Abstract
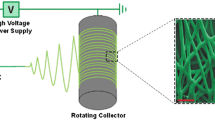
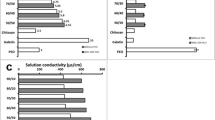
In this work, poly(vinyl alcohol)chitosan (PVA/CS) nanofibers were produced by solution blow spinning (SBS). The influence of chitosan addition on solution viscosity as well as on thermal and morphological properties of PVA/CS nanofibers were analyzed. A green production route was used using distilled water as solvent without crosslinking agents. Spun fibers were characterized by scanning electron microscopy (SEM), thermogravimetric analysis (TGA), differention scanning calorimetry (DSC), Fourier transform infrared (FTIR), porosity, water uptake and swelling behavior.The greater the amount of CS in the PVA solutions, the higher the viscosity of the spinning solutions, hindering the nanofibers formation. PVA/CS nanofiber mats produced by SBS presented a randomly interconnected and highly porous structure, with diameters ranging from 251 to 377 nm. An increase in the thermal stability and a reduction in both water uptake and swelling behavior of the hybrid nanofibers were observed with the addition of CS.








Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
All data and materials are available in the manuscript.
References
Medeiros ES, Glenn GM, Klamczynski AP, Orts WJ, Mattoso LH (2009) Solution blow spinning: a new method to produce micro-and nanofibers from polymer solutions. J Appl Polym Sci 113:2322–2330
Oliveira JE, Moraes EA, Costa RG, Afonso AS, Mattoso LH, Orts WJ, Medeiros ES (2011) Nano and submicrometric fibers of poly (D, L-lactide) obtained by solution blow spinning: process and solution variables. J Appl Polym Sci 122:3396–3405
Oliveira JE, Mattoso LHC, Medeiros ES, Zucolotto V (2012) Poly (lactic acid)/carbon nanotube fibers as novel platforms for glucose biosensors. Biosensors 2:70–82
Santos AM, Medeiros EL, Blaker JJ, Medeiros ES (2016) Aqueous solution blow spinning of poly (vinyl alcohol) micro-and nanofibers. Mater Lett 176:122–126
Baker MI, Walsh SP, Schwartz Z, Boyan BD (2012) A review of polyvinyl alcohol and its uses in cartilage and orthopedic applications. J Biomedical Mater Res Part B: Appl Biomaterials 100:1451–1457
Kumar A, Han SS (2017) PVA-based hydrogels for tissue engineering: a review. Int J Polym Mater Polym Biomaterials 66:159–182
Cho D, Netravali AN, Joo YL (2012) Mechanical properties and biodegradability of electrospun soy protein Isolate/PVA hybrid nanofibers. Polym Degrad Stab 97:747–754
Qiu K, Netravali AN (2013) A composting study of membrane-like polyvinyl alcohol based resins and nanocomposites. J Polym Environ 21:658–674
LogithKumar R, KeshavNarayan A, Dhivya S, Chawla A, Saravanan S, Selvamurugan N (2016) A review of chitosan and its derivatives in bone tissue engineering. Carbohydr Polym 151:172–188
Levengood SKL, Zhang M (2014) Chitosan-based scaffolds for bone tissue engineering. J Mater Chem B 2:3161–3184
Tan W, Li Q, Dong F, Wei L, Guo Z (2016) Synthesis, characterization, and antifungal property of chitosan ammonium salts with halogens. Int J Biol Macromol 92:293–298
Aktürk A, Cenik B, Aydoğdu Z, Taygun ME, GÜLER FK, Küçükbayrak S (2019) Fabrication and characterization of polyvinyl alcohol/gelatin/silver nanoparticle nanocomposite materials. Eurasian J Biol Chem Sci 2:1–6
Zheng X, Bian T, Zhang Y, Zhang Y, Li Z (2020) Construction of ion-imprinted nanofiber chitosan films using low-temperature thermal phase separation for selective and efficiency adsorption of Gd (III). Cellulose 27:455–467
Elsabee MZ, Naguib HF, Morsi RE (2012) Chitosan based nanofibers, review. Mater Sci Engineering: C 32:1711–1726
Kamaci UD, Peksel A (2020) Fabrication of PVA-chitosan-based nanofibers for phytase immobilization to enhance enzymatic activity. Int J Biol Macromol 164:3315–3322
Cui Z, Zheng Z, Lin L, Si J, Wang Q, Peng X, Chen W (2018) Electrospinning and crosslinking of polyvinyl alcohol/chitosan composite nanofiber for transdermal drug delivery. Adv Polym Technol 37:1917–1928
