Abstract
This study aimed to create composite nonwoven fabric from polylactic acid (PLA) and nano-silver coated titanium dioxide (Ag/TiO2) for the degradation of carbaryl insecticide in water under UV irradiation. The obtained composite nonwoven exhibited a yellow-gold color and similar thermal and physical characteristics, including fiber size and a narrow size distribution, to the PLA nonwoven. Furthermore, it exhibited superior mechanical properties compared to the PLA nonwoven, particularly in terms of breaking strength. Among the composite nonwovens, the one with the masterbatch added at 10 phr (PLA-2) demonstrated the highest breaking strength. Additionally, it was noteworthy that all ratios of the composite nonwoven displayed excellent carbaryl insecticide decomposition efficiency under UV light, consistently achieving around 40% degradation. Furthermore, these composite nonwovens proved reusable for up to three cycles without a loss in efficiency. These findings suggest that composite nonwovens made from nano-silver coated titanium dioxide photocatalysts and biodegradable polylactic acid hold promise as alternative materials for the decomposition of carbaryl insecticide in natural water sources.
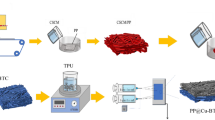
Graphical Abstract







Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
All data generated or analyzed during this study are included in this published article.
References
Rad SM, Ray AK, Barghi S (2022) Water pollution and agriculture pesticide. Clean Technol 4:1088–1102. https://doi.org/10.3390/cleantechnol4040066
Hassaan MA, Nemr AE (2020) Pesticides pollution: classifications, human health impact, extraction and treatment techniques. Egypt J Aquat Res 46:207–220. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejar.2020.08.007
Sujinnapram S, Wongrerkdee S (2023) Synergistic effects of structural, crystalline, and chemical defects on the photocatalytic performance of Y-doped ZnO for carbaryl degradation. J Environ Sci 124:667–677. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jes.2021.11.035
Zhang T, Jiang W, Cao Y, Zhu C, Toukouki S, Yao S (2022) A facile one-pot synthesis of ionic liquid@porous organic frameworks for rapid high-capacity removal of heavy metal ions, pesticides and aflatoxin from two non-food bioactive products. Ind Crops Prod 181:114859. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.indcrop.2022.114859
El-saeid MH, BaQais A, Alshabanat M (2022) Study of the photocatalytic degradation of highly abundant pesticides in agricultural soils. Molecules 27:634. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules27030634
Siampiringue M, Chahboune R, Wong-Wah-Chung P, Sarakha M (2019) Carbaryl photochemical degradation on soil model surfaces. Soil Syst 3:17. https://doi.org/10.3390/soilsystems3010017
Jampawal J, Supothina S, Chuaybamroong P (2022) Solar photocatalytic degradation of carbaryl in water using TiO2–coated filters with different binders and effect of the operating conditions. Environ Sci Pollut Res 29:88027–88040. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-022-21907-2
Martin JD, Crawford CG, Larson SJ (2003) Pesticides in streams—preliminary results from cycle I of the national water quality assessment program (NAWQA). United States Geological Survey. Reston, VA, USA, pp 1992–2001. https://doi.org/10.3133/cir1291
Walters J, Goh KS, Li L, Feng H, Hernandez J, White J (2003) Environmental monitoring of carbaryl applied in urban areas to control the glassy-winged sharpshooter in California. Environ Monit Assess 82:265–280. https://doi.org/10.1023/a:1021942301187
Arancibia-Bulnes CA, Bandala ER, Estrada CA (2002) Radiation absorption and rate constants for carbaryl photocatalytic degradation in a solar collector. Catal Today 76:149–159. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0920-5861(02)00215-8
Dai K, Chen H, Li X, Chen H, Huang Q (2011) Photocatalytic degradation of carbaryl over novel MWNT-TiO2 nanocomposite under visible light irradiation. Adv Mater Res 233–235:476–480. https://doi.org/10.4028/www.scientific.net/AMR.233-235.476
Malhotra M, Sudhaik A, Sonu, Raizada P, Ahamad T, Nguyen V-H, Le QV, Selvasembian R, Mishra AK, Singh P (2023) An overview on cellulose-supported photocatalytic materials for the efficient removal of toxic dyes. Ind Crops Prod 202:117000. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.indcrop.2023.117000
Tomašević A, Mijin D, Marinković A, Cvijetić I, Gašić S (2019) Photocatalytic degradation of carbamate insecticides: effect of different parameters. J Pesticides Phytomedicine (Belgrade) 34(3–4):193–200. https://doi.org/10.2298/PIF1904193T
El-Shafai NM, El-Khouly ME, El-Kemary M, Ramadan MS, Derbalah AS, Masoud MS (2019) Fabrication and characterization of graphene oxide–titanium dioxide nanocomposite for degradation of some toxic insecticides. J Ind Eng Chem 69:315–323. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jiec.2018.09.045
Bekrani M, Zohoori S, Davodiroknabadi A (2020) Producing multifunctional cotton fabrics using nano CeO2 doped with nano TiO2 and ZnO. Autex Res J 20(1):78–84. https://doi.org/10.2478/aut-2019-0057
Ghiasi Y, Davodiroknabadi A, Zohoori S (2021) Electrospinning of wheat bran cellulose/TiO2/ZnO nanofiber and investigating the UV blocking and bactericidal properties. Bull Mater Sci 44:89. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12034-021-02406-5
Yamin F, Naddafiun F, Zohoori S (2022) Electrospinning of eucalyptus cellulose nano fiber and improving its properties by doping nano materials. J Nat Fibers 19(13):6770–6779. https://doi.org/10.1080/15440478.2021.1932675
