Abstract
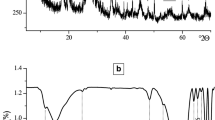
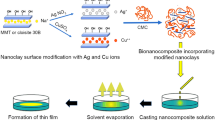
A study was carried out on the effect of gamma irradiation on the mechanical and thermal properties of carboxymethyl cellulose (CMC)/Ca-montmorillonite clay composite, prepared by blending using solvent method. In this study, carboxymethyl cellulose was used as a hosting matrix where clay was added to there at different contents: 0.25, 0.5, 1, 1.5 wt%, as a filler. The polymer composite films were cross-linked by irradiation with different integral doses. The results showed that the tensile strength (TS) increased continuously with radiation dose up to 10 kGy, beyond which declined. Meanwhile, TS exhibited increases with clay load ratio. However, the elongation at break (Eb) decreased continuously with dose and clay percentage within the developed composite films. Variation in structure and thermal properties were studied using X-ray diffractometion (XRD), scanning electron microscopy (SEM), Fourier-transform infrared spectroscopy (FTIR) and thermogravimetric analysis (TGA) techniques. The produced CMC/clay composites were implemented in removing copper (II) ions from a synthesized wastewater. The isotherm models and kinetic studies for the adsorption of Cu (II) onto CMC/clay were carried out. The results revealed that 0.1 g fabricated composite film irradiated at 10 kGy significantly removed copper (II) ions with adsorption capacity of 54.6 mg/g at optimum conditions: pH = 5, contact time = 300 min.













Similar content being viewed by others
References
M.R. Awual, I.M.M. Rahman, T. Yaita, M.A. Khaleque, M. Ferdows, pH dependent Cu(II) and Pd(II) ions detection and removal from aqueous media by an efficient mesoporous adsorbent. Chem. Eng. J. 236, 100–109 (2014)
Medicine I.O, Dietary reference intakes for Vitamin A, vitamin K, arsenic, boron, chromium, copper, iodine, iron, manganese, molybdenum, nickel, silicon, vanadium, and zinc (The National Academies Press, Washington, DC, 2001)
C.G. VanGinkel, S. Gayton, The biodegradability and nontoxicity of carboxymethyl cellulose (DS 0.7) and intermediates. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 15, 270–274 (1996)
M.E. Mahmoud, A.E.H. Abdou, M.E. Sobhy, N.A. Fekry, Solid-solid crosslinking of carboxymethyl cellulose nanolayer on titanium oxide nanoparticles as a novel biocomposite for efficient removal of toxic heavy metals from water. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 105, 1269–1278 (2017)
L.Y. Wang, M.J. Wang, Removal of heavy metal ions by poly(vinyl alcohol) and Carboxymethyl cellulose composite hydrogels prepared by a freeze-thaw method. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 4, 2830–2837 (2016)
Y. Zhang, Y. Liu, X. Wang, Z. Sun, J. Ma, T. Wu, F. Xing, J. Gao, Porous grapheme oxide/carboxymethyl cellulose monoliths, with high metal ion adsorption. Carbohyd. Polym. 101, 392–400 (2014)
S. Bang, Y.G. Ko, W.I. Kim, D. Cho, W.H. Park, O.H. Kwon, Preventing postoperative tissue adhesion using injectable carboxymethyl cellulose-pullulan hydrogels. Int. J. Biol Macromol. 105, 886–893 (2017)
