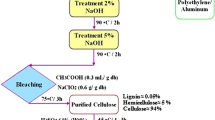
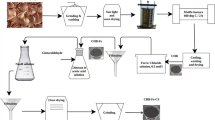
Abstract
In this study, a novel binary grafted polydopamine/polyacrylamide onto magnetic sporopollenin (PDA/PAAm@Fe3O4@SP) was synthesized in one step polymerization strategy to investigate its removal performance of 2,4-dichlorophenoxyacetic acid (2,4-D). The response surface methodology (RSM) was applied to evaluate the effects of the process factors including pH (2–8), adsorbent concentration (0.5-2 g/L), initial 2,4-D concentration (Co) (20–80 mg/L), and contact time (30–180 min) for the 2,4-D removal performance. The central composite design (CCD) through RSM was utilized to design the experiments as well as to optimize and model the 2,4-D adsorption process. The ANOVA results clearly shows that the quadratic model (p < 0.0001) was sufficient to the best predicting of the removal performance of 2,4-D (R2 = 0.99). The optimum conditions for the maximum 2,4-D removal (88.31%) was achieved at pH of 3.51, adsorbent concentration of 0.75 g/L, Co of 52.85 mg/L, and contact time of 148.53 min. The adsorption kinetic was represented by both Weber-Morris (R2 = 0.99) and pseudo-second-order models (R2 = 0.99). The isotherm for 2,4-D completely fitted the Dubinin-Radushkevich (D-R) and Langmuir models with R2 values of 0.98. The obtained outcomes indicated that the prepared material may be utilized as an alternative adsorbent for the removal of 2,4-D from waterbodies and the RSM method can be utilized as an eco-friendly and low-cost statistical approach for the elimination of 2,4-D.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Georgin J, Franco DSP, Schadeck Netto M, Allasia D, Foletto EL, Oliveira LFS, Dotto GL (2021) Transforming shrub waste into a high-efficiency adsorbent: Application of Physalis peruvian chalice treated with strong acid to remove the 2,4-dichlorophenoxyacetic acid herbicide. J Environ Chem Eng 9:104574. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jece.2020.104574
Wu H, Gong L, Zhang X, He F, Li Z (2021) Bifunctional porous polyethyleneimine-grafted lignin microspheres for efficient adsorption of 2,4-dichlorophenoxyacetic acid over a wide pH range and controlled release. Chem Eng J 411:128539. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2021.128539
Yousefzadeh S, Ahmadi E, Gholami M, Ghaffari HR, Azari A, Ansari M, Miri M, Sharafi K, Rezaei S (2017) A comparative study of anaerobic fixed film baffled reactor and up-flow anaerobic fixed film fixed bed reactor for biological removal of diethyl phthalate from wastewater: a performance, kinetic, biogas, and metabolic pathway study. Biotechnol Biofuels 10:139. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13068-017-0826-9
Güher H, Öterler B, Elipek B, Yeler O, Aydin GB (2022) Spatial and temporal evaluation of the physicochemical quality of domestic/industrial water in the Kırklareli Reservoir (Turkish Thrace). J Serb Chem Soc 87:389–399. https://doi.org/10.2298/JSC210601074G
Zadeh RJ, Sayadi MH, Rezaei MR (2021) Synthesis of Thiol modified magMCM-41 nanoparticles with rice husk ash as a robust, high effective, and recycling magnetic sorbent for the removal of herbicides. J Environ Chem Eng 9:104804. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jece.2020.104804
Mansab S, Rafique U (2021) In situ remediation of 2,4-dicholrophenoxyacetic acid herbicide using amine-functionalized imidazole coordination complexes. Environ Sci Pollut Res 28:15099–15113. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-020-11741-9
Azari A, Salari M, Dehghani MH, Alimohammadi M, Ghaffari H, Sharafi K, Shariatifar N, Baziar M (2017) Efficiency of magnitized graphene oxide nanoparticles in removal of 2,4-dichlorophenol from aqueous solution. J Mazandaran Univ Med Sci 26:265–281
Tan KL, Foo KY (2021) Preparation of MIL-100 via a novel water-based heatless synthesis technique for the effective remediation of phenoxyacetic acid-based pesticide. J Environ Chem Eng 9:104923. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jece.2020.104923
Hong Q, Liu C, Wang Z, Li R, Liang X, Wang Y, Zhang Y, Song Z, Xiao Z, Cui T, Heng B, Xu B, Qi F, Ikhlaq A (2021) Electron transfer enhancing Fe(II)/Fe(III) cycle by sulfur and biochar in magnetic FeS@biochar to active peroxymonosulfate for 2,4-dichlorophenoxyacetic acid degradation. Chem Eng J 417:129238. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2021.129238
Berizi Z, Hashemi SY, Hadi M, Azari A, Mahvi AH (2016) The study of non-linear kinetics and adsorption isotherm models for Acid Red 18 from aqueous solutions by magnetite nanoparticles and magnetite nanoparticles modified by sodium alginate. Water Sci Technol 74:1235–1242. https://doi.org/10.2166/wst.2016.320
