Abstract
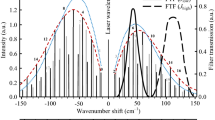
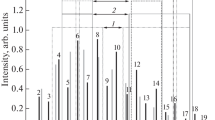
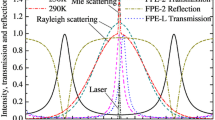
We perform the rotational Raman temperature measurements in the troposphere and lower stratosphere with high performance. Depending on the aerosol content and presence of clouds in the lower troposphere, the rotational Raman lidar (RRL) is the lidar technique of choice for temperature measurements. However, the Raman filter design is a technical difficulty in RRL systems. Considering the higher spectral resolution and compactness, we select several photonic crystals to construct a novel spectroscopic filter for extracting the required rotational Raman spectrum (RRS) signals of atmospheric molecules. We describe in detail the principle to design the photonic-crystal filter. To verify the feasibility of the novel spectroscopic filter, we carry out some numerical calculations, and our results show that the novel spectroscopic filter has the capability to fine draw the required RRS signal and suppress sufficiently elastic signals. For the RRL system which uses the novel spectroscopic filter, we obtain that a statistical temperature error is less than 1 K up to a height of 3.2 and 5.6 km for daytime and nighttime measurements, respectively. Our simulation conditions are as follows: 532 nm laser with 500 mJ energy, and 10 Hz pulse repeating rate, a 300 mm diameter Cassegrain reflecting telescope with 1000 mm focus length, 0.2 mm diameter multimode optical fiber which sets the field of view (FOV) of receiving system to 0.2 mrad, 45 m range resolution, 9 min observation time, overall optical-system efficiency of 0.6, and a special atmospheric model which integrates the US standard model of 1976 with an actual Mie scattering profile obtained from practical observations.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
U. N. Singh, P. Keckhut, T. J. McGee, et al., J. Geophys. Res., 101, 10287 (1996).
K. D. Evans, S. H. Melfi, R. A. Ferrare, and D. A. Whiteman, J. Appl. Opt., 36, 2594 (1997).
F. K. Theopld and J. Bosenberg, J. Atmos. Ocean. Technol., 10, 165 (1993).
D. Hua, M. Uchida, and T. Kobayashi, J. Appl. Opt., 44, 1305 (2005).
A. Behrendt and J. Reichardt, J. Appl. Opt., 39, 1372 (2000).
A. Behrendt, T. Nakamura, M. Onishi, et al., J. Appl. Opt., 41, 7657 (2002).
A. Behrendt, T. Nakamura, and T. Tsuda, J. Appl. Opt., 43, 2930 (2004).
A. Behrendt, “Temperature measurements with lidar,” in: C. Weitkamp (Ed.), Lidar: Range-Resolved Optical Remote Sensing of the Atmosphere, Springer Series in Optical Sciences, Springer, New York (2005), Vol. 102, 273.
M. Radlach, A. Behrendt, and V. Wulfmeyer, Atmos. Chem. Phys., 8, 159 (2008).
D. Kim and H. Cha, J. Kor. Phys. Soc., 39, 838 (2001).
I. Balin, I. Serikov, S. Bobrovnikov, et al., J. Appl. Phys. B., 79, 775 (2004).
Y. F. Arshinov, S. M. Bobrovnikov, V. E. Zuev, et al., J. Appl. Opt., 22, 2984 (1983).
A. Ansmann, Yu. Arshinov, S. Bobrovnikov, et al., Proc. SPIE, 3583, 49l (1998).
J. Su, Y. Zhang, Y. Zhao, et al., Chinese J. Lasers, 34, 92 (2007) [in Chinese].
J. Mao, D. Hua, and Y. Wang, et al., Opt. Commun., 282, 3313 (2009).
J. Liu, D. Hua, and Y. Li, “Rotational Raman lidar for daytime-temperature profiling of the atmospheric boundary layer,” Acta Opt. Sinica, 27, 755 (2007) [in Chinese].
J. Mao, D. Hua, L. Hu, et al., “Design of spectroscopic filter of optical-fiber rotational Raman lidar for temperature profiling,” Acta Opt. Sinica, 230, 7 (2010) [in Chinese].
X. Lv, “The research in application of the photonic crystal filter,” Urumqi: Master Papers of Xinjiang University (2006), Vol. 6.
S. Shu and M. Chen, “Design of one-dimensional photonic-crystal filter,” J. Guilin Uni. Electron. Technol., 28, 210 (2008).
Z. Yuan, X. Lu, W. Ou, and S. Li, Laser Infrared, 36, 203 (2006).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mao, J., Zhao, H., Sheng, H. et al. A novel spectroscopic filter used in rotational Raman lidar for the temperature profiling. J Russ Laser Res 34, 129–138 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10946-013-9333-z
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10946-013-9333-z