Abstract
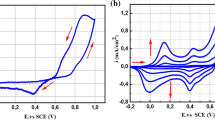
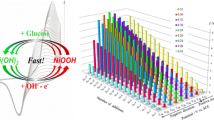
Flower-like carbon and nitrogen atomic doped NiO nanocomposite (CN-NiO) has been derived from the Ni-MOF/polyaniline (PANI) calcined at high temperature, which is used to construct a nonenzymic electrochemical sensor by coating it on glassy carbon electrode (GCE). The results of electrochemical tests show that the CN-NiO@GCE has the linear dependency of current response on glucose concentration ranged from 5.0 × 10–7 to 3 × 10–3 mol/L. It has higher sensitivity (1144 μA/mM/cm2) and lower detection limit (5.0 × 10–7 mol/L). In addition, the resulting CN-NiO@GCE shows long-term stability. At the same time, this electrode has good selectivity, with no electrochemical response to the interfering concomitant such as urea, nifedipine, ascorbic acid and dopamine. It indicates that Ni-MOF-derived CN-doped NiO nanocomposites are good electrochemical sensing materials, which find potential application to fabricate nonenzymic electrochemical recognition and detection devices.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
J. Lee, O.K. Farha, J. Roberts, K.A. Scheidt, S.T. Nguyen, J.T. Hupp, Metal–organic framework materials as catalysts. Chem. Soc. Rev. 38, 1450–1459 (2009)
J.R. Li, R.J. Kuppler, H.C. Zhou, Selective gas adsorption and separation in metal–organic frameworks. Chem. Soc. Rev. 38, 1477–1504 (2009)
N.L. Rosi, J. Eckert, M. Eddaoudi, D.T. Vodak, J. Kim, M. O’Keeffe, O.M. Yaghi, Hydrogen storage in microporous metal organic frameworks. Science 300, 1127–1129 (2003)
J.Y. An, S.J. Geib, N.L. Rosi, Cation-triggered drug release from a porous zinc-adeninate metal–organic framework. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 131, 8376–8377 (2009)
R.C. Huxford, J. Della Rocca, W.B. Lin, Metal-organic frameworks as potential drug carriers. Curr. Opin. Chem. Biol. 14, 262–268 (2010)
S.T. Meek, J.A. Greathouse, M.D. Allendorf, Metal–organic frameworks: a rapidly growing class of versatile nanoporous materials. Adv. Mater. 23, 249–267 (2011)
B. Liu, H. Shioyama, T. Akita, Q. Xu, Metal-organic framework as a template for porous carbon synthesis. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 130, 5390–5391 (2008)
A. Banerjee, U. Singh, V. Aravindan, M. Srinivasan, S. Ogale, Synthesis of CuO nanostructures from Cu-based metal organic framework (MOF-199) for application as anode for Li-ion batteries. Nano Energy 2, 1158–1163 (2013)
S. Premlatha, P. Sivasakthi, G.N.K. Ramesh Bapu, Electrodeposition of a 3D hierarchical porous flower-like cobalt–MWCNT nanocomposite electrode for non-enzymatic glucose sensing. RSC Adv. 5, 74374–74380 (2015)
C. Chen, Q. Xie, D. Yang, H. Xiao, Y. Fu, Y. Tan, S. Yao, Recent advances in electrochemical glucose biosensors: a review. RSC Adv. 3, 4473–4491 (2013)
M.S. Steiner, A. Duerkop, O.S. Wolfbeis, Optical methods for sensing glucose. Chem. Soc. Rev. 40, 4805–4839 (2011)
K. Lange, B.E. Rapp, M. Rapp, Surface acoustic wave biosensors: a review. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 391, 1509–1519 (2008)
P.R. Miller, S.A. Skoog, T.L. Edwards, D.R. Wheeler, X. Xiao, S.M. Brozik, R. Polsky, R.J. Narayan, Hollow microneedle-based sensor for multiplexed transdermal electrochemical sensing. J. Vis. Exp. 64, e4067 (2012)
K. Billingsley, M.K. Balaconis, J.M. Dubach, N. Zhang, E. Lim, K.P. Francis, H.A. Clark, Fluorescent nano-optodes for glucose detection. Anal. Chem. 82, 3707–3713 (2010)
