Abstract
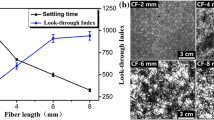
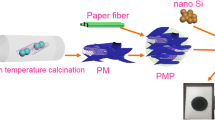
It is crucial to develop high porosity and permeability carbon fiber paper for improving the performance of proton exchange membrane fuel cell. Herein, Porous carbon paper with gradient structure (GCP) was prepared by the process of impregnation with a solution of phenolic resin /carbon black composites, overlayer molding, carbonization and graphitization. Specially, conductive carbon black was modified by silane coupling agent (KH-550) and in-situ polymerization with phenolic resin to improve its dispersion uniformity. The microstructure, porosity, gas permeability, electric resistance and mechanic properties of the as-prepared GCP are characterized. The resultant GCP has a gradual transition of porosity from bottom layer to top layer, which constitutes diffusion channels conducive to the transport of gas and liquid. In addition, GCP exhibits superior gas permeability, conductivity, corrosion resistance and tensile strength over commercial carbon paper (CCP). It has potential application prospects for further improving the performance of fuel cells.







Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
No datasets were generated or analysed during the current study.
References
J. Sim, M. Kang, K. Min, Effects of basic gas diffusion layer components on PEMFC performance with capillary pressure gradient[J]. Int. J. Hydrog. Energy. 46(54), 27731–27748 (2021)
E. Pahon, D. Bouquain, D. Hissel et al., Performance analysis of proton exchange membrane fuel cell in automotive applications[J]. J. Power Sources. 510, 230385 (2021)
F. Aldakheel, M.S. Ismail, K.J. Hughes et al., Gas permeability, wettability and morphology of gas diffusion layers before and after performing a realistic ex-situ compression test[J]. Renew. Energy. 151, 1082–1091 (2020)
L. Chen, Y.F. Wang, W.Q. Tao, Experimental study on the effect of temperature and water content on the thermal conductivity of gas diffusion layers in proton exchange membrane fuel cell[J]. Therm. Sci. Eng. Progress. 19, 100616 (2020)
R.B. Mathur, P.H. Maheshwari, T.L. Dhami et al., Processing of carbon composite paper as electrode for fuel cell[J]. J. Power Sources. 161(2), 790–798 (2006)
X.J. Zhang, H. Pei, Z.M. Shen, Carbon Fiber Paper modified with Carbon Nanotube for Proton Exchange Membrane Fuel Cell[J]. Adv. Mater. Res., 2010, 139–141: 76–79
C.H. Liu, T.H. Ko, Y.K. Liao, Effect of carbon black concentration in carbon fiber paper on the performance of low-temperature proton exchange membrane fuel cells[J]. J. Power Sources. 178(1), 80–85 (2008)
S. Tan, J. Li, L. Zhou et al., Hydrophilic carbon fiber paper based electrode coated with graphene for high performance supercapacitors[J]. Mater. Lett. 233, 278–281 (2018)
S. Kaushal, A.K. Sahu, M. Rani et al., Multiwall carbon nanotubes tailored porous carbon fiber paper-based gas diffusion layer performance in polymer electrolyte membrane fuel cell[J]. Renew. Energy. 142, 604–611 (2019)
A.C. Turkmen, C. Celik, The effect of different gas diffusion layer porosity on proton exchange membrane fuel cells[J]. Fuel. 222, 465–474 (2018)
L. Chen, R. Lin, S. Tang et al., Structural design of gas diffusion layer for proton exchange membrane fuel cell at varying humidification[J]. J. Power Sources. 467, 228355 (2020)
Z. Zhan, J. Xiao, D. Li et al., Effects of porosity distribution variation on the liquid water flux through gas diffusion layers of PEM fuel cells[J]. J. Power Sources. 160(2), 1041–1048 (2006)
B.K. Kanchan, P. Randive, S. Pati, Numerical investigation of multi-layered porosity in the gas diffusion layer on the performance of a PEM fuel cell[J]. Int. J. Hydrog. Energy. 45(41), 21836–21847 (2020)
Y.X. Huang, C.H. Cheng, X.D. Wang et al., Effects of porosity gradient in gas diffusion layers on performance of proton exchange membrane fuel cells[J]. Energy. 35(12), 4786–4794 (2010)
