Abstract
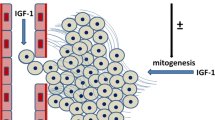
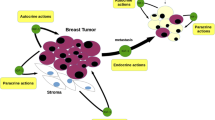
The insulin-like growth factors, IGF-I and IGF-II, have endocrine as well as autocrine-paracrine actions on tissue growth. Both IGF ligands are expressed within developing mammary tissue throughout postnatal stages with specific sites of expression in the epithelial and stromal compartments. The elucidation of circulating versus local actions and of epithelial versus stromal actions of IGFs in stimulating mammary epithelial development has been the focus of several laboratories. The recent studies addressing IGF ligand function provide support for the hypotheses that (1) the diverse sites of IGF expression may mediate different cellular outcomes, and (2) IGF-I and IGF-II are distinctly regulated and have diverse functions in mammary development. The mechanisms for IGF function likely are mediated, in part, through diverse IGF signaling receptors. The local actions of the IGF ligands and receptors as revealed through recent publications are the focus of this review.
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- IGF:
-
Insulin like-growth factor
- IGF-IR:
-
IGF-type I receptor
- IR:
-
insulin receptor
- hybridR:
-
IGF-IR:IR hybrid receptor
- GH:
-
growth hormone
- LID:
-
liver-specific IGF-I deletion
- ALS:
-
acid labile subunit
- IGFBP:
-
IGF binding proteins
- TEB:
-
terminal end bud
- PR:
-
progesterone receptor
- PRLR:
-
prolactin receptor
- C/EBP-β:
-
CCAAT/enhancer binding protein-beta
- E/P:
-
estrogen/progesterone
- KO:
-
knockout
- MEC:
-
mammary epithelial cell
- MMTV:
-
mouse mammary tumor virus
- EGF:
-
epidermal growth factor
- BrdU:
-
bromodeoxyuridine
References
Butler AA, LeRoith D. Minireview: tissue-specific versus generalized gene targeting of the igf1 and igf1r genes and their roles in insulin-like growth factor physiology. Endocrinology 2001;142(5):1685–8. doi:10.1210/en.142.5.1685.
LeRoith D. Clinical relevance of systemic and local IGF-I: lessons from animal models. Pediatr Endocrinol Rev 2008;5(Suppl 2):739–43.
Liu JL, Yakar S, LeRoith D. Conditional knockout of mouse insulin-like growth factor-1 gene using the Cre/loxP system. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med 2000;223(4):344–51. doi:10.1046/j.1525-1373.2000.22349.x.
Yakar S, Pennisi P, Wu Y, Zhao H, LeRoith D. Clinical relevance of systemic and local IGF-I. Endocr Dev 2005;9:11–6. doi:10.1159/000085718.
Frasca F, Pandini G, Scalia P, Sciacca L, Mineo R, Costantino A, et al. Insulin receptor isoform A, a newly recognized high-affinity insulin-like growth factor II receptor in fetal and cancer cells. Mol Cell Biol 1999;19:3278–88.
Benyoucef S, Surinya KH, Hadaschik D, Siddle K. Characterization of insulin/IGF hybrid receptors: contributions of the insulin receptor L2 and Fn1 domains and the alternatively spliced exon 11 sequence to ligand binding and receptor activation. Biochem J 2007;403(3):603–13. doi:10.1042/BJ20061709.
Pandini G, Frasca F, Mineo R, Sciacca L, Vigneri R, Belfiore A. Insulin/insulin-like growth factor I hybrid receptors have different biological characteristics depending on the insulin receptor isoform involved. J Biol Chem 2002;277(42):39684–95. doi:10.1074/jbc.M202766200.
Slaaby R, Schaffer L, Lautrup-Larsen I, Andersen AS, Shaw AC, Mathiasen IS, et al. Hybrid receptors formed by insulin receptor (IR) and insulin-like growth factor I receptor (IGF-IR) have low insulin and high IGF-1 affinity irrespective of the IR splice variant. J Biol Chem 2006;281(36):25869–74. doi:10.1074/jbc.M605189200.
