTS Maglev train.














Similar content being viewed by others
References
Trabelsi, Z., Hannachi, E., Alotaibi, S.A., Slimani, Y., Almessiere, M.A., Baykal, A. Superconductivity phenomenon: fundamentals and theories. Superconducting Materials. Springer, Singapore. (2022)
Okano, M., Iwamoto, T., Furuse, M., Fuchino, S., Ishii, I.: Running performance of a pinning-type superconducting magnetic levitation guide. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 43, 999–1002 (2006)
Deng, Z., Li, J., Zhang, W., Gou, Y., Ren, Y., Zheng, J.: High temperature superconducting magnetic levitation vehicles: dynamic characteristics while running on a ring test line. IEEE Veh. Technol. Mag. 12(3), 95–102 (2017)
Werfel F.N., et al.: Superconductor bearings, flywheels and transportation, Supercond. Sci. Technol., 25 Art. No.014007 (2012)
Hull, J.R.: Superconducting bearings. Supercond. Sci. Technol. 13, R1–R15 (2000)
Murakami, M.: Processing and applications of bulk RE-Ba-Cu-O superconductors. Int. J. Appl. Ceram. Technol. 4, 225–241 (2007)
Ki, T., Jeong, S., Han, Y.H., et al.: Thermal packaging of high temperature superconductor bulk for superconducting flywheel energy storage. IEEE Trans. Appl. Supersond. 25(3), 5701104 (2013)
Nakamura, T., Tamada, D.D., Yanagi, Y., et al.: Development of a superconducting bulk magnet for NMR and MRI. J. Magn. Reson. 259, 68–75 (2015)
Hamrita, A., Slimani, Y., Ben, S.M., K., Hannachi E., Bessais L., Ben Azzouz F., Ben Sale M.: Superconducting properties of polycrystalline YBa2Cu3O7–d prepared by sintering of ball-milled precursor powder. Ceram. Int. 40(1), 1461–1470 (2014)
Ben Salem, M.K., Hannachi, E., Slimani, Y., Hamrita, A., Zouaoui, M., Bessais, L., Ben, S.M., Ben, A.F.: SiO2 nanoparticles addition effect on microstructure and pinning properties in YBa2Cu3Oy. Ceram. Int. 40(3), 4953–4962 (2014)
Slimani, Y., Hannachi, E., Ben, S.M., K., Hamrita A., Varilci A., Dachraoui W., Ben Salem M., Ben Azzouz F.: Comparative study of nano-sized particles CoFe2O4 effects on superconducting properties of Y-123 and Y-358. Physica B: Condensed Matte. 450(1), 7–15 (2014)
Slimani Y., Hannachi E., Ben Salem M. K., Hamrita A., Ben Salem M. & Ben Azzouz F.: Excess Conductivity study in nano-CoFe2O4-Added YBa2Cu3O7−d and Y3Ba5Cu8O18±x superconductors. J. Supercond. Nov. Magn. 28, 3001–3010 (2015)
Slimani, Y., Almessiere, M.A., Hannachi, E., Mumtaz, M., Manikandan, A., Baykal, A., Ben, A.F.: Improvement of flux pinning ability by tungsten oxide nanoparticles added in YBa2Cu3Oy superconductor. Ceram. Int. 45(6), 6828–6835 (2019)
Hannachi, E., Almessiere, M.A., Slimani, Y., Baykal, A., Ben, A.F.: AC susceptibility investigation of YBCO superconductor added by carbon nanotubes. J. Alloy. Compd. 812(5), 152150 (2020)
Koblischka-Veneva A., Koblischka. M. R.: High-Tc cuprate superconductors: materials, structures and properties. Superconducting Materials. Springer, Singapore. (2022)
Moon, F.C., Yanoviak, M.M., Ware, R.: Hysteretic levitation forces in superconducting ceramics. Appl. Phys. Lett. 52(18), 1534–1536 (1998)
Wang, X.: Research on guidance force of high temperature superconductor YBCO bulks over the permanent magnet guideway. Southwest Jiaotong University, Chengdu (2003)
Ren, Z.: Experimental study and numerical calculation of high temperature superconducting magnetic levitation on permanent magnet guideway. Southwest Jiaotong University, Chengdu (2004)
Navau, C., Sanchez, A., Pardo, E., et al.: Equilibrium positions due to different cooling processes in superconducting levitation systems. Supercond. Sci. Technol. 17(7), 828–832 (2004)
Li, J., Li, H., Zheng, J., Zheng, B., Huang, H., Deng, Z.: Nonlinear vibration behaviors of high-T-c superconducting bulks in an applied permanent magnetic array field. J. Appl. Phys. 121(24), 243901 (2017)
Li, H., Liu, D., Hong, Y., Yu, J., Zheng, J., Deng, Z.: Modeling and identification of the hysteresis nonlinear levitation force in HTS maglev systems. Supercond. Sci. Technol. 33(5), 054001 (2020)
Yang, J., Chi, M., Wu, X., Ji, Y., Liang, S.: A simulation on levitation force and guidance force of the HTSC bulk under the permanent magnetic guideway’s stochastic excitation. J. Supercond. Novel Magn. 34, 3099–3114 (2021)
Chen, L., Deng, Z., Deng, B., Zheng, J.: Numerical simulations on the vertical dynamic characteristics of high-temperature superconducting bulk. J. Supercond. Novel Magn. 34, 683–694 (2021)
Huang, H., Deng, Z., Zhang, X., Cheng, Y., Hong, Y., Li, H.: Numerical simulation and parameter identification of dynamic levitation force of HTS pinning Maglev for engineering application. J. Supercond. Novel Magn. 34, 2753–2760 (2021)
Gou, X., Zheng, X., Zhou, Y.: Drift of levitated/suspended body in high-tc superconducting levitation systems under vibration—part i: a criterion based on magnetic force-gap relation for gap varying with time. IEEE Trans. Appl. Supercond. 17(3), 3795–3802 (2007)
Weinberger, B.R., Lynds, L., Hull, J.R.: Magnetic bearings using high-temperature superconductors: some practical considerations. Supercond. Sci. Technol. 3(7), 381–388 (1990)
Suginra, T., Shimizu, T., Tange, T.: Effect of the ratio between the natural frequencies of a high-Tc superconducting bearing system on internal resonance. Physica C 468(15–20), 2119–2124 (2008)
Tsuda, M., Kojina, T., Yagai, T., et al.: Vibration characteristics in magnetic levitation type seismic isolation device composed of multiple HTS bulks and permanent magnets. IEEE Trans. Appl. Supercond. 17(2), 2059–2062 (2007)
Li, H., Deng, Z., Li, J., Li, Y., Zheng, J.: Lateral motion stability of high-temperature superconducting maglev systems derived from a nonlinear guidance force hysteretic model. Supercond. Sci. Technol. 31(7), 075010 (2018)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ji, Y., Chi, M., Yang, J. et al. The Levitation Characteristics of HTS Bulks Under the Effect of Bridge Deflection Coupled with Random Excitations. J Supercond Nov Magn 35, 3157–3175 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10948-022-06319-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10948-022-06319-0