I.S. Lim, J.Y. Park, D.G. Kang et al., Numerical study for in-plane gradient effects of cathode gas diffusion layer on PEMFC under low humidity condition[J]. Int. J. Hydrog. Energy. 45(38), 19745–19760 (2020)
H. Wang, G. Yang, S. Li et al., Numerical study on permeability of gas diffusion layer with porosity gradient using lattice boltzmann method[J]. Int. J. Hydrog. Energy. 46(42), 22107–22121 (2021)
L. Yan, Y. Cui, G. Gou et al., Liquefaction of lignin in hot-compressed water to phenolic feedstock for the synthesis of phenol-formaldehyde resins[J]. Compos. Part. B: Eng. 112, 8–14 (2017)
W. Qiao, S. Li, G. Guo et al., Synthesis and characterization of phenol-formaldehyde resin using enzymatic hydrolysis lignin[J]. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 21, 1417–1422 (2015)
L. Zhang, Y. Zhang, L. Wang et al., Phenolic resin modified by boron-silicon with high char yield[J]. Polym. Test. 73, 208–213 (2019)
M. Wang, M. Leitch, (Charles), C. Xu, Synthesis of phenol–formaldehyde resol resins using organosolv pine lignins[J]. European Polymer Journal, 2009, 45(12): 3380–3388
H.P. Xu, Z.M. Dang, M.J. Jiang et al., Enhanced dielectric properties and positive temperature coefficient effect in the binary polymer composites with surface modified carbon black[J]. J. Mater. Chem. 18(2), 229–234 (2007)
W. Wu, S. Cong, Silica- and diatomite-modified fluorine rubber nanocomposites[J]. Bull. Mater. Sci. 42(4), 176 (2019)
J. Yin, J. Zhou, X. Li et al., Enhanced gas-flow-induced voltage in graphene[J]. Appl. Phys. Lett. 99(7), 073103 (2011)
Y.J. Heo, M. Park, W.S. Kang et al., Preparation and characterization of carbon black/pitch-based carbon fiber paper composites for gas diffusion layers[J]. Compos. Part. B: Eng. 159, 362–368 (2019)
D. Ye, Q. Lan, Q. Liao et al., Role of defects and oxygen-functional groups in carbon paper cathode for high-performance direct liquid fuel cells[J]. Carbon. 192, 170–178 (2022)
J. Jia, J. Ju, S. Liu et al., Preparation and mechanical properties of C/C composites reinforced with arrayed SiC columnar pins[J]. Ceram. Int. 47(17), 24262–24269 (2021)
T. Denaro, V. Baglio, M. Girolamo et al., Investigation of low cost carbonaceous materials for application as counter electrode in dye-sensitized solar cells[J]. J. Appl. Electrochem. 39(11), 2173–2179 (2009)
L. Yue, S. Wang, T. Araki et al., Effect of water distribution in gas diffusion layer on proton exchange membrane fuel cell performance[J]. Int. J. Hydrog. Energy. 46(3), 2969–2977 (2021)
D.A. Dikin, S. Stankovich, E.J. Zimney et al., Preparation and characterization of graphene oxide paper[J]. Nature. 448(7152), 457–460 (2007)
Z. Zhang, Y. Fang, Q. Chen et al., Molecular dynamics simulation of the impact of the surface topology of carbon black on the mechanical properties of elastomer nanocomposites[J]. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 25(7), 5602–5612 (2023)
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the National Key R&D Program of China (grant number 2019YFB1504502) and Foshan Science and Technology Innovation Project (grant number 1920001004360).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Ting Lei conceived the idea, Li Li and Yuyan Wang carried out the sample synthesis, characterization, performance measurement and original manuscript writing, Zhiyong Xie helped with the sample synthesis and data curation, Yili Liang and Ting Lei edited and revised the manuscript. The manuscript was written through contributions of all authors. All authors have read the manuscript and approved to submit to your journal.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Consent to publish
Consent to Publish the authors are indeed informed and agree to publish.
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Li, L., Wang, Y., Lei, T. et al. Structure and properties of carbon fiber paper with gradient porous structure. J Porous Mater 31, 887–895 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10934-024-01566-z
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10934-024-01566-z