Hadsell D, Bonnette S. IGF and insulin action in the mammary gland: lessons from transgenic and knockout mouse models. J Mammary Gland Biol Neoplasia 2000;5(1):19–30. doi:10.1023/A:1009559014703.
Wood T, Richert M, Stull M, Allar M. The insulin-like growth factors (IGFs) and IGF binding proteins in postnatal development of murine mammary glands. J Mammary Gland Biol Neoplasia 2000;5(1):31–42. doi:10.1023/A:1009511131541.
Baker J, Lie JP, Robertson EJ, Efstratiadis A. Role of insulin-like growth factors in embryonic and postnatal growth. Cell 1993;75:73–82.
Liu JP, Baker J, Perkins AS, Robertson EJ, Efstratiadis A. Mice carrying null mutations of the genes encoding insulin-like growth factor I (Igf-1) and type 1 IGF receptor (Igf1r). Cell 1993;75:59–72.
Froesch E, Schmid C, Schwander J, Zapf J. Actions of insulin-like growth factors. Annu Rev Physiol 1985;47:443–67. doi:10.1146/annurev.ph.47.030185.002303.
Roberts CT, Owens JA, Sferruzzi-Perri AN. Distinct actions of insulin-like growth factors (IGFs) on placental development and fetal growth: lessons from mice and guinea pigs. Placenta 2008;29(Suppl A):S42–4S7.
Liu JL, LeRoith D. Insulin-like growth factor I is essential for postnatal growth in response to growth hormone. Endocrinology 1999;140(11):5178–84. doi:10.1210/en.140.11.5178.
Sjogren K, Liu JL, Blad K, Skrtic S, Vidal O, Wallenius V, et al. Liver-derived insulin-like growth factor I (IGF-I) is the principal source of IGF-I in blood but is not required for postnatal body growth in mice. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 1999;96(12):7088–92. doi:10.1073/pnas.96.12.7088.
Yakar S, Liu JL, Stannard B, Butler A, Accili D, Sauer B, et al. Normal growth and development in the absence of hepatic insulin-like growth factor I. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 1999;96(13):7324–9. doi:10.1073/pnas.96.13.7324.
Yakar S, Rosen CJ, Beamer WG, Ackert-Bicknell CL, Wu Y, Liu JL, et al. Circulating levels of IGF-1 directly regulate bone growth and density. J Clin Invest 2002;110(6):771–81.
Richards RG, Klotz DM, Walker MP, Diaugustine RP. Mammary gland branching morphogenesis is diminished in mice with a deficiency of insulin-like growth factor-I (IGF-I), but not in mice with a liver-specific deletion of IGF-I. Endocrinology 2004;145(7):3106–10. doi:10.1210/en.2003-1112.
Lembo G, Rockman HA, Hunter JJ, Steinmetz H, Koch WJ, Ma L, et al. Elevated blood pressure and enhanced myocardial contractility in mice with severe IGF-1 deficiency. J Clin Invest 1996;98(11):2648–55. doi:10.1172/JCI119086.
Allar MA, Wood TL. Expression of the insulin-like growth factor binding proteins during postnatal development of the murine mammary gland. Endocrinology 2004;145(5):2467–77. doi:10.1210/en.2003-1641.
Boutinaud M, Shand JH, Park MA, Phillips K, Beattie J, Flint DJ, et al. A quantitative RT-PCR study of the mRNA expression profile of the IGF axis during mammary gland development. J Mol Endocrinol 2004;33(1):195–207. doi:10.1677/jme.0.0330195.
Modha G, Blanchard A, Iwasiow B, Mao XJ, Troup S, Adeyinka A, et al. Developmental changes in insulin-like growth factor I receptor gene expression in the mouse mammary gland. Endocr Res 2004;30(1):127–40. doi:10.1081/ERC-120029892.
Richert M, Wood T. Expression and regulation of insulin-like growth factors and their binding proteins in the normal breast. In: Manni A, editor. Endocrinology of breast cancer. Totowa, NJ: Humana; 1999. p. 39–52.
