Abstract
The increasing viral species have ruined people's health and the world's economy. Therefore, it is urgent to design bio-responsive materials to provide a vast platform for detecting a different family's passive or active virus. One can design a reactive functional unit for that moiety based on the particular bio-active moieties in viruses. Nanomaterials as optical and electrochemical biosensors have enabled better tools and devices to develop rapid virus detection. Various material science platforms are available for real-time monitoring and detecting COVID-19 and other viral loads. In this review, we discuss the recent advances of nanomaterials in developing the tools for optical and electrochemical sensing COVID-19. In addition, nanomaterials used to detect other human viruses have been studied, providing insights for developing COVID-19 sensing materials. The basic strategies for nanomaterials develop as virus sensors, fabrications, and detection performances are studied. Moreover, the new methods to enhance the virus sensing properties are discussed to provide a gateway for virus detection in variant forms. The study will provide systematic information and working of virus sensors. In addition, the deep discussion of structural properties and signal changes will offer a new gate for researchers to develop new virus sensors for clinical applications.
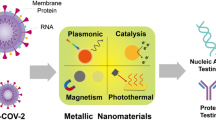
Graphical Abstract




© 2018, American Chemical Society

© 2017, Springer Nature


© 2022 The Authors. Published by American Chemical Society

© 2020 Elsevier Inc

© 2020 American Chemical Society

© 2021 American Chemical Society

© 2020 Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved

© 2021, American Chemical Society

© 2019 American Chemical Society

Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
This is a review article; therefore, this does not contain any data. Permission has been taken to incorporate figures from published articles.
References
Molloy EJ, Bearer CB (2021) Pediatric Research and COVID-19: the changed landscape. Pediatr Res 2021:1–2. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41390-021-01857-0
Jia P, Peng Jia C (2021) A changed research landscape of youth’s obesogenic behaviours and environments in the post-COVID-19 era. Obes Rev 22:e13162. https://doi.org/10.1111/OBR.13162
Hoofman J, Secord E (2021) The Effect of COVID-19 on Education. Pediatr Clin North Am 68:1071–1079. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.PCL.2021.05.009
Xiang S, Rasool S, Hang Y, Javid K, Javed T, Artene AE (2021) The Effect of COVID-19 Pandemic on Service Sector Sustainability and Growth. Front Psychol 12:1178. https://doi.org/10.3389/FPSYG.2021.633597/BIBTEX
Quek AML, Ooi DSQ et al (2022) Zinc and vitamin C intake increases spike and neutralising antibody production following SARS-CoV-2 infection. Clin Transl Med 12:e731. https://doi.org/10.1002/ctm2.731
Nicholas W, Sood N, Lam CN et al (2022) Did prioritizing essential workers help to achieve racial/ethnic equity in early COVID-19 vaccine distribution ? The LA pandemic surveillance cohort study. Am J Ind Med 65:231–241. https://doi.org/10.1002/ajim.23335
Singh P, Singh D, Sa P et al (2021) Insights from nanotechnology in COVID-19: prevention, detection, therapy and immunomodulation. Nanomedicine 16:1219–1235. https://doi.org/10.2217/NNM-2021-0004
Menni C, Valdes AM, Freidin MB et al (2020) Real-time tracking of self-reported symptoms to predict potential COVID-19. Nat Med 26:1037–1040. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41591-020-0916-2
Chang MC, Hur J, Park D (2020) Interpreting the COVID-19 test results: a guide for physiatrists. Am J Phys Med Rehabil 99:583–585. https://doi.org/10.1097/PHM.0000000000001471
Sule WF, Oluwayelu DO (2020) Real-time RT-PCR for COVID-19 diagnosis: challenges and prospects. Pan Afr Med J 35:121. https://doi.org/10.11604/PAMJ.SUPP.2020.35.24258
Wisnewski AV, Luna JC, Redlich CA (2021) Human IgG and IgA responses to COVID-19 mRNA vaccines. PLoS ONE 16:e0249499. https://doi.org/10.1371/JOURNAL.PONE.0249499
Chao YX, Rötzschke O, Tan EK (2020) The role of IgA in COVID-19. Brain Behav Immun 87:182–183. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.BBI.2020.05.057
Tang Z, Kong N, Zhang X et al (2020) A materials-science perspective on tackling COVID-19. Nat Rev Mater 5:847–860. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41578-020-00247-y
Sreepadmanabh M, Sahu AK, Chande A (2020) COVID-19: Advances in diagnostic tools, treatment strategies, and vaccine development. J Biosci 45:148. https://doi.org/10.1007/S12038-020-00114-6
Khan RS, Rehman IU (2020) Spectroscopy as a tool for detection and monitoring of Coronavirus (COVID-19). Expert Rev Mol Diagn 20:647–649. https://doi.org/10.1080/14737159.2020.1766968
Obata J, Kawakami N, Tsutsumi A et al (2021) Icosahedral 60-meric porous structure of designed supramolecular protein nanoparticle TIP60. Chem Commun 57:10226–10229. https://doi.org/10.1039/D1CC03114G
Kawakami N, Kondo H, Matsuzawa Y et al (2018) Design of hollow protein nanoparticles with modifiable interior and exterior surfaces. Angew Chemie - Int Ed 57