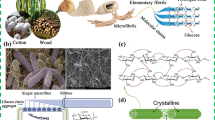
Abstract
Conversion of the renewable biopolymers to magnetic adsorbents is a sustainable approach for environmental concerns. Herein, the microwave-assisted micro-carboxymethylated cellulose (MCMC) with DS = 0.76, the in situ polymerized acrylamide, and nano g-Fe2O3–SO3H were fabricated in a three-dimensional hydrogel network by one-pot radical polymerization with an aromatic bis-amide cross-linker. This SO3H/phenyl implanted various methods characterized nano-composite hydrogel as a granular porous network with excellent swelling performance for the adsorption of heavy metal ions (HMIs). The results of the influences of pH, organic solvent, and salt onto the hydrogel swelling capacity (SC) showed an increase by raising the pH, a decrease in organic solvents, and a decrease in chloride salt solutions by order of Na+ < Ca2+ < Fe3+. The mechanism and kinetics of hydrogel swelling with a capacity of 60.7 g/g were consistent with the non-Fickian diffusion and Schott's second-order kinetic models. As an adsorbent, the hydrogel removed Pb2+ and Hg2+ with an adsorption capacity 91.12 mg/g and 79.64 mg/g at neutral pH 7. The adsorption isotherms of hydrogel for Pb2+ and Hg2+ were adequately fitted with the Langmuir model (R2 = 0.99). The chelation of carboxylate groups to HMIs, electrostatic interactions between the charged surface groups and HMIs, and hydrogen bonding are significant parameters of the adsorption mechanism. The successive adsorption/desorption cycles for HMIs removal offer high potential of this hydrogel for the treatment of industrial wastewaters.
















Similar content being viewed by others
References
Qasem NA, Mohammed RH, Lawal DU (2021) Removal of heavy metal ions from wastewater: a comprehensive and critical review. NPJ Clean Water 4(1):1–15
Malik LA, Bashir A, Qureashi A, Pandith AH (2019) Detection and removal of heavy metal ions: a review. Environ Chem Lett 17(4):1495–1521
Wu Y, Pang H, Liu Y, Wang X, Yu S, Fu D, Chen J, Wang X (2019) Environmental remediation of heavy metal ions by novel-nanomaterials: a review. Environ Pollut 246:608–620
Krabbenhoft DP, Sunderland EM (2013) Global change and mercury. Science 341(6153):1457–1458
Sonmez B, Celikkol AN (2021) Pullulan based hydrogels for the removal of various metal ions from aqueous solutions. J Environ Chem Eng 9(5):106188–106196
Khozemy EE, Nasef SM, Mohamed TM (2020) Radiation synthesis of superabsorbent hydrogel (wheat flour/acrylamide) for removal of mercury and lead ions from waste solutions. J Inorg Organomet Polym Mater 30(5):1669–1685
Setoodehkhah M, Momeni S (2018) Water soluble schiff base functinalized Fe3O4 magnetic nano-particles as a novel adsorbent for the removal of Pb(II) and Cu(II) metal ions from aqueous solutions. J Inorg Organomet Polym Mater 28(3):1098–1106
Brodkin E, Copes R, Mattman A, Kennedy J, Kling R, Yassi A (2007) Lead and mercury exposures: interpretation and action. CMAJ 176(1):59–63
Zahir F, Rizwi SJ, Haq SK, Khan RH (2005) Low dose mercury toxicity and human health. Environ Toxicol Pharmacol 20(2):351–360
Gil A, Amiri MJ, Abedi-Koupai J, Eslamian S (2018) Adsorption/reduction of Hg (II) and Pb (II) from aqueous solutions by using bone ash/nZVI composite: effects of aging time, Fe loading quantity and co-existing ions. Environ Sci Pollut Res 25(3):2814–2829
Gong Y, Wang Y, Lin N, Wang R, Wang M, Zhang X (2022) Iron-based materials for simultaneous removal of heavy metal (loid) s and emerging organic contaminants from the aquatic environment: Recent advances and perspectives. Environ Pollut 299:118871–118885
Shrestha R, Ban S, Devkota S, Sharma S, Joshi R, Tiwari AP, Kim HY, Joshi MK (2021) Technological trends in heavy metals removal from industrial wastewater: A review. J Environ Chem Eng 9(4):105688–105706