Y. Huang, X. Dong, Y. Shi, C.M. Li, L.J. Li, P. Chen, Nanoelectronic biosensors based on CVD grown graphene. Nanoscale 2, 1485–1488 (2010)
J. Wang, Electrochemical glucose biosensors. Chem. Rev. 108, 814–825 (2010)
S. Ci, T. Huang, Z. Wen, S. Cui, S. Mao, D.A. Steeber, J. Chen, Nickel oxide hollow microsphere for non-enzyme glucose detection. Biosens. Bioelectron. 54, 251–257 (2014)
G.G. Guilbault, G.J. Lubrano, An enzyme electrode for the amperometric determination of glucose. Anal. Chim. Acta 64, 439–455 (1973)
Z.G. Zhu, L. Garcia-Gancedo, A.J. Flewitt, H.Q. Xie, F. Moussy, W.I. Milne, A critical review of glucose biosensors based on carbon nanomaterials: carbon nanotubes and graphene. Sensors 12, 5996–6022 (2012)
R. Devasenathipathy, C. Karuppiah, S.M. Chen, S. Palanisamy, B.S. Lou, M. Ajmal Ali, F.M.A. Al-Hemaid, A sensitive and selective enzyme-free amperometric glucose biosensor using a composite from multi-walled carbon nanotubes and cobalt phthalocyanine. RSC Adv. 5, 26762–26768 (2015)
L.C. Jiang, W.D. Zhang, A highly sensitive nonenzymatic glucose sensor based on CuO nanoparticles-modified carbon nanotube electrode. Biosens. Bioelectron. 25, 1402–1407 (2010)
H. Wang, H.S. Casalongue, Y.Y. Liang, H.J. Dai, Ni(OH)2 Nanoplates grown on graphene as advanced electrochemical pseudocapacitor materials. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 132, 7472–7477 (2010)
Y. Wang, Q.S. Zhu, H.G. Zhang, Fabrication of β-Ni(OH)2 and NiO hollow spheres by a facile template free process. Chem. Commun. 41, 5231–5233 (2005)
B. Zhao, X.K. Ke, J.H. Bao, C.L. Wang, L. Dong, Y.W. Chen, H.L. Chen, Synthesis of flower-like NiO and effects of morphology on its catalytic properties. J. Phys. Chem. C 113, 14440–14447 (2009)
Y. Zhang, F.G. Xu, Y.J. Sun, Y. Shi, Z.W. Wen, Z. Li, Assembly of Ni(OH)2 nanoplates on reduced graphene oxide: a two dimensional nanocomposite for enzyme-free glucose sensing. J. Mater. Chem. 21, 16949–16954 (2011)
W. Zuo, G. Yu, Z. Dong, A MOF-derived nickel based N-doped mesoporous carbon catalyst with high catalytic activity for the reduction of nitroarenes. RSC Adv. 6, 11749 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1039/C5RA23082A
S. Zheng, X. Li, B. Yan, Q. Hu, Y. Xu, X. Xiao, H. Xue, H. Pang, Transition-metal (Fe Co, Ni) based metal-organic frameworks for electrochemical energy storage. Adv. Energy Mater. 18, 1602733 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1002/aenm.201602733
Y. Yan, P. Gu, S. Zheng, M. Zheng, H. Pang, H. Xue, Facile synthesis of an accordion-like Ni-MOF superstructure for high-performance flexible supercapacitors. J. Mater. Chem. A 4, 8 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1039/C6TA08331E
P. Du, Y. Dong, C. Liu, W. Wei, D. Liu, P. Liu, Fabrication of hierarchical porous nickel based metal-organic framework (Ni-MOF) constructed with nanosheets as novel pseudo-capacitive material for asymmetric supercapacitor. J. Colloid Interfaces Sci. 518, 57–68 (2018)
Z. Lv, Q. Fan, Y. Xie, Z. Chen, A. Alsaedi, T. Hayat, X. Wang, C. Chen, MOFs-derived magnetic chestnut shell-like hollow sphere NiO/Ni@C composites and their removal performance for arsenic(V). Chem. Eng. J. 362, 413–421 (2019)
S. Liu, J. Tian, L. Wang, Y. Zhang, X. Qin, Y. Luo, A.M. Asiri, A.O. Al-Youbi, X. Sun, Hydrothermal treatment of grass: a low-cost, green route to nitrogen-doped, carbon-rich, photoluminescent polymer nanodots as an effective fluorescent sensing platform for label-free detection of Cu(II) ions. Adv. Mater. 24, 2037–2041 (2012)
