Abstract
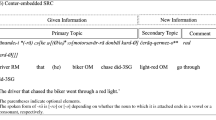
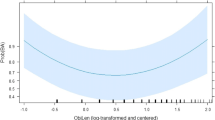
Verb-doubling, where a copy of the main verb occurs both before and after the direct object, is a structure commonly used in Chinese in sentences containing a frequency or duration phrase. In Cantonese, verb-doubling is highly optional and therefore problematic for existing syntactic, semantic, and pragmatic accounts of its distribution in Mandarin. The current study investigates the role of grammatical weight and syntactic priming in the choice of verb-doubling in Cantonese. Following (Hawkins in Efficiency and complexity in grammars, Oxford University Press, Oxford, 2004) theory of efficiency and complexity in grammars, we hypothesized that speakers would choose verb-doubling over the canonical structure more often when the object NP was heavy, in order to minimize processing domains. In addition, we expected an effect of syntactic priming whereby the choice of structure is influenced by a previously encountered structure. The results of two elicited production experiments revealed no weight-based preference for verb-doubling, and only minor effects of grammatical weight, but clear effects of syntactic priming: (1) for both canonical primes and verb-doubling primes, speakers tended to repeat previously heard structures; (2) the priming effect was just as strong in the heavy NP condition, where speakers made more errors recalling the semantic content of the sentence, suggesting that semantic information is represented separately from syntactic information; (3) the priming effect was stronger for informationally accurate responses, suggesting that recently activated structures are easier to produce than other structures under conditions of increased cognitive load. We conclude that the choice between verb-doubling and canonical structure in Cantonese is easily influenced by the structure of recently encountered sentences, with weight effects, if any, being more difficult to detect.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Arnold J. E., Wasow T., Asudeh A., Alrenga P. (2004) Avoiding attachment ambiguities: The role of constituent ordering. Journal of Memory and Language 51: 55–70
Arnold J. E., Wasow T., Losongco A., Ginstrom R. (2000) Heaviness vs. newness: The effects of structural complexity and discourse status on constituent ordering. Language 76: 28–55
Bock J. K. (1986) Syntactic persistence in language production. Cognitive Psychology 18: 355–387
Bock J. K., Dell G. S., Chang F., Onishi K. H. (2007) Persistent structural priming from language comprehension to language production. Cognition 104: 437–458
Bock J. K., Griffin Z. M. (2000) The persistence of structural priming: Transient activation or implicit learning? Journal of Experimental Psychology: General 129: 177–192
Bock J.K., Loebell H. (1990) Framing sentences. Cognition 35: 1–39
Bresnan J. W. (2006) Is syntactic knowledge probabilistic? Experiments with the English dative alternation. In: Featherston S., Sternefeld W. (eds) Roots: Linguistics in, search of its evidential base. Mouton de Gruyter, Berlin, pp 75–96
Chang C. H.-H. (1991) Thematic structure and verb copying in Mandarin Chinese. Language Sciences 13: 399–419
Cheung, K. S. A. (2006). Processing Factors in Language Comprehension and Production: The Case of Cantonese Dative Constructions. MPhil thesis, University of Hong Kong.
Ching, H. L. H. (2008). The advantages of topicalization: An experimental study of sentence processing in Cantonese. MPhil thesis, University of Hong Kong.