Mansouri F, Chouchene K, Roche N, Ksibi M (2021) Removal of Pharmaceuticals from water by adsorption and advanced oxidation processes: State of the art and trends. Appl Sci 11(14):6659–6694
Liu N, Dai W, Fei F, Xu H, Lei J, Quan G, Zheng Y, Zhang X, Tang L (2022) Insights into the photocatalytic activation persulfate by visible light over ReS2/MIL-88B (Fe) for highly efficient degradation of ibuprofen: Combination of experimental and theoretical study. Sep Purif Technol 297:121545–121555
Tamaddon F, Nasiri A, Yazdanpanah G (2020) Photocatalytic degradation of ciprofloxacin using CuFe2O4@methyl cellulose based magnetic nanobiocomposite. MethodsX 7:100764–100772
Lin N, Gong Y, Wang R, Wang Y, Zhang X (2022) Critical review of perovskite-based materials in advanced oxidation system for wastewater treatment: Design, applications and mechanisms. J Hazard Mater 424:127637–127661
Yang Y, Li X, Jie B, Zheng Z, Li J, Zhu C, Wang S, Xu J, Zhang X (2022) Electron structure modulation and bicarbonate surrounding enhance Fenton-like reactions performance of Co-Co PBA. J Hazard Mater 437:129372–129385
Langbehn RK, Michels C, Soares HM (2021) Antibiotics in wastewater: From its occurrence to the biological removal by environmentally conscious technologies. Environ Pollut 275:116603–116619
Fu Z-J, Jiang S-K, Chao X-Y, Zhang C-X, Shi Q, Wang Z-Y, Liu M-L, Sun S-P (2022) Removing miscellaneous heavy metals by all-in-one ion exchange-nanofiltration membrane. Water Res 222:118888–118897
Chakraborty R, Asthana A, Singh AK, Jain B, Susan ABH (2022) Adsorption of heavy metal ions by various low-cost adsorbents: a review. Int J Environ Anal Chem 102(2):342–379
Ma L, Zhang X, Ikram M, Ullah M, Wu H, Shi K (2020) Controllable synthesis of an intercalated ZIF-67/EG structure for the detection of ultratrace Cd2+, Cu2+, Hg2+ and Pb2+ ions. Chem Eng J 395:125216–125228
Li W, Zhang L, Hu D, Yang R, Zhang J, Guan Y, Lv F, Gao H (2021) A mesoporous nanocellulose/sodium alginate/carboxymethyl-chitosan gel beads for efficient adsorption of Cu2+ and Pb2+. Int J Biol Macromol 187:922–930
Zhang K, Luo X, Yang L, Chang Z, Luo S (2021) Progress toward hydrogels in removing heavy metals from water: problems and solutions: a review. ACS ES&T Water 1(5):1098–1116
Tamaddon F, Mosslemin MH, Asadipour A, Gharaghani MA, Nasiri A (2020) Microwave-assisted preparation of ZnFe2O4@ methyl cellulose as a new nano-biomagnetic photocatalyst for photodegradation of metronidazole. Int J Biol Macromol 154:1036–1049
Wu S, Guo J, Wang Y, Huang C, Hu Y (2021) Facile preparation of magnetic sodium alginate/carboxymethyl cellulose composite hydrogel for removal of heavy metal ions from aqueous solution. J Mater Sci 56(23):13096–13107
Ma Q, Wang W, Ge W, Xia L, Li H, Song S (2021) Preparation of carboxymethyl cellulose-based hydrogel supported by two-dimensional montmorillonite nanosheets for methylene blue removal. J Polym Environ 29(12):3918–3931
dos Santos DM, de Lacerda BA, Ascheri DPR, Signini R, de Aquino GLB (2015) Microwave-assisted carboxymethylation of cellulose extracted from brewer’s spent grain. Carbohydr Polym 131:125–133
Karzar Jeddi M, Mahkam M (2019) Magnetic nano carboxymethyl cellulose-alginate/chitosan hydrogel beads as biodegradable devices for controlled drug delivery. Int J Biol Macromol 135:829–838
Godiya CB, Cheng X, Li D, Chen Z, Lu X (2019) Carboxymethyl cellulose/polyacrylamide composite hydrogel for cascaded treatment/reuse of heavy metal ions in wastewater. J Hazard Mater 364:28–38
Varaprasad K, Jayaramudu T, Sadiku ER (2017) Removal of dye by carboxymethyl cellulose, acrylamide and graphene oxide via a free radical polymerization process. Carbohydr Polym 164:186–194
Kaith BS, Singh A, Sharma AK, Sud D (2021) Hydrogels: synthesis, classification, properties and potential applications: a brief review. J Polym Environ 29(12):3827–3841