Rambabu K, AlYammahi J, Bharath G, Thanigaivelan A, Sivarajasekar N, Banat F (2021) Nano-activated carbon derived from date palm coir waste for efficient sequestration of noxious 2,4-dichlorophenoxyacetic acid herbicide. Chemosphere 282:131103. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2021.131103
Ren D, Yu H, Wu J, Wang Z, Zhang S, Zhang X, Gong X (2020) The study on adsorption behavior of 2,4-DCP in solution by biomass carbon modified with CTAB-KOH. Water Sci Technol 82:1535–1546. https://doi.org/10.2166/wst.2020.418
Kırbıyık Ç, Pütün AE, Pütün E (2017) Equilibrium, kinetic, and thermodynamic studies of the adsorption of Fe(III) metal ions and 2,4-dichlorophenoxyacetic acid onto biomass-based activated carbon by ZnCl2 activation. Surf Interfaces 8:182–192. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.surfin.2017.03.011
Azari A, Gholami M, Torkshavand Z, Yari A, Ahmadi E, Kakavandi B (2015) Evaluation of basic violet 16 adsorption from aqueous solution by magnetic zero valent iron-activated carbon nanocomposite using response surface method: Isotherm and kinetic studies. J Mazandaran Univ Med Sci 24:333–347
Salomón YLdO, Georgin J, Franco DSP, Netto MS, Piccilli DGA, Foletto EL, Oliveira LFS, Dotto GL (2021) High-performance removal of 2,4-dichlorophenoxyacetic acid herbicide in water using activated carbon derived from Queen palm fruit endocarp (Syagrus romanzoffiana). J Environ Chem Eng 9:104911. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jece.2020.104911
Ali I, Afshinb S, Poureshgh Y, Azari A, Rashtbari Y, Feizizadeh A, Hamzezadeh A, Fazlzadeh M (2020) Green preparation of activated carbon from pomegranate peel coated with zero-valent iron nanoparticles (nZVI) and isotherm and kinetic studies of amoxicillin removal in water. Environ Sci Pollut Res 27:36732–36743. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-020-09310-1
Bilgic A (2021) Novel BODIPY-based fluorescent Lycopodium clavatum sporopollenin microcapsules for detection and removal of Cu(II) ions. Colloids Surf A 631:127658. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.colsurfa.2021.127658
Bilgic A, Cimen A, Kursunlu AN, Karapınar HS (2022) Novel fluorescent microcapsules based on sporopollenin for removal and detection of Cu (II) ions in aqueous solutions: Eco-friendly design, fully characterized, photophysical&physicochemical data. Microporous Mesoporous Mater 330:111600. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.micromeso.2021.111600
Kamboh MA, Arain SS, Jatoi AH, Sherino B, Algarni TS, Al-onazi WA, Al-Mohaimeed AM, Rezania S (2021) Green sporopollenin supported cyanocalixarene based magnetic adsorbent for pesticides removal from water: Kinetic and equilibrium studies. Environ Res 201:111588. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envres.2021.111588
Yılmaz Ş, Zengin A, Şahan T, Zorer ÖS (2021) Utilization of a novel polymer–clay material for high elimination of hazardous radioactive contamination uranium(VI) from aqueous environments. Environ Technol Innovation 23:101631. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eti.2021.101631
Şahin S, Emik S (2018) Fast and highly efficient removal of 2,4-D using amino-functionalized poly (glycidyl methacrylate) adsorbent: Optimization, equilibrium, kinetic and thermodynamic studies. J Mol Liq 260:195–202. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molliq.2018.03.091
Ai L, Zhou Y, Jiang J (2011) Removal of methylene blue from aqueous solution by montmorillonite/CoFe2O4 composite with magnetic separation performance. Desalination 266:72–77. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.desal.2010.08.004
Fayazi M, Afzali D, Taher MA, Mostafavi A, Gupta VK (2015) Removal of Safranin dye from aqueous solution using magnetic mesoporous clay: optimization study. J Mol Liq 212:675–685. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molliq.2015.09.045
Chang J, Ma J, Ma Q, Zhang D, Qiao N, Hu M, Ma H (2016) Adsorption of methylene blue onto Fe3O4/activated montmorillonite nanocomposite. Appl Clay Sci 119:132–140. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.clay.2015.06.038
Hajighasemkhan A, Taghavi L, Moniri E, Hassani AH, Panahi HA (2022) Adsorption kinetics and isotherms study of 2,4-dichlorophenoxyacetic acid by 3dimensional/graphene oxide/magnetic from aquatic solutions. Int J Environ Anal Chem 102:1171–1191. https://doi.org/10.1080/03067319.2020.1734194
Zhang C, Ma M-Q, Chen T-T, Zhang H, Hu D-F, Wu B-H, Ji J, Xu Z-K (2017) Dopamine-triggered one-step polymerization and codeposition of acrylate monomers for functional coatings. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 9:34356–34366. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsami.7b11092
