Abstract
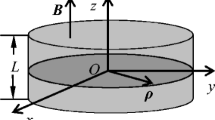
In this article, the influence of the electron velocity, the hydrogenic impurity, and the temperature on the properties of bound magnetopolarons in quantum disks in a magnetic field is studied by using the Lee-Low-Pines-Takda transformation. The results of the numerical calculation indicate that the vibration frequency of bound magnetopolarons \(\lambda \) increases with the increasing resonant frequency of the magnetic field \(\omega _\mathrm{c} \), the electron–LO phonon coupling strength \(\alpha \), the electron velocity u, and the dielectric constant ratio \(\eta \); and decreases with the increasing temperature T and the quantum disks thickness L. The Rashba spin splitting energy of the magnetopolarons \(E_\mathrm{R} (\pm )\) is composed of the Rashba spin splitting energy of the electron in zero magnetic field \(E_{\mathrm{SO}} (\pm )\) and the additional energy \(\Delta E_{\mathrm{R-ph}} \) caused by LO phonon effect. The bound magnetopolarons interaction energy \(E_{\mathrm{e-ph}} \) is composed of the electron–LO phonon interaction energy \(E_{\mathrm{e-ph}}^{\mathrm{(0)}} \), the additional energy \(\Delta E_{\mathrm{e-ph}}^{\mathrm{(u)}}\) caused by the electron velocity, and the additional energy \(\Delta E_{\mathrm{e-ph}}^{\mathrm{(c)}} \) caused by hydrogenic impurity. The absolute values of the \(E_{\mathrm{e-ph}}^{\mathrm{(0)}}\), \(\Delta E_{\mathrm{e-ph}}^{\mathrm{(u)}}\), and \(\Delta E_{\mathrm{e-ph}}^{\mathrm{(c)}}\) increase with the increasing resonant frequency of the external magnetic field \(\omega _\mathrm{c} \), the electron–LO phonon coupling strength \(\alpha \), the electron velocity u, and the dielectric constant ratio \(\eta \); and decrease with the increasing temperature T and the quantum disks thickness L. The influences of the electron–LO phonon interaction and the Rashba spin–orbit coupling effect cannot be ignored when studying bound magnetopolarons in quantum disks. The electron–LO phonon interaction is greatly influenced by the electron velocity u, the dielectric constant ratio \(\eta \), the temperature T, and the quantum disks thickness L. But the Rashba spin–orbit interaction of polarons mainly depends on the electron velocity u and the Rashba spin–orbit coupling strength \(\alpha _\mathrm{R} \).






Similar content being viewed by others
References
J. Liu, J.L. Xiao, S.F. Huo, Z.Y. Chen, Commun. Theor. Phys. 48, 930 (2007)
Z.X. Li, J.L. Xiao, A.H. Liu et al., Int. J. Nanosci. 10, 501 (2011)
W.P. Li, J.W. Yin, Y.F. Yu, J.L. Xiao, J. Low Temp. Phys. 160, 195 (2010)
J.W. Yin, W.P. Li, Y.F. Yu, J.L. Xiao, J. Low Temp. Phys. 163, 53 (2011)
S.P. Shan, S.H. Chen, J.L. Xiao, J. Low Temp. Phys. 176, 93 (2014)
C.L. Fai, V. Teboul, A. Monteil, S. Maabou, I. Nsangou, Condens. Matter Phys. 8, 639 (2005)
E.I. Rashba, Phys. Rev. B 62, 16267 (2000)
E. Tsitsishvili, G.S. Lozano, A.O. Gogolin, Phys. Rev. B 70, 115316 (2004)
C. Tapash, P. Pekka, Phys. Rev. B 71, 113305 (2005)
K. Kash, A. Scherer, J.M. Worlock et al., Appl. Phys. Lett. 49, 1043 (1986)
M.A. Reed, J.N. Randall, R.J. Aggarwal et al., Phys. Rev. Lett. 60, 535 (1988)
C.Y. Chen, W.S. Li, X.Y. Teng, S.D. Liang, Physica B 245, 92 (1998)
S. Fafard, D. Leonard, J.L. Merz et al., Appl. Phys. Lett. 66, 1767 (1995)
J.X. Wang, X.W. Sun, Y. Yang et al., Nanotechnology 22, 325704 (2011)
C. Lin, S. Park, H. Kim et al., Bull. Korean Chem. Soc. 33, 1993 (2012)
F.M. Peeters, V.A. Schweigert, Phys. Rev. B 53, 1468 (1996)
R. Price, X. Zhu, S.D. Sarma et al., Phys. Rev. B 51, 2017 (1995)
G. Lommer, F. Malcher, U. Rossler, Phys. Rev. Lett. 60, 728 (1988)
Q.F. Sun, J. Wang, H. Guo, Phys. Rev. B 71, 165310 (2005)
O. Voskoboynikov, C.P. Lee, O. Tretyak, Phys. Rev. B 63, 165306 (2001)
N. Tokuda, J. Phys. C Solid State Phys. 13, L851 (1980)
T.D. Lee, F.M. Low, D. Pines, Phys. Rev. 90, 297 (1953)
M.A. Brummell, R.J. Nicholas, M.A. Hopkins et al., Phys. Rev. Lett. 58, 77 (1987)
T. Chakraborty, P. Pietiläinen, Phys. Rev. B 71, 113305 (2005)
Acknowledgments
This work is supported by National Nature Science Foundation of Hebei Province, China (E2013407119) and the Items of Institution of Higher Education Scientific Research of Hebei Province, China (ZD20131008).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, Y., Han, C., Xin, W. et al. Influence of Electron Velocity and Hydrogenic Impurity on the Properties of the Bound Magnetopolarons in Quantum Disks in a Magnetic Field. J Low Temp Phys 180, 330–341 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10909-015-1317-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10909-015-1317-7