Zainal SH, Mohd NH, Suhaili N, Anuar FH, Lazim AM, Othaman R (2021) Preparation of cellulose-based hydrogel: a review. J Mater Res Technol 10:935–952
Mondal S, Das S, Nandi AK (2020) A review on recent advances in polymer and peptide hydrogels. Soft Matter 16(6):1404–1454
Anjali J, Jose VK, Lee J-M (2019) Carbon-based hydrogels: synthesis and their recent energy applications. J Mater Chem A 7(26):15491–15518
Dacrory S, Kamal KH, Kamel S (2021) EDTA-functionalized magnetic graphene oxide/polyacrylamide grafted carboxymethyl cellulose hydrogel for removal of Pb+ 2 from aqueous solution. J Polym Environ 15:1–14
Mohammadi R, Saboury A, Javanbakht S, Foroutan R, Shaabani A (2021) Carboxymethylcellulose/polyacrylic acid/starch-modified Fe3O4 interpenetrating magnetic nanocomposite hydrogel beads as pH-sensitive carrier for oral anticancer drug delivery system. Eur Polym J 153:110500–110509
Lin Q, Gao M, Chang J, Ma H (2016) Adsorption properties of crosslinking carboxymethyl cellulose grafting dimethyldiallylammonium chloride for cationic and anionic dyes. Carbohydr Polym 151:283–294
Javanbakht S, Nabi M, Shadi M, Amini MM, Shaabani A (2021) Carboxymethyl cellulose/tetracycline@UiO-66 nanocomposite hydrogel films as a potential antibacterial wound dressing. Int J Biol Macromol 188:811–819
Mohamood T, Fattima’Al-Zahara N, Abdul Halim AH, Zainuddin N, (2021) Carboxymethyl cellulose hydrogel from biomass waste of oil palm empty fruit bunch using calcium chloride as crosslinking agent. Polymers 13(23):4056–4072
Capanema NSV, Mansur AAP, de Jesus AC, Carvalho SM, de Oliveira LC, Mansur HS (2018) Superabsorbent crosslinked carboxymethyl cellulose-PEG hydrogels for potential wound dressing applications. Int J Biol Macromol 106:1218–1234
Hashem M, Sharaf S, Abd El-Hady MM, Hebeish A (2013) Synthesis and characterization of novel carboxymethylcellulose hydrogels and carboxymethylcellulolse-hydrogel-ZnO-nanocomposites. Carbohydr Polym 95(1):421–427
Hosseinzadeh H, Javadi A (2016) Fabrication and characterization of CMC-based magnetic superabsorbent hydrogel nanocomposites for crystal violet removal. Polym Adv Technol 27(12):1609–1616
Zeng X, Zhang G, Junfeng Zhu WuZ (2022) Adsorption of heavy metal ions in water by surface functionalized magnetic composites: a review. Environ Sci: Water Res Technol 5(5):1–32
Ren J, Zhu Z, Qiu Y, Yu F, Ma J, Zhao J (2021) Magnetic field assisted adsorption of pollutants from an aqueous solution: a review. J Hazard Mater 408:124846–124857
Kumar A, Kuang Y, Liang Z, Sun X (2020) Microwave chemistry, recent advancements, and eco-friendly microwave-assisted synthesis of nanoarchitectures and their applications: a review. Materials Today Nano 11:100076–100096
Karmakar M, Mondal H, Ghosh NN, Chattopadhyay PK, Singha NR (2021) Synthesis of gum tragacanth-grafted pentapolymer hydrogels for As (III) exclusion: Roles of microwaves, RSM optimization, and DFT studies. Int J Biol Macromol 184:909–925
Tamaddon F, Ahmadi-AhmadAbadi E, Khoje-neamah E (2022) Nano-carboxymethylcellulose, polyacrylamide, and γ-Fe2O3–SO3H cross-linked to a hydrophobic linker: an organic-inorganic hydrogel for adsorptive removal of dyes. J Mol Struct 1270:133872–133886
Koukabi N, Kolvari E, Zolfigol MA, Khazaei A, Shaghasemi BS, Fasahati B (2012) A magnetic particle-supported sulfonic acid catalyst: tuning catalytic activity between homogeneous and heterogeneous catalysis. Adv Synth Catal 354(10):2001–2008
Tamaddon F, Arab D, Ahmadi-AhmadAbadi E (2020) Urease immobilization on magnetic micro/nano-cellulose dialdehydes: urease inhibitory of Biginelli product in Hantzsch reaction by urea. Carbohydr Polym 229:115471–115481
Tamaddon F, Kargar-Shooroki H, Jafari AA (2013) Molybdate and silica sulfuric acids as heterogeneous alternatives for synthesis of gem-bisamides and bisurides from aldehydes and amides, carbamates, nitriles or urea. J Mol Catal A 368–369:66–71