Richert M, Wood T. The insulin-like growth factors (IGF) and IGF type I receptor during postnatal growth of the murine mammary gland: sites of messenger ribonucleic acid expression and potential functions. Endocrinology 1999;140:454–61. doi:10.1210/en.140.1.454.
Walden P, Ruan W, Feldman M, Kleinberg D. Evidence that the mammary fat pad mediates the action of growth hormone in mammary gland development. Endocrinology 1998;139:659–62. doi:10.1210/en.139.2.659.
Grimm SL, Seagroves TN, Kabotyanski EB, Hovey RC, Vonderhaar BK, Lydon JP, et al. Disruption of steroid and prolactin receptor patterning in the mammary gland correlates with a block in lobuloalveolar development. Mol Endocrinol 2002;16(12):2675–91. doi:10.1210/me.2002-0239.
Seagroves TN, Krnacik S, Raught B, Gay J, Burgess-Beusse B, Darlington GJ, et al. C/EBPβ, but not C/EBPα, is essential for ductal morphogenesis, lobuloalveolar proliferation, and functional differentiation in the mouse mammary gland. Genes Dev 1998;12:1917–28. doi:10.1101/gad.12.12.1917.
Seagroves TN, Lydon JP, Hovey RC, Vonderhaar BK, Rosen JM. C/EBPbeta (CCAAT/enhancer binding protein) controls cell fate determination during mammary gland development. Mol Endocrinol 2000;14(3):359–68. doi:10.1210/me.14.3.359.
Shyamala G, Barcellos-Hoff MH, Toft D, Yang X. In situ localization of progesterone receptors in normal mouse mammary glands: absence of receptors in the connective and adipose stroma and a heterogeneous distribution in the epithelium. J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol 1997;63:251–9. doi:10.1016/S0960-0760(97)00128-3.
Silberstein GB, Van Horn K, Shyamala G, Daniel CW. Progesterone receptors in the mouse mammary duct: distribution and developmental regulation. Cell Growth Differ 1996;7:945–52.
Zeps N, Bentel JM, Papadimitriou JM, Dawkins HJ. Murine progesterone receptor expression in proliferating mammary epithelial cells during normal pubertal development and adult estrous cycle. Association with eralpha and erbeta status. J Histochem Cytochem 1999;47(10):1323–30.
Brisken C, Ayyannan A, Nguyen C, Heineman A, Reinhardt F, Tan J, et al. IGF-2 is a mediator of prolactin-induced morphogenesis in the breast. Dev Cell 2002;3(6):877–87. doi:10.1016/S1534-5807(02)00365-9.
Hovey RC, Harris J, Hadsell DL, Lee AV, Ormandy CJ, Vonderhaar BK. Local insulin-like growth factor-II mediates prolactin-induced mammary gland development. Mol Endocrinol 2003;17(3):460–71. doi:10.1210/me.2002-0214.
Kleinberg D, Feldman M, Ruan W. IGF-I: An essential factor in terminal end bud formation and ductal morphogenesis. J Mammary Gland Biol Neoplasia 2000;5(1):7–17. doi:10.1023/A:1009507030633.
Ruan W, Kleinberg D. Insulin-like growth factor I is essential for terminal end bud formation and ductal morphogenesis during mammary development. Endocrinology 1999;140:5075–81. doi:10.1210/en.140.11.5075.
Loladze AV, Stull MA, Rowzee AM, Demarco J, Lantry JH 3rd, Rosen CJ, et al. Epithelial-specific and stage-specific functions of insulin-like growth factor-I during postnatal mammary development. Endocrinology 2006;147(11):5412–23. doi:10.1210/en.2006-0427.
Stull MA, Richert MM, Loladze AV, Wood TL. Requirement for insulin-like growth factor-I in epidermal growth factor-mediated cell cycle progression of mammary epithelial cells. Endocrinology 2002;143:1872–9. doi:10.1210/en.143.5.1872.
Adesanya OO, Zhou J, Samathanam C, Powell-Braxton L, Bondy CA. Insulin-like growth factor 1 is required for G2 progression in the estradiol-induced mitotic cycle. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 1999;96(6):3287–91. doi:10.1073/pnas.96.6.3287.