Ma M-Q, Zhang C, Chen T-T, Yang J, Wang J-J, Ji J, Xu Z-K (2019) Bioinspired polydopamine/polyzwitterion coatings for underwater anti-oil and -freezing surfaces. Langmuir 35:1895–1901. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.langmuir.8b02320
Amiri MJ, Bahrami M, Beigzadeh B, Gil A (2018) A response surface methodology for optimization of 2,4-dichlorophenoxyacetic acid removal from synthetic and drainage water: a comparative study. Environ Sci Pollut Res 25:34277–34293. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-018-3327-x
Gharibzadeh F, Rezaei Kalantary R, Nasseri S, Esrafili A, Azari A (2016) Reuse of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) contaminated soil washing effluent by bioaugmentation/biostimulation process. Sep Purif Technol 168:248–256. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.seppur.2016.05.022
Yang J, Shojaei S, Shojaei S (2022) Removal of drug and dye from aqueous solutions by graphene oxide: adsorption studies and chemometrics methods. npj Clean Water 5:5. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41545-022-00148-3
Mohammed A-SY, Dyab AKF, Taha F, Abd El-Mageed AIA (2022) Pollen-derived microcapsules for aspirin microencapsulation: in vitro release and physico-chemical studies. RSC Adv 12:22139–22149. https://doi.org/10.1039/D2RA02888C
Bilgic A, Cimen A, Bastug E, Kursunlu AN (2022) Fluorescent sporopollenin microcapsule modified by BODIPY for sensitive&selective recognition and efficient removal of Cu (II) from aqueous solution. Chem Eng Res Des 178:61–72. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cherd.2021.12.014
Yılmaz Ş, Zengin A, Akbulut Y, Şahan T (2019) Magnetic nanoparticles coated with aminated polymer brush as a novel material for effective removal of Pb(II) ions from aqueous environments. Environ Sci Pollut Res 26:20454–20468. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-019-05360-2
Yaacob SFFS, Razak NSA, Aun TT, Rozi SKM, Jamil AKM, Mohamad S (2018) Synthesis and characterizations of magnetic bio-material sporopollenin for the removal of oil from aqueous environment. Ind Crops Prod 124:442–448. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.indcrop.2018.08.024
Thakur A, Ranote S, Kumar D, Bhardwaj KK, Gupta R, Chauhan GS (2018) Synthesis of a PEGylated dopamine ester with enhanced antibacterial and antifungal activity. ACS Omega 3:7925–7933. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsomega.8b01099
Feng L, Yang H, Dong X, Lei H, Chen D (2018) pH-sensitive polymeric particles as smart carriers for rebar inhibitors delivery in alkaline condition. J Appl Polym Sci 135:45886. https://doi.org/10.1002/app.45886
Baran T, Sargin I, Kaya M, Menteş A, Ceter T (2017) Design and application of sporopollenin microcapsule supported palladium catalyst: Remarkably high turnover frequency and reusability in catalysis of biaryls. J Colloid Interface Sci 486:194–203. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcis.2016.09.071
Liu W, Yang Q, Yang Z, Wang W (2016) Adsorption of 2,4-D on magnetic graphene and mechanism study. Colloids Surf A 509:367–375. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.colsurfa.2016.09.039
Turan E, Zengin A, Suludere Z, Kalkan N, Tamer U (2022) Construction of a sensitive and selective plasmonic biosensor for prostate specific antigen by combining magnetic molecularly-imprinted polymer and surface-enhanced Raman spectroscopy. Talanta 237:122926. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.talanta.2021.122926
Luo B, Wang X, Wang Y, Li L (2014) Fabrication, characterization, properties and theoretical analysis of ceramic/PVDF composite flexible films with high dielectric constant and low dielectric loss. J Mater Chem A 2:510–519. https://doi.org/10.1039/C3TA14107A
Sereshti H, Toloutehrani A, Nodeh HR (2020) Determination of cholecalciferol (vitamin D3) in bovine milk by dispersive micro-solid phase extraction based on the magnetic three-dimensional graphene-sporopollenin sorbent. J Chromatogr B 1136:121907. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jchromb.2019.121907
Chandrasekaram K, Alias Y, Fathullah SF, Lee VS, Haron N, Raoov M, Zakaria N, Mohamad S (2021) Sporopollenin supported ionic liquids biosorbent for enhanced selective adsorption of 2,4-dinitrophenol from aqueous environment. Mater Today Commun 28:102587. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mtcomm.2021.102587