N.S.V. Capanema, A.A.P. Mansur, A.C. de Jesus, S.M. Carvalho, L.C. de Oliveira, H.S. Mansur, Superabsorbent crosslinked carboxymethyl cellulose-PEG hydrogels for potential wound dressing applications. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 106, 1218–1234 (2018)
M.N. Nadagouda, R.S. Varma, Synthesis of thermally stable Carboxymethyl cellulose/metal biodegradable nanocomposites for potential biological applications. Biomacromolecules 8, 2762–2767 (2007)
M.Q. Gutiérrez, I. Echeverría, M. Ihl, V. Bifani, A.N. Maur, Carboxymethylcellulose–montmorillonite nanocomposite films activated with murta (Ugni molinae Turcz) leaves extract. Carbohydr. Polym. 87, 1495–1502 (2012)
M.S. Nazir, M.H.M. Kassim, L. Mohapatra, M.A. Gilani, M.R. Raza, K. Majeed, Characteristic properties of nanoclays and characterization of nanoparticulates and nanocomposites. In nanoclay reinforced polymer composites (Springer, Singapore, 2016), pp. 35–55
S.E. Bailey, T.J. Olin, R.M. Bricka, D.D. Adrian, A review of potentially low-cost sorbents for heavy metals. Water Res. 33, 2469–2479 (1999)
X.L. Wu, S.T. Donglin Zhao, X.L. Yang, Impact of solution chemistry conditions on the sorption behavior of Cu(II) on Lin’an Montmorillonite. Desalination 269(1-3), 84–91 (2011)
C.O. Ijagbemi, M.H. Baek, D.S. Kim, Montmorillonite surface properties and sorption characteristics for heavy metal removal from aqueous solutions. J. Hazard. Mater. 166, 538–546 (2009)
S.Q. Zhang, W.G. Hou, Adsorption behavior of Pb(II) on Montmorillonite. Colloids Surf. A. 320(1-3), 92–97 (2008)
Y. Bulut, G. Akcay, D. Elma, I.E. Serhatl, Synthesis of clay-based superabsorbent composite and its sorption capability. J. Hazard. Mater. 171, 717–723 (2009)
S. Saber-Samandari, S. Saber-Samandari, M. Gazi, Cellulose-graft-polyacrylamide/ hydroxyapatite composite hydrogel with possible application in removal of Cu (II) ions. React. Funct. Polym. 73, 1523–1530 (2013)
R. Ahmad, I. Hasan, L-cystein modified bentonite-cellulose nanocomposite (cellu/ cys-bent) for adsorption of Cu2+, Pb2+, and Cd2+ ions from aqueous solution. Sep. Sci. Technol. 51, 381–394 (2016)
H. Soltani, A. Belmokhtar, F.Z. Zeggai, A. Benyoucef, S. Bousalem, K. Bachari, Copper(II) removal from aqueous solutions by PANI-clay hybrid material: Fabrication, characterization, adsorption and kinetics study. J. Inorg. Organomet. Polym. Mater. 29, 841–850 (2019)
M.E. Khalifa, E.A. Abdelrahman, M.M. Hassanien, W.A. Ibrahim, Application of mesoporous silica nanoparticles Modifed with Dibenzoylmethane as a novel composite for Efcient removal of Cd(II), Hg(II), and Cu(II) ions from aqueous media. J. Inorg. Organomet. Polym. Mater. 30, 2182–2196 (2020)
K. Menad, A. Feddag, T. Juhna, Copper(II)–humic acid adsorption process using microporous-zeolite Na-X. J. Inorg. Organomet. Polym. Mater. 29, 1–16 (2019)
N.A. Dahlana, A.K. Veeramachineni, S.J. Langford, J. Pushpamalar, Developing of a magnetite film of carboxymethyl cellulose grafted carboxymethyl polyvinyl alcohol (CMC-g-CMPVA) for copper removal. Carbohydrate Polymers 173, 619–630 (2017)
B. Ôzkahraman, I. Acar, S. Emik, Removal of Cu2+ and Pb2+ ions using CMC based Thermoresponsive nanocomposite hydrogel. Clean (Weinh) 39(7), 658–664 (2011)
N. Reddy, Y. Yang, Citric acid cross-linking of starch films. Food Chem. 118(3), 702–711 (2010)