Stull MA, Rowzee AM, Loladze AV, Wood TL. Growth factor regulation of cell cycle progression in mammary epithelial cells. J Mammary Gland Biol Neoplasia 2004;9(1):15–26. doi:10.1023/B:JOMG.0000023585.95430.f4.
de Ostrovich KK, Lambertz I, Colby JK, Tian J, Rundhaug JE, Johnston D, et al. Paracrine overexpression of insulin-like growth factor-1 enhances mammary tumorigenesis in vivo. Am J Pathol 2008;173(3):824–34. doi:10.2353/ajpath.2008.071005.
Ciarloni L, Mallepell S, Brisken C. Amphiregulin is an essential mediator of estrogen receptor alpha function in mammary gland development. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 2007;104(13):5455–60. doi:10.1073/pnas.0611647104.
Fernandez AM, Dupont J, Farrar RP, Lee S, Stannard B, Le Roith D. Muscle-specific inactivation of the IGF-I receptor induces compensatory hyperplasia in skeletal muscle. J Clin Invest 2002;109(3):347–55.
DeChiara TM, Efstratiadis A, Robertson EJ. A growth-deficiency phenotype in heterozygous mice carrying an insulin-like growth factor II gene disrupted by gene targeting. Nature 1990;345:78–80. doi:10.1038/345078a0.
Werner H, Weinstein D, Bentov I. Similarities and differences between insulin and IGF-I: structures, receptors, and signalling pathways. Arch Physiol Biochem 2008;114(1):17–22. doi:10.1080/13813450801900694.
Korner C, Nurnberg B, Uhde M, Braulke T. Mannose 6-phosphate/insulin-like growth factor II receptor fails to interact with G-proteins. Analysis of mutant cytoplasmic receptor domains. J Biol Chem 1995;270(1):287–95. doi:10.1074/jbc.270.1.287.
Nissley P, Lee L, Kiess W. Evidence against a role for insulin-like growth factor II in the autonomous growth of rat 18,54-SF cells. Mol Cell Endocrinol 1991;75(3):213–9. doi:10.1016/0303-7207(91)90163-M.
Nissley P, Lopaczynski W. Insulin-like growth factor receptors. Growth Factors 1991;5(1):29–43. doi:10.3109/08977199109000269.
Bailyes EM, Nave BT, Soos MA, Orr SR, Hayward AC, Siddle K. Insulin receptor/IGF-I receptor hybrids are widely distributed in mammalian tissues: quantification of individual receptor species by selective immunoprecipitation and immunoblotting. Biochem J 1997;327(Pt 1):209–15.
Johansson GS, Arnqvist HJ. Insulin and IGF-I action on insulin receptors, IGF-I receptors and hybrid insulin/IGF-I receptors in vascular smooth muscle cells. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab 2006;291:E1124–1130.
Moxham CP, Duronio V, Jacobs S. Insulin-like growth factor I receptor beta-subunit heterogeneity. Evidence for hybrid tetramers composed of insulin-like growth factor I and insulin receptor heterodimers. J Biol Chem 1989;264(22):13238–44.
Soos MA, Field CE, Siddle K. Purified hybrid insulin/insulin-like growth factor-I receptors bind insulin-like growth factor-I, but not insulin, with high affinity. Biochem J 1993;290(Pt 2):419–26.
Kasuya J, Paz IB, Maddux BA, Goldfine ID, Hefta SA, Fujita-Yamaguchi Y. Characterization of human placental insulin-like growth factor-I/insulin hybrid receptors by protein microsequencing and purification. Biochemistry 1993;32(49):13531–6. doi:10.1021/bi00212a019.
Soos MA, Siddle K. Immunological relationships between receptors for insulin and insulin-like growth factor I. Evidence for structural heterogeneity of insulin-like growth factor I receptors involving hybrids with insulin receptors. Biochem J 1989;263(2):553–63.
Frattali AL, Pessin JE. Relationship between alpha subunit ligand occupancy and beta subunit autophosphorylation in insulin/insulin-like growth factor-1 hybrid receptors. J Biol Chem 1993;268(10):7393–400.