Sayğılı GA (2020) Conversion of a renewable bio-resource to a functional composite material: Product design, comprehensive characterization and adsorption of 2,4-D herbicide. Sustainable Chem Pharm 18:100338. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scp.2020.100338
Taktak F, İlbay Z, Şahin S (2015) Evaluation of 2,4-D removal via activated carbon from pomegranate husk/polymer composite hydrogel: Optimization of process parameters through face centered composite design. Korean J Chem Eng 32:1879–1888. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11814-015-0010-5
Jawad AH, Rangabhashiyam S, Abdulhameed AS, Syed-Hassan SSA, Alothman ZA, Wilson LD (2022) Process optimization and adsorptive mechanism for reactive blue 19 dye by magnetic crosslinked chitosan/MgO/Fe3O4 biocomposite. J Polym Environ 30:2759–2773. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10924-022-02382-9
Ramya V, Murugan D, Lajapathirai C, Saravanan P, Sivasamy A (2019) Removal of toxic pollutants using tannery sludge derived mesoporous activated carbon: experimental and modelling studies. J Environ Chem Eng 7:102798. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jece.2018.11.043
Aswani MT, Yadav M, Vinod Kumar A, Tiwari S, Kumar T, Pavan Kumar MV (2020) Ultrasound–acid modified Merremia vitifolia biomass for the biosorption of herbicide 2,4-D from aqueous solution. Water Sci Technol 82:468–480. https://doi.org/10.2166/wst.2020.346
Vinayagam R, Pai S, Murugesan G, Varadavenkatesan T, Narayanasamy S, Selvaraj R (2022) Magnetic activated charcoal/Fe2O3 nanocomposite for the adsorptive removal of 2,4-Dichlorophenoxyacetic acid (2,4-D) from aqueous solutions: synthesis, characterization, optimization, kinetic and isotherm studies. Chemosphere 286:131938. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2021.131938
Mall ID, Srivastava VC, Kumar GVA, Mishra IM (2006) Characterization and utilization of mesoporous fertilizer plant waste carbon for adsorptive removal of dyes from aqueous solution. Colloids Surf A 278:175–187. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.colsurfa.2005.12.017
Izanloo M, Esrafili A, Jafari AJ, Farzadkia M, Behbahani M, Sobhi HR (2019) Application of a novel bi-functional nanoadsorbent for the simultaneous removal of inorganic and organic compounds: equilibrium, kinetic and thermodynamic studies. J Mol Liq 273:543–550. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molliq.2018.10.013
Brito GM, Roldi LL, Schetino M, Checon Freitas JC, Cabral Coelho ER (2020) High-performance of activated biocarbon based on agricultural biomass waste applied for 2,4-D herbicide removing from water: adsorption, kinetic and thermodynamic assessments. J Environ Sci Health Part B 55:767–782. https://doi.org/10.1080/03601234.2020.1783178
Alikhani N, Farhadian M, Goshadrou A, Tangestaninejad S, Eskandari P (2021) Photocatalytic degradation and adsorption of herbicide 2,4-dichlorophenoxyacetic acid from aqueous solution using TiO2/BiOBr/Bi2S3 nanostructure stabilized on the activated carbon under visible light. Environ Nanotechnol Monit Manage 15:100415. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enmm.2020.100415
Feng S, Huang X, Zhu G, Zheng W, Shao C, Zhou N (2019) Anti-crushing millimeter composite beads for removing 2,4-dichlorophenoxyacetic acid from aqueous solution. Desalin Water Treat 170:211–224. https://doi.org/10.5004/dwt.2019.24721
Binh QA, Nguyen H-H (2020) Investigation the isotherm and kinetics of adsorption mechanism of herbicide 2,4-dichlorophenoxyacetic acid (2,4-D) on corn cob biochar. Bioresour Technol Rep 11:100520. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biteb.2020.100520
Funding
The authors declare that no funds, grants, or other support were received during the preparation of this manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
ŞY performed investigation, methodology, experiments, material synthesis and characterization, data analysis, writing-original draft preparation and editing. Data analysis, methodology, material synthesis and characterization, writing-reviewing and editing were performed by AZ and TŞ. İHG helped with the investigation and data analysis.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors have no relevant financial or non-financial interests to disclose.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Yılmaz, Ş., Zengin, A., Şahan, T. et al. Efficient Removal of 2,4-Dichlorophenoxyacetic Acid from Aqueous Medium Using Polydopamine/Polyacrylamide Co-deposited Magnetic Sporopollenin and Optimization with Response Surface Methodology Approach. J Polym Environ 31, 36–49 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10924-022-02617-9
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10924-022-02617-9