R. Sothornvit, J.M. Krochta, Plasticizers in edible films and coatings, in Innovations in food packaging, ed. by J. H. Han, (Academic Press, London, 2005), pp. 403–433
S. Rivero, L. Damonte, M.A. García, A. Pinotti, An insight into the role of glycerol in chitosan films. Food Biophy. 11(2), 117–127 (2016)
M. Lavorgna, F. Piscitelli, P. Mangiacapra, G. Buonocore, Study of the combined effect of both clay and glycerol plasticizer on the properties of chitosan films. Carbohydr. Polym. 82, 291–298 (2010)
H.L. Abd El-Mohdy, E.A. Hegazy, E.M. El-Nesr, M.A. El-Wahab, Synthesis, characterization and properties of radiation-induced Starch/(EG-co-MAA) hydrogels. Arab J. Chem. 9, S1627 (2016)
M.B. El-Arnaouty, A.M. Abdel Ghaffar, A.A. Abdel Baky, S.A. Shama, Radiation synthesis of hydrogels based on carboxymethyl cellulose and its application in removal of pollutants from wastewater. J. Vinyl Addit 25(S1), E35–E43 (2017)
F. Veglio, F. Beolchini, A. Gasbarro, Biosorption of toxic metals: An equilibrium study using free cells of Arthrobacter sp. Process Biochem. 32(2), 99–105 (1997)
N.M. Ismail, A. Bono, A.C.R. Valintinus, S. Nilus, L.M. Chng, Optimisation of reaction conditions for preparing carboxymethyl cellulose. J. Appl. Sci. 21, 2530–2536 (2010)
L. Wu, X. Lin, X. Zhou, X. Luo, Removal of uranium and fluorine from wastewater by double-functional microsphere adsorbent of SA/CMC loaded with calcium and aluminum. Appl. Surf. Sci. 384, 466–479 (2016)
C.M. Zvinowanda, J.O. Okonkwo, P.N. Shabalala, N.M. Agyei, A novel adsorbent for heavy metal remediation in aqueous environments. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Tech. 6, 425–434 (2009)
C. Iosu, S.A. Odoemelam, Studies on adsorbent dosage, particle sizes and pH constraints on biosorption of Pb (II) and Cd (II) ions from aqueous solution using modified and unmodified Crasstrotrea Gasar. Int Arch Appl Sci Technol 1, 62–68 (2010)
P.A. Brown, S.A. Gill, S.T. Allen, Metal removal from wastewater using peat. Water Res. 34, 3907–3916 (2000)
N.M. Mahmoodi, R. Salehi, M. Arami, H. Bahrami, Dye removal from colored textile wastewater using chitosan in binary systems. Desalin 267, 64–72 (2011)
M.R. Samarghandi, M. Hadi, S. Moayedi, F.B. Askari, Two-parameter isotherms of methyl orange sorption by pinecone derived activated carbon. Iran. J. Environ. Health Sci. Eng. 6(4), 285–294 (2009)
S. Aber, A. Khataee, M. Sheydaei, Optimization of activated carbon fiber preparation from Kenaf using K2HPO4 as chemical activator for adsorption of phenolic compounds. Bioresour. Technol. 100, 6586–6591 (2009)
M. Zulfiqar, S. Chowdhury, A. Omar, Hydrothermal synthesis of multiwalled TiO2 nanotubes and its photocatalytic activities for Orange II removal. Sep. Sci. Technol. 53, 1412–1422 (2018)
Y.S. Ho, Citation review of Lagergren kinetic rate equation on adsorption reactions. Scientometrics 59, 171–177 (2004)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gad, Y.H., Ali, H.E. & Hegazy, ES.A. Radiation-Induced Improving Mechanical and Thermal Properties of Carboxymethyl Cellulose/Clay Composite for Application in Removal of Copper(II) Ions from Wastewater. J Inorg Organomet Polym 31, 2083–2094 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10904-020-01850-w
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10904-020-01850-w