Dai H, Zhang Y, Ma L, Zhang H, Huang H (2019) Synthesis and response of pineapple peel carboxymethyl cellulose-g-poly (acrylic acid-co-acrylamide)/graphene oxide hydrogels. Carbohydr Polym 215:366–376
Dai H, Huang H (2017) Enhanced swelling and responsive properties of pineapple peel carboxymethyl cellulose-g-poly(acrylic acid-co-acrylamide) superabsorbent hydrogel by the introduction of carclazyte. J Agric Food Chem 65(3):565–574
Sun X-F, Xie Y, Shan S, Li W, Sun L (2022) Chemically-crosslinked xylan/graphene oxide composite hydrogel for copper ions removal. J Polym Environ 30:1–15
Singha NR, Dutta A, Mahapatra M, Roy JSD, Mitra M, Deb M, Chattopadhyay PK (2019) In situ attachment of acrylamido sulfonic acid-based monomer in terpolymer hydrogel optimized by response surface methodology for individual and/or simultaneous removal (s) of M (III) and cationic dyes. ACS Omega 4(1):1763–1780
Schott H (1992) Swelling kinetics of polymers. J Macromol Sci Part B 31(1):1–9
Wang Y, Wang W, Shi X, Wang A (2013) Enhanced swelling and responsive properties of an alginate-based superabsorbent hydrogel by sodium p-styrenesulfonate and attapulgite nanorods. Polym Bull 70(4):1181–1193
Gao T, Wang W, Wang A (2011) A pH-sensitive composite hydrogel based on sodium alginate and medical stone: synthesis, swelling, and heavy metal ions adsorption properties. Macromol Res 19(7):739–748
Akl M, Ismail MA, Hashem MA, Ali DA (2021) Novel NS modified cellulose: synthesis, spectroscopic characterization and adsorption studies of Cu2+, Hg2+ and Pb2+ from environmental water samples. Res square 1:1–34
Yang S, Fu S, Liu H, Zhou Y, Li X (2011) Hydrogel beads based on carboxymethyl cellulose for removal heavy metal ions. J Appl Polym Sci 119(2):1204–1210
Özkahraman B, Acar I, Emik S (2011) Removal of Cu2+ and Pb2+ ions using CMC based thermoresponsive nanocomposite hydrogel. CLEAN-Soil, Air, Water 39(7):658–664
Hu Z-H, Omer AM, Ouyang Xk YuD (2018) Fabrication of carboxylated cellulose nanocrystal/sodium alginate hydrogel beads for adsorption of Pb (II) from aqueous solution. Int J Biol Macromol 108:149–157
Mohammed N, Baidya A, Murugesan V, Kumar AA, Ganayee MA, Mohanty JS, Tam KC, Pradeep T (2016) Diffusion-controlled simultaneous sensing and scavenging of heavy metal ions in water using atomically precise cluster–cellulose nanocrystal composites. ACS Sustain Chem Eng 4(11):6167–6176
Rong L, Zhu Z, Wang B, Mao Z, Xu H, Zhang L, Zhong Y, Sui X (2018) Facile fabrication of thiol-modified cellulose sponges for adsorption of Hg 2+ from aqueous solutions. Cellulose 25(5):3025–3035
Acknowledgements
The authors gratefully admit partial support of this work by the Yazd University Research Council.
Funding
The authors declare that no funds, grants, or other support were received during the preparation of this manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
FT Conceptualization, Supervision, Project administration, Methodology, Formal analysis, Data curation, Writing-review and editing. EA-A Methodology, Original draft, Conceptualization, Formal analysis, Investigation. F.T. wrote the main manuscript text and E.A. prepared figures . All authors reviewed the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors report no declarations of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Tamaddon, F., Ahmadi-AhmadAbadi, E. Microwave-Assisted Fabrication of a pH/Salt Responsive Hydrogel from the Micro-CMC, In Situ Polymerized Acrylamide, and Nanoγ-Fe2O3–SO3H Cross-Linked by a Phenyl Bisamide Linker for Pb2+ and Hg2+ Removal. J Polym Environ 31, 461–478 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10924-022-02616-w
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10924-022-02616-w