Pandini G, Vigneri R, Costantino A, Frasca F, Ippolito A, Fujita-Yamaguchi Y, et al. Insulin and insulin-like growth factor-I (IGF-I) receptor overexpression in breast cancers leads to insulin/IGF-I hybrid receptor overexpression: evidence for a second mechanism of IGF-I signaling. Clin Cancer Res 1999;5(7):1935–44.
Bonnette SG, Hadsell DL. Targeted disruption of the IGF-I receptor gene decreases cellular proliferation in mammary terminal end buds. Endocrinology 2001;142:4937–45. doi:10.1210/en.142.11.4937.
Carboni JM, Lee AV, Hadsell DL, Rowley BR, Lee FY, Bol DK, et al. Tumor development by transgenic expression of a constitutively active insulin-like growth factor I receptor. Cancer Res 2005;65(9):3781–7. doi:10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-04-4602.
Jones RA, Campbell CI, Gunther EJ, Chodosh LA, Petrik JJ, Khokha R, et al. Transgenic overexpression of IGF-IR disrupts mammary ductal morphogenesis and induces tumor formation. Oncogene 2007;26(11):1636–44. doi:10.1038/sj.onc.1209955.
Robinson G, Accili D, Hennighausen L. Rescue of mammary epithelium of early lethal phenotypes by embryonic mammary gland transplantation as exemplified with insulin receptor null mice. In: Ip N, Asch B, editors. Methods in mammary gland biology and breast cancer research. New York: Kluwer; 2000. p. 307–16.
Kitamura T, Kahn CR, Accili D. Insulin receptor knockout mice. Annu Rev Physiol 2003;65:313–32. doi:10.1146/annurev.physiol.65.092101.142540.
Kondo T, Hafezi-Moghadam A, Thomas K, Wagner DD, Kahn CR. Mice lacking insulin or insulin-like growth factor 1 receptors in vascular endothelial cells maintain normal blood-brain barrier. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 2004;317:315–20. doi:10.1016/j.bbrc.2004.03.043.
Cullen K, Smith H, Hill S, Rosen N, Lippman M. Growth factor messenger RNA expression by human breast fibroblasts from benign and malignant lesions. Cancer Res 1991;51:4978–85.
Cullen KJ, Allison A, Martire I, Ellis M, Singer C. Insulin-like growth factor expression in breast cancer epithelium and stroma. Breast Cancer Res Treat 1992;22:21–9. doi:10.1007/BF01833330.
Paik S. Expression of IGF-I and IGF-II mRNA in breast tissue. Breast Cancer Res Treat 1992;22(1):31–8. doi:10.1007/BF01833331.
Singer C, Rasmussen A, Smith HS, Lippman ME, Lynch HT, Cullen KJ. Malignant breast epithelium selects for insulin-like growth factor II expression in breast stroma: evidence for paracrine function. Cancer Res 1995;55(11):2448–54.
Happerfield LC, Miles DW, Barnes DM, Thomsen LL, Smith P, Hanby A. The localization of the insulin-like growth factor receptor 1 (IGFR-1) in benign and malignant breast tissue. J Pathol 1997;183(4):412–7. doi:10.1002/(SICI)1096-9896(199712)183:4>412::AID-PATH944<3.0.CO;2-4.
Zhang H, Pelzer AM, Kiang DT, Yee D. Down-regulation of type I insulin-like growth factor receptor increases sensitivity of breast cancer cells to insulin. Cancer Res 2007;67(1):391–7. doi:10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-06-1712.
Grimm SL, Rosen JM. The role of C/EBPbeta in mammary gland development and breast cancer. J Mammary Gland Biol Neoplasia 2003;8(2):191–204. doi:10.1023/A:1025900908026.
Heckman BM, Chakravarty G, Vargo-Gogola T, Gonzales-Rimbau M, Hadsell DL, Lee AV, et al. Crosstalk between the p190-B RhoGAP and IGF signaling pathways is required for embryonic mammary bud development. Dev Biol 2007;309(1):137–49. doi:10.1016/j.ydbio.2007.07.002.