Satpathy A, Pal A, Sengupta S, Das A, Hasan M, Ratha I, Barui A, Bodhak S (2019) Bioactive nano-hydroxyapatite doped electrospun PVA-chitosan composite nanofibers for bone tissue engineering applications. J Indian Inst Sci 99:289–302
Naeimi A, Payandeh M, Ghara AR, Ghadi FE (2020) In vivo evaluation of the wound healing properties of bio-nanofiber chitosan/polyvinyl alcohol incorporating honey and Nepeta dschuparensis. Carbohydr Polym 240:116315
Lemraski EG, Jahangirian H, Dashti M, Khajehali E, Sharafinia S, Rafiee-Moghaddam R, Webster TJ (2021) Antimicrobial double-layer wound dressing based on chitosan/polyvinyl alcohol/copper: in vitro and in vivo assessment. Int J Nanomed 16:223
Ranjbar-Mohammadi M, Sa’di V, Moezzi M, Saghafi R (2022) Fabrication and characterization of Antibacterial suture yarns containing PLA/Tetracycline Hydrochloride-PVA/Chitosan Nanofibers. Fibers Polym :1–10
Liu R, Xu X, Zhuang X, Cheng B (2014) Solution blowing of chitosan/PVA hydrogel nanofiber mats. Carbohydr Polym 101:1116–1121
Ghorbani F, Zamanian A, Behnamghader A, Daliri Joupari M (2018) A novel pathway for in situ synthesis of modified gelatin microspheres by silane coupling agents as a bioactive platform. J Appl Polym Sci 135:46739
Akampumuza O, Gao H, Zhang H, Wu D, Qin XH (2018) Raising nanofiber output: the progress, mechanisms, challenges, and reasons for the pursuit. Macromol Mater Eng 303:1700269
Persano L, Camposeo A, Tekmen C, Pisignano D (2013) Industrial upscaling of electrospinning and applications of polymer nanofibers: a review. Macromol Mater Eng 298:504–520
Behrens AM, Casey BJ, Sikorski MJ, Wu KL, Tutak W, Sandler AD, Kofinas P (2014) In situ deposition of PLGA nanofibers via solution blow spinning. ACS Macro Lett 3:249–254
Zhang L, Kopperstad P, West M, Hedin N, Fong H (2009) Generation of polymer ultrafine fibers through solution (air-) blowing. J Appl Polym Sci 114:3479–3486
Miranda KW, Mattoso LH, Bresolin JD, Hubinger SZ, Medeiros ES, de Oliveira JE (2019) Polystyrene bioactive nanofibers using orange oil as an ecofriendly solvent. J Appl Polym Sci 136:47337
Gontard N, Duchez C, CUQ JL, Guilbert S (1994) Edible composite films of wheat gluten and lipids: water vapour permeability and other physical properties. Int J Food Sci Technol 29:39–50
de Souza Costa-Júnior E, Pereira MM, Mansur HS (2009) Properties and biocompatibility of chitosan films modified by blending with PVA and chemically crosslinked. J Mater Science: Mater Med 20:553–561
Shenoy SL, Bates WD, Frisch HL, Wnek GE (2005) Role of chain entanglements on fiber formation during electrospinning of polymer solutions: good solvent, non-specific polymer–polymer interaction limit. Polymer 46:3372–3384
Agrawal P, Pramanik K (2016) Chitosan-poly (vinyl alcohol) nanofibers by free surface electrospinning for tissue engineering applications. Tissue Eng Regenerative Med 13:485–497
El-hefian EA, Nasef MM, Yahaya AH (2010) Rheological and morphological studies of chitosan/agar/poly (vinyl alcohol) blends. J Appl Sci Res 6:460–468
Mucha M (1998) Rheological properties of chitosan blends with poly (ethylene oxide) and poly (vinyl alcohol) in solution. Reactive Funct Polym 38:19–25
Amri N, Ghemati D, Bouguettaya N, Aliouche D (2019) Swelling kinetics and rheological behavior of chitosan-PVA/montmorillonite hybrid polymers. Periodica Polytech Chem Eng 63:179–189
Mucha M, Pawlak A (2005) Thermal analysis of chitosan and its blends. Thermochimica acta 427:69–76
Vega-Cázarez CA, López-Cervantes J, Sánchez-Machado DI, Madera-Santana TJ, Soto-Cota A, Ramírez-Wong B (2018) Preparation and properties of chitosan–PVA fibers produced by wet spinning. J Polym Environ 26:946–958
Ü, DURU KAMACI APEKSEL (2022) Poly (vinyl alcohol)-based Electrospun Nanofibers: Characterization and Phytase Immobilization. BIOINTERFACE RESEARCH IN APPLIED CHEMISTRY 12
Guimarães AdAS (2018) Hidrogéis à Base de Quitosana/Poli(Álcool Vinílico) para liberação de fármaco visando uso potencial como curativo, Programa de Pós-Graduação em Ciência e Engenharia de Materiais, Universidade Federal da Paraíba, João Pessoa, p. 163