Corley M., Scheepers C. (2002) Syntactic priming in English sentence production: Categorical and latency evidence from an internet-based study. Psychonomic Bulletin and Review 9: 126–131
Fan K., Lee T., Lun C., Luke K. K., Tung P., Cheung K. H. (1997) Guide to LSHK Cantonese Romanization of Chinese characters. Linguistic Society of Hong Kong, Hong Kong
Ferreira V. S., Dell G. S. (2000) Effect of ambiguity and lexical availability on syntactic and lexical production. Cognitive Psychology 40: 296–340
Francis E.J. (2010) Grammatical weight and relative clause extraposition in English. Cognitive Linguistics. 21: 35–74
Hartsuiker R. J., Kolk H. H. J. (1998) Syntactic facilitation in agrammatic sentence production. Brain and Language 62: 221–254
Hawkins J. A. (1994) A performance theory of order and constituency. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge
Hawkins J. A. (2001) Why are categories adjacent?. Journal of Linguistics 37: 1–34
Hawkins J. A. (2004) Efficiency and complexity in grammars. Oxford University Press, Oxford
Hsieh M.-L. (1992) Analogy as a type of interaction: The case of verb copying. Journal of the Chinese Language Teachers Association 27: 75–92
Huang, C. T. J. (1982). Logical Relations in Chinese and the Theory of Grammar. Ph.D. Dissertation, MIT.
Li Y.-H. A. (1990) Order and constituency in Mandarin Chinese. Kluwer, Dordrecht
Liu X. (1996) The verb copying construction—a case of discourse backgrounding. Journal of the Chinese Language Teachers Association 31: 57–75
Liu X. (1997) The verb-copying construction and imperfectivity. Journal of the Chinese Language Teachers Association 32: 1–13
Liu, Y. H. S. (2006). An experimental study of verb-doubling and domain minimization in Cantonese. BCogSc thesis, University of Hong Kong.
Lohse B. L., Hawkins J. A., Wasow T. (2004) Domain minimization in English verb-particle constructions. Language 80: 238–261
Matthews S., Yeung L. Y. Y. (2001) Processing motivations for topicalization in Cantonese. In: Horie K., Sato S. (eds) Cognitive-functional linguistics in an East Asian context. Kurosio, Tokyo, pp 81–102
Matthews S., Yip V. (1994) Cantonese: A comprehensive grammar. Routledge, London
Paris M. -C. (1988) Durational complements and verb copying in Chinese. Tsing Hua Journal of Chinese Studies 28: 423–439
Paul W. (2002) Proxy categories in phrase structure theory and the Chinese VP. Cahiers de Linguistique Asie Orientale 31: 137–174
Potter M. C., Lombardi L. (1990) Regeneration in the short-term recall of sentences. Journal of Memory Language 29: 633–654
Potter M. C., Lombardi L. (1998) Syntactic priming in immediate recall of sentences. Journal of Memory and Language 38: 265–282
Rohdenburg G. (1999) Clausal complementation and cognitive complexity in English. In: Neumann F. W., Schülting S. (eds) Anglistentag 1998 Erfurt. Wissenschaftlicher Verlag, Trier, pp 101–112
Smith M., Wheeldon L. (2001) Syntactic priming in spoken sentence production: An online study. Cognition 78: 123–164
Stallings L. M., MacDonald M. C., O’Seaghdha P. G. (1998) Phrasal ordering constraints in sentence production: Phrase length and verb disposition in heavy-NP shift. Journal of Memory and Language 39: 392–417
Tai J. H.-Y. (1985) Temporal sequence and Chinese word order. In: Haiman J. (eds) Iconicity in syntax. John Benjamins, Amsterdam, pp 49–72
Wasow T. (1997) End-weight from the speaker’s perspective. Journal of Psycholinguistic Research 26: 347–361
Wasow T. (2002) Postverbal Behavior. CSLI Publications, Stanford
Uszkoreit H., Brants T., Duchier D., Krenn B., Konieczny L., Oepen S., Skut W. (1998) Studien zur performanzorientierten Linguistik: Aspekte der Relativsatzextraposition im Deutschen. Kognitionswissenschaft 7: 129–133
Yamashita H. (2002) Scrambled sentences in Japanese: Linguistic properties and motivations for production. Text 22: 597–633
Yamashita H., Chang F. (2001) Long before short preference in the production of a head-final language. Cognition 81: B45–B55
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Francis, E.J., Matthews, S., Wong, R.W.Y. et al. Effects of Weight and Syntactic Priming on the Production of Cantonese Verb-Doubling. J Psycholinguist Res 40, 1–28 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10936-010-9152-0
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10936-010-9152-0