J. Shen, Q. Wang, K. Zhang, S. Wang, L. Li, S. Dong, S. Zhao, J. Chen, R. Sun, Y. Wang, Z. Jian, W. Zhang, Flexible carbon cloth based solid-state supercapacitor from hierarchical holothurian-morphological NiCo2O4@NiMoO4/PANI. Electrochim. Acta 320, 134578 (2019)
T. Choi, S.H. Kim, C.W. Lee, H. Kim, S.K. Choi, S.H. Kim, E. Kim, J. Park, H. Kim, Synthesis of carbon nanotube–nickel nanocomposites using atomic layer deposition for high-performance non-enzymatic glucose sensing. Biosens. Bioelectron 63, 325–330 (2015)
Y. Jiang, S. Yu, J. Li, L. Jia, C. Wang, Improvement of sensitive Ni(OH)2 non-enzymatic glucose sensor based on carbon nanotube/polyimide membrane. Carbon 63, 367–375 (2013)
X. Niu, M. Lan, H. Zhao, C. Chen, Highly sensitive and selective nonenzymatic detection of glucose using three-dimensional porous nickel nanostructures. Anal. Chem. 85, 3561–3569 (2013)
Q. Wang, S. Wang, J. Shang, S. Qiu, W. Zhang, X. Wu, J. Li, W. Chen, X. Wang, Enhanced electronic communication and electrochemical sensitivity benefiting from the cooperation of quadruple hydrogen bonding and π−π interactions in graphene/multi-walled carbon nanotube hybrids. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 9, 6255–6264 (2017)
Q. Sheng, K. Luo, J. Zheng, H. Zhang, Enzymatically induced formation of neodymium hexacyanoferrate nanoparticles on the glucose oxidase/chitosan modified glass carbon electrode for the detection of glucose. Biosens. Bioelectron 24, 430–432 (2008)
H. Liu, X. Wu, B. Yang, Z. Li, L. Lei, X. Zhang, Three-dimensional porous NiO nanosheets vertically grown on graphite disks for enhanced performance non-enzymatic glucose sensor. Electrochim. Acta 174, 745–752 (2015)
P.K. Kannan, C.S. Rout, High performance non-enzymatic glucose sensor based on one-step electrodeposited nickel sulfide. Chem. Eur. J. 21, 9355–9359 (2015)
J. Yang, M. Cho, C. Pang, Y. Lee, Highly sensitive non-enzymatic glucose sensor based on over-oxidized polypyrrole nanowires modified with Ni(OH)2 nanoflakes. Sens. Actuators B 211, 93–101 (2015)
L. Wang, Y. Tang, L. Wang, H. Zhu, X. Meng, Y. Chen, Y. Sun, X.J. Yang, P. Wan, Fast conversion of redox couple on Ni(OH)2/C nanocomposite electrode for high-performance non-enzymatic glucose sensor. J. Solid State Electrochem. 19, 851–860 (2015)
P. Lu, Y. Lei, S. Lu, Q. Wang, Q. Liu, Three-dimensional roselike α-Ni(OH)2 assembled from nanosheet building blocks for non-enzymatic glucose detection. Anal. Chim. Acta 880, 42–51 (2015)
P. Lu, Q. Liu, Y. Xiong, Q. Wang, Y. Lei, S. Lu, L. Lu, L. Yao, Nanosheets-assembled hierarchical microstructured Ni(OH)2 hollow spheres for highly sensitive enzyme-free glucose sensors. Electrochim. Acta 168, 148–156 (2015)
Acknowledgements
Authors acknowledged the financial support from the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 21772152); the Scientific Research Foundation for the Returned Overseas Chinese Scholars, State Education Ministry; the Natural Science Foundation of Shaanxi Province (No. 2019JM-270).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jia, S., Wang, Q. & Wang, S. Ni-MOF/PANI-Derived CN-Doped NiO Nanocomposites for High Sensitive Nonenzymic Electrochemical Detection. J Inorg Organomet Polym 31, 865–874 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10904-020-01767-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10904-020-01767-4