Ramesh S, Lungaro L, Tsikritsis D, Weflen E, Rivero IV, Elfick APD (2018) Fabrication and evaluation of poly (lactic acid), chitosan, and tricalcium phosphate biocomposites for guided bone regeneration. J Appl Polym Sci 135:46692
Ruiz CV, López-González M, Giraldo O (2021) Composite films based on salicylic acid-layered zinc hydroxide and polyvinyl alcohol: Preparation, characterization, properties and potential applications. Polym Test 94:107057
Bonilla J, Fortunati L, Atarés A, Chiralt JM, Kenny (2014) Physical, structural and antimicrobial properties of poly vinyl alcohol–chitosan biodegradable films. Food Hydrocolloids 35:463–470
Koosha M, Mirzadeh H (2015) Electrospinning, mechanical properties, and cell behavior study of chitosan/PVA nanofibers. J Biomedical Mater Res Part A 103:3081–3093
Parin FN, Ullah S, Yildirim K, Hashmi M, Kim I-S (2021) Fabrication and characterization of electrospun folic acid/hybrid fibers: in vitro controlled release study and cytocompatibility assays. Polymers 13:3594
Yang W, Fortunati E, Bertoglio F, Owczarek J, Bruni G, Kozanecki M, Kenny J, Torre L, Visai L, Puglia D (2018) Polyvinyl alcohol/chitosan hydrogels with enhanced antioxidant and antibacterial properties induced by lignin nanoparticles. Carbohydr Polym 181:275–284
Wang W, Zhang H, Shen J, Ye M (2018) Facile preparation of magnetic chitosan/poly (vinyl alcohol) hydrogel beads with excellent adsorption ability via freezing-thawing method. Colloids Surf a 553:672–680
Choo K, Ching YC, Chuah CH, Julai S, Liou N-S (2016) Preparation and characterization of polyvinyl alcohol-chitosan composite films reinforced with cellulose nanofiber. Materials 9:644
Parın FN, Ullah A, Yeşilyurt A, Parın U, Haider MK, Kharaghani D (2022) Development of PVA–psyllium husk meshes via emulsion electrospinning: Preparation, characterization, and antibacterial activity. Polymers 14:1490
Pereira Jr VA, de Arruda INQ, Stefani R (2015) Active chitosan/PVA films with anthocyanins from Brassica oleraceae (Red Cabbage) as time–temperature indicators for application in intelligent food packaging. Food Hydrocolloids 43:180–188
Ma G, Yang D, Su D, Mu X, Kennedy JF, Nie J (2010) Preparation and properties of water-soluble chitosan and polyvinyl alcohol blend films as potential bone tissue engineering matrix. Polym Adv Technol 21:189–195
Parın FN, Aydemir Çİ, Taner G, Yıldırım K (2022) Co-electrospun-electrosprayed PVA/folic acid nanofibers for transdermal drug delivery: Preparation, characterization, and in vitro cytocompatibility. J Ind Text 51:1323S–1347S
Parın FN, Yıldırım K (2021) Preparation and characterisation of vitamin-loaded electrospun nanofibres as promising transdermal patches. Fibres & Textiles in Eastern Europe
Budlayan MLM, Oracion JPL, La Rosa L, Rodriguez MJD, Patricio JN, Perez S, Arco SD, Manigo JP, Eleanor S, Arnold C (2022) Preparation of spin-coated poly (vinyl alcohol)/chitosan/Gold nanoparticles Composite and its potential for colorimetric detection of cyanide in Water. Pol J Environ Stud 31:1–8
Abureesh MA, Oladipo AA, Gazi M (2016) Facile synthesis of glucose-sensitive chitosan–poly (vinyl alcohol) hydrogel: drug release optimization and swelling properties. Int J Biol Macromol 90:75–80
Satpathy A, Pal A, Sengupta S, Das A, Hasan MM, Ratha I, Barui A, Bodhak S (2019) Bioactive nano-hydroxyapatite doped electrospun PVA-chitosan composite nanofibers for bone tissue engineering applications. J Indian Inst Sci 99:289–302
Rezaei A, Katoueizadeh E, Zebarjad SM (2023) Investigating of the influence of zinc oxide nanoparticles morphology on the properties of electrospun polyvinyl alcohol/chitosan (PVA/CS) nanofibers. J Drug Deliv Sci Technol :104712
Oskouei B, Dehghan G, Mahdavi M, Feizi MAH (2023) Preparation and characterization of novel antimicrobial Cu-Al layered double hydroxide filled polyvinyl alcohol/chitosan nanofibers with peroxidase-mimic activity. Appl Clay Sci 237:106914
Paipitak K, Pornpra T, Mongkontalang P, Techitdheer W, Pecharapa W (2011) Characterization of PVA-chitosan nanofibers prepared by electrospinning. Procedia Eng 8:101–105
