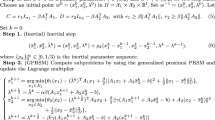Abstract
In this paper, we are concerned with a class of structured optimization problems frequently arising from image processing and statistical learning, where the objective function is the sum of a quadratic term and a nonsmooth part, and the constraint set consists of a linear equality constraint and two simple convex sets in the sense that projections onto simple sets are easy to compute. To fully exploit the quadratic and separable structure of the problem under consideration, we accordingly propose a partially inertial Douglas–Rachford splitting method. It is noteworthy that our algorithm enjoys easy subproblems for the case where the underlying two simple convex sets are not the whole spaces. Theoretically, we establish the global convergence of the proposed algorithm under some mild conditions. A series of computational results on the constrained Lasso and constrained total-variation (TV) based image restoration demonstrate that our proposed method is competitive with some state-of-the-art first-order solvers.








Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
Enquiries about data availability should be directed to the authors.
References
Alvarez, F.: Weak convergence of a relaxed and inertial hybrid projection-proximal point algorithm for maximal monotone operators in Hilbert space. SIAM J. Optim. 14(3), 773–782 (2004)
Alves, M.M., Eckstein, J., Geremia, M., Melo, J.G.: Relative-error inertial-relaxed inexact versions of Douglas–Rachford and ADMM splitting algorithms. Comput. Optim. Appl. 75(2), 389–422 (2020)
Attouch, H., Peypouquet, J., Redont, P.: A dynamical approach to an inertial forward-backward algorithm for convex minimization. SIAM J. Optim. 24(1), 232–256 (2014)
Barzilai, J., Borwein, J.: Two-point step size gradient methods. IMA J. Numer. Anal. 8, 141–148 (1988)
Bennett, J., Lanning, S.: The Netflix prize. In Proceedings of KDD Cup and Workshop, vol. 2007, p. 35. New York (2007)
Bertsekas, D., Tsitsiklis, J.: Parallel and Distributed Computation. Numerical Methods. Prentice-Hall, Englewood Cliffs (1989)
Bot, R.I., Csetnek, E.R.: An inertial alternating direction method of multipliers. Minimax Theory Appl. 1, 29–49 (2016)
Boţ, R.I., Csetnek, E.R., Hendrich, C.: Inertial Douglas–Rachford splitting for monotone inclusion problems. Appl. Math. Comput. 256, 472–487 (2015)
Boţ, R.I., Csetnek, E.R., László, S.C.: An inertial forward–backward algorithm for the minimization of the sum of two nonconvex functions. EURO J. Comput. Optim. 4(1), 3–25 (2016)
Boyd, S., Parikh, N., Chu, E., Peleato, B., Eckstein, J.: Distributed optimization and statistical learning via the alternating direction method of multipliers. Found. Trends Mach. Learn. 3, 1–122 (2010)
Briceno-Arias, L.M., Combettes, P.L.: A monotone+ skew splitting model for composite monotone inclusions in duality. SIAM J. Optim. 21(4), 1230–1250 (2011)
Cai, X., Guo, K., Jiang, F., Wang, K., Wu, Z., Han, D.: The developments of proximal point algorithms. J. Oper. Res. Soc. China 10(2), 197–239 (2022)
Chambolle, A., Pock, T.: A first-order primal-dual algorithm for convex problems with applications to imaging. J. Math. Imaging Vis. 40, 120–145 (2011)
Chambolle, A., Pock, T.: On the ergodic convergence rates of a first-order primal-dual algorithm. Math. Program. 159(1–2), 253–287 (2016)
Chen, C., Chan, R.H., Ma, S., Yang, J.: Inertial proximal ADMM for linearly constrained separable convex optimization. SIAM J. Imaging Sci. 8(4), 2239–2267 (2015)
Chen, C., He, B., Yuan, X.: Matrix completion via alternating direction method. IMA J. Numer. Anal. 32, 227–245 (2012)
Chen, Y., Nasrabadi, N.M., Tran, T.D.: Hyperspectral image classification using dictionary-based sparse representation. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote sens. 49(10), 3973–3985 (2011)
Cheng, H., Liu, Z., Yang, L., Chen, X.: Sparse representation and learning in visual recognition: theory and applications. Signal Process. 93(6), 1408–1425 (2013)
Dai, Y., Fletcher, R.: Projected Barzilai–Borwein methods for large-scale box-constrained quadratic programming. Numer. Math. 100, 21–47 (2005)
Deng, Z., Liu, S.: Inertial generalized proximal Peaceman–Rachford splitting method for separable convex programming. Calcolo 58(1), 1–30 (2021)
Dou, M., Li, H., Liu, X.: An inertial proximal Peaceman–Rachford splitting method. Sci. Sin. Math. 47(2), 333–348 (2016)
Eaves, B.: On the basic theorem of complementarity. Math. Program. 1, 68–75 (1971)
Facchinei, F., Pang, J.: Finite-Dimensional Variational Inequalities and Complementarity Problems. Springer, New York (2003)
Gabay, D., Mercier, B.: A dual algorithm for the solution of nonlinear variational problems via finite element approximations. Comput. Math. Appl. 2, 16–40 (1976)
Gaines, B.R., Kim, J., Zhou, H.: Algorithms for fitting the constrained Lasso. J. Comput. Graph. Stat. 27(4), 861–871 (2018)
Glowinski, R., Marrocco, A.: Approximation par éléments finis d’ordre un et résolution par pénalisation-dualité d’une classe de problèmes non linéaires. R.A.I.R.O. R2, 41–76 (1975)
Goldberg, K., Roeder, T., Gupta, D., Perkins, C.: Eigentaste: a constant time collaborative filtering algorithm. Inf. Retr. J. 4(2), 133–151 (2001)
Han, D.: A survey on some recent developments of alternating direction method of multipliers. J. Oper. Res. Soc. China 10, 1–52 (2022)
Han, D., He, H., Yang, H., Yuan, X.: A customized Douglas–Rachford splitting algorithm for separable convex minimization with linear constraints. Numer. Math. 127, 167–200 (2014)
Han, D., Xu, W., Yang, H.: An operator splitting method for variational inequalities with partially unknown mappings. Numer. Math. 111, 207–237 (2008)
Hansen, P.C., Nagy, J.G., O’leary, D.P.: Deblurring images: matrices, spectra, and filtering. SIAM (2006)
He, B., Liao, L., Wang, S.: Self-adaptive operator splitting methods for monotone variational inequalities. Numer. Math. 94, 715–737 (2003)
He, H., Cai, X., Han, D.: A fast splitting method tailored for Dantzig selectors. Comput. Optim. Appl. 62, 347–372 (2015)
He, H., Xu, H.K.: Splitting methods for split feasibility problems with application to dantzig selectors. Inverse Probl. 33(5), 055003 (2017)
Hu, L., Zhang, W., Cai, X., Han, D.: A parallel operator splitting algorithm for solving constrained total-variation retinex. Inverse Probl. Imaging 14(6), 1135 (2020)
Iordache, M.D., Bioucas-Dias, J.M., Plaza, A.: Sparse unmixing of hyperspectral data. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote. Sens. 49(6), 2014–2039 (2011)
Liu, Y.J., Sun, D., Toh, K.C.: An implementable proximal point algorithmic framework for nuclear norm minimization. Math. Program. 133(1), 399–436 (2012)
Lorenz, D.A., Pock, T.: An inertial forward-backward algorithm for monotone inclusions. J. Math. Imaging Vis. 51(2), 311–325 (2015)
Morini, S., Porcelli, M., Chan, R.: A reduced Newton method for constrained linear least squares problems. J. Comput. Appl. Math. 233, 2200–2212 (2010)
Polyak, B.T.: Some methods of speeding up the convergence of iteration methods. USSR Comput. Math. Math. Phys. 4(5), 1–17 (1964)
Rockafellar, R.: On the maximal monotonicity of subdifferential mappings. Pac. J. Math. 33(1), 209–216 (1970)
Rudin, L., Osher, S., Fatemi, E.: Nonlinear total variation based noise removal algorithms. Phys. D 60, 227–238 (1992)
Tibshirani, R.: Regression shrinkage and selection via the Lasso. J. R. Stat. Soc. Ser. B 58, 267–288 (1996)
Toh, K., Yun, S.: An accelerated proximal gradient algorithm for nuclear norm regularized least squares problems. Pac. J. Optim. 6, 615–640 (2010)
Varga, R.: Matrix Iterative Analysis. Prentice-Hall, Englewood Cliffs (1966)
Wang, X., Yuan, X.: The linearized alternating direction method of multipliers for Dantzig selector. SIAM J. Sci. Comput. 34, A2792–A2811 (2012)
Wu, L., Yang, Y., Liu, H.: Nonnegative-lasso and application in index tracking. Comput. Stat. Data Anal. 70, 116–126 (2014)
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to thank the two anonymous referees for their valuable comments, which helped us improve the quality of this paper. H. He was supported in part by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (NSFC) No. 12371303 and Ningbo Natural Science Foundation (No. 2023J014). D. Han was supported by NSFC Nos. 12126603 and 12131004 and Ministry of Science and Technology of China (Grant No. 2021YFA1003600).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors have not disclosed any competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Qu, Y., He, H. & Han, D. A Partially Inertial Customized Douglas–Rachford Splitting Method for a Class of Structured Optimization Problems. J Sci Comput 98, 9 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10915-023-02397-x
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10915-023-02397-x