Dulbecco R, Unger M, Armstrong B, Bowman M, Syka P. Epithelial cell types and their evolution in the rat mammary gland determined by immunological markers. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 1983;80(4):1033–7. doi:10.1073/pnas.80.4.1033.
Williams JM, Daniel CW. Mammary ductal elongation: differentiation of myoepithelium and basal lamina during branching morphogenesis. Dev Biol 1983;97(2):274–90. doi:10.1016/0012-1606(83)90086-6.
Gudjonsson T, Adriance MC, Sternlicht MD, Petersen OW, Bissell MJ. Myoepithelial cells: their origin and function in breast morphogenesis and neoplasia. J Mammary Gland Biol Neoplasia 2005;10(3):261–72. doi:10.1007/s10911-005-9586-4.
Hu M, Yao J, Carroll DK, Weremowicz S, Chen H, Carrasco D, et al. Regulation of in situ to invasive breast carcinoma transition. Cancer Cell 2008;13(5):394–406. doi:10.1016/j.ccr.2008.03.007.
Lee AV, Zhang P, Ivanova M, Bonnette S, Oesterreich S, Rosen JM, et al. Developmental and hormonal signals dramatically alter the localization and abundance of insulin receptor substrate proteins in the mammary gland. Endocrinology 2003;144(6):2683–94. doi:10.1210/en.2002-221103.
Arsenijevic Y, Weiss S, Schneider B, Aebischer P. Insulin-like growth factor-I is necessary for neural stem cell proliferation and demonstrates distinct actions of epidermal growth factor and fibroblast growth factor-2. J Neurosci 2001;21(18):7194–202.
Bendall SC, Stewart MH, Menendez P, George D, Vijayaragavan K, Werbowetski-Ogilvie T, et al. IGF and FGF cooperatively establish the regulatory stem cell niche of pluripotent human cells in vitro. Nature 2007;448(7157):1015–21. doi:10.1038/nature06027.
Wang L, Schulz TC, Sherrer ES, Dauphin DS, Shin S, Nelson AM, et al. Self-renewal of human embryonic stem cells requires insulin-like growth factor-1 receptor and ERBB2 receptor signaling. Blood 2007;110(12):4111–9. doi:10.1182/blood-2007-03-082586.
Zhang CC, Lodish HF. Insulin-like growth factor 2 expressed in a novel fetal liver cell population is a growth factor for hematopoietic stem cells. Blood 2004;103(7):2513–21. doi:10.1182/blood-2003-08-2955.
Dontu G, Abdallah WM, Foley JM, Jackson KW, Clarke MF, Kawamura MJ, et al. In vitro propagation and transcriptional profiling of human mammary stem/progenitor cells. Genes Dev 2003;17(10):1253–70. doi:10.1101/gad.1061803.
Hsieh J, Aimone JB, Kaspar BK, Kuwabara T, Nakashima K, Gage FH. IGF-I instructs multipotent adult neural progenitor cells to become oligodendrocytes. J Cell Biol 2004;164(1):111–22. doi:10.1083/jcb.200308101.
Yamaguchi Y, Flier JS, Benecke H, Ransil BJ, Moller DE. Ligand-binding properties of the two isoforms of the human insulin receptor. Endocrinology 1993;132(3):1132–8. doi:10.1210/en.132.3.1132.
Kiess W, Blickenstaff GD, Sklar MM, Thomas CL, Nissley SP, Sahagian GG. Biochemical evidence that the type II insulin-like growth factor receptor is identical to the cation-independent mannose 6-phosphate receptor. J Biol Chem 1988;263(19):9339–44.
Tong PY, Tollefsen SE, Kornfeld S. The cation-independent mannose 6-phosphate receptor binds insulin-like growth factor II. J Biol Chem 1988;263(6):2585–8.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Grant Support: National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases DK60612 and National Cancer Institute CA120850 to TLW
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Rowzee, A.M., Lazzarino, D.A., Rota, L. et al. IGF Ligand and Receptor Regulation of Mammary Development. J Mammary Gland Biol Neoplasia 13, 361–370 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10911-008-9102-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10911-008-9102-8