Asakereh M, Zohoori S, Mohammadisaghand F, Sabzali M, Mohammadisaghand R, Soltani B (2022) Extracting hazelnutgreen shell cellulose and electrospinning nanofibers doped with gelatin/nano silver. J Nat Fibers 19(17):15552–15562. https://doi.org/10.1080/15440478.2022.2131024
Sukthavorn K, Nootsuwan N, Veranitisagul C, Laobuthee A (2023) Enhanced antibacterial activity of composite fibers from polylactic acid and nanosilver-coated ground tea leaves for sustainable green composite textiles. Polye Eng Sci 63:2129–2137. https://doi.org/10.1002/pen.26351
Naddafiun F, Zohoori S, Yamin F, Torabi N, Chadorkafoor F, Nasiripoor R, Jalalian Y (2023) Doping cork fibers with nanomaterials for the removal of organo-phosphorous pesticide. J Text Inst. https://doi.org/10.1080/00405000.2023.2274627
Sukthavorn K, Nootsuwan N, Wuttisarn R, Jongrungruangchok S, Veranitisagul C, Laobuthee A (2021) Golden glittering biocomposite fibers from poly(lactic acid) and nanosilver-coated titanium dioxide with unique properties; antimicrobial, photocatalytic, and ion-sensing properties. ACS Omega 6:16307–16315. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsomega.1c00657
Chieng BW, Ibrahim NA, Yunus WMZW, Hussein MZ (2014) Poly(lactic acid)/poly(ethylene glycol) polymer nanocomposites: effects of graphene nanoplatelets. Polymers 6:93–104. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym6010093
Fonseca C, Ochoa A, Ulloa MT, Alvarez E, Canales D, Zapata PA (2015) Poly(lactic acid)/TiO2 nanocomposites as alternative biocidal and antifungal materials. Mater Sci Eng C 57:314–320. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.msec.2015.07.069
Bergaliyeva S, Sales DL, Cabello JMJ, Pintos PB, Delgado NF, Gago PM, Zammit A, Molina SI (2023) Thermal and mechanical properties of reprocessed polylactide/titanium dioxide nanocomposites for material extrusion additive manufacturing. Polymers 15:3458. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym15163458
Zorah M, Mustapa IR, Daud N, Nahida JH, Sudin NAS, Majhool AA, Mahmoudi E (2020) Improvement thermomechanical properties of polylactic acid via titania nanofillers reinforcement. J Adv Res Fluid Mech Therm Sci 70:97–111. https://doi.org/10.37934/arfmts.70.1.97111
Andrade-Guel M, Ávila-Orta CA, Cabello-Alvarado C, Cadenas-Pliego G, Esparza-González SC, Pérez-Alvarez M, Quiñones-Jurado ZV (2021) Non-woven fabrics based on nanocomposite nylon 6/ZnO obtained by ultrasound-assisted extrusion for improved antimicrobial and adsorption methylene blue dye properties. Polymers 13:1888. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym13111888
Sukthavorn K, Nootsuwan N, Veranitisagul C, Laobuthee A (2022) Development of luminescence composite materials from poly(lactic acid) and europium-doped magnesium aluminate for textile applications and 3D printing process. Polym Compos 43:6637–6646. https://doi.org/10.1002/pc.26978
Alberton J, Martelli SM, Fakhouri FM, Soldi V (2014) Mechanical and moisture barrier properties of titanium dioxide nanoparticles and halloysite nanotubes reinforced polylactic acid (PLA). IOP Conf Ser Mater Sci Eng 64:01201. https://doi.org/10.1088/1757-899X/64/1/012010
Shi C, Hou X, Li X, Ge M (2017) Preparation and characterization of persistent luminescence of regenerated cellulose fiber. J Mater Sci Mater Electron 28:1015–1021. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-016-5622-y
Xiu H, Bai HW, Huang CM, Xu CL, Li XY, Fu Q (2013) Selective localization of titanium dioxide nanoparticles at the interface and its effect on the impact toughness of poly(L-lactide)/poly(ether)urethane blends. Express Polym Lett 7:261–271. https://doi.org/10.3144/expresspolymlett.2013.24
Shi J, Zhang L, Xiao P, Huang Y, Chen P, Wang X, Gu J, Zhang J, Chen T (2018) Biodegradable PLA nonwoven fabric with controllable wettability for efficient water purification and photocatalysis degradation. ACS Sustainable Chem Eng 6:2445–2452. https://doi.org/10.1021/acssuschemeng.7b03897
Yuliati L, Roslan NA, Siah WR, Lintang HO (2017) Cobalt oxide-modified titanium dioxide nanoparticle photocatalyst for degradation of 2,4-dichlorophenoxyacetic acid. Indones J Chem 17(2):284–290. https://doi.org/10.22146/ijc.22624
Acknowledgements
The authors extend their gratitude to the following organizations for their generous financial support: The National Research Council of Thailand (NRCT) via the Kasetsart University Research and Development Institute (KURDI), FF(KU) 13.66. Additionally, the authors would like to express their appreciation for the invaluable assistance provided in terms of processing machines by The Department of Textile Engineering and the Department of Materials and Metallurgical Engineering, Faculty of Engineering, Rajamangala University of Technology Thanyaburi (RMUTT), Thailand.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
K.S. and N.N. designed the experiments, investigation, validation, visualization, data curation, and writing the original draft; R.R. and T.R. performed the experiments and analyzed the data; C.V. and A.L. contributed to formal analysis, writing-reviewing, and editing. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing Interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Ethical Approval
Not applicable.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Sukthavorn, K., Nootsuwan, N., Rajendran, R. et al. Polylactic Acid Composite Nonwoven Fabric Incorporating Nano-Silver Coated Titanium Dioxide for Photocatalytic Degradation of Carbaryl in Water. J Polym Environ (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10924-024-03272-y
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10924-024-03272-y