Jia Y-T, Gong J, Gu X-H, Kim H-Y, Dong J, Shen X-Y (2007) Fabrication and characterization of poly (vinyl alcohol)/chitosan blend nanofibers produced by electrospinning method. Carbohydr Polym 67:403–409
Zhang Y, Huang X, Duan B, Wu L, Li S, Yuan X (2007) Preparation of electrospun chitosan/poly (vinyl alcohol) membranes. Colloid Polym Sci 285:855–863
Adeli H, Khorasani MT, Parvazinia M (2019) Wound dressing based on electrospun PVA/chitosan/starch nanofibrous mats: fabrication, antibacterial and cytocompatibility evaluation and in vitro healing assay. Int J Biol Macromol 122:238–254
Larranaga A, Alonso-Varona A, Palomares T, Rubio‐Azpeitia E, Aldazabal P, Martin FJ, Sarasua JR (2015) Effect of bioactive glass particles on osteogenic differentiation of adipose‐derived mesenchymal stem cells seeded on lactide and caprolactone based scaffolds. J Biomedical Mater Res Part A 103:3815–3824
Lisboa H (2018) Reinforcement of poly (vinyl alcohol) films with alpha-chitin nanowhiskers. Polímeros:0–0
Monteiro MM (2017) Preparation and characterization of polymeric films from polyvinyl Alcohol (PVA)/Methylcellulose (MC) for the controlled release of the agrochemical Terbuthylazine, Graduação em Química. Universidade Federal De Uberlândia, Ituiutaba
Zeng S, Ye J, Cui Z, Si J, Wang Q, Wang X, Peng K, Chen W (2017) Surface biofunctionalization of three-dimensional porous poly (lactic acid) scaffold using chitosan/OGP coating for bone tissue engineering. Mater Sci Engineering: C 77:92–101
Lu L, Peng F, Jiang Z, Wang J (2006) Poly (vinyl alcohol)/chitosan blend membranes for pervaporation of benzene/cyclohexane mixtures. J Appl Polym Sci 101:167–173
Galstyan A, Strokov K (2022) Influence of photosensitizer concentration and polymer composition on photoinduced antimicrobial activity of PVA-and PVA-chitosan-based electrospun nanomaterials cross-linked with tailor-made silicon (IV) phthalocyanine. Photochem Photobiol Sci :1–12
Ali M, Gherissi A (2017) Synthesis and characterization of the composite material PVA/chitosan/5% sorbitol with different ratio of chitosan. Int J Mech Mechatron Eng 17:15–28
Januariyasa IK, Ana ID, Yusuf Y (2020) Nanofibrous poly (vinyl alcohol)/chitosan contained carbonated hydroxyapatite nanoparticles scaffold for bone tissue engineering. Mater Sci Engineering: C 107:110347
Pervez MN, Stylios GK (2018) Investigating the synthesis and characterization of a novel green H2O2-assisted, water-soluble chitosan/polyvinyl alcohol nanofiber for environmental end uses. Nanomaterials 8:395
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to acknowledge the donation of PVA by the Kuraray company and the support of Dr. Renate Wellen in analyzing the DSC data.
Funding
The authors would like to thank CAPES (code 001), CNPq (grant 420004/2018-1 and 309771/2021-8) and FAPESQ (PRONEX - FAPESQ/PB – MCT/CNPq) for financial support.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All authors contributed to the development of the research. The preparation of the material, data collection and analysis were carried out by Glauber Rodrigues Cerqueira de Cerqueira, Déborah dos Santos Gomes, Rayssa de Sousa Victor and Lucas Ricardo Fernandes Figueiredo. The first draft of the manuscript was written by Glauber Rodrigues Cerqueira de Cerqueira, Déborah dos Santos Gomes and Rayssa de Sousa Victor. And subsequent versions of the manuscript were revised and edited by Eliton Souto De Medeiros, Gelmires de Araújo Neves, Romualdo Rodrigues Menezes and Suédina Maria de Lima Silva. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or inter-pretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript, or in the decision to publish the results.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Cerqueira, G.R.C., Gomes, D.S., Victor, R.S. et al. Development of PVA/chitosan Nanofibers by a Green Route Using Solution Blow Spinning. J Polym Environ 32, 1489–1499 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10924-023-03033-3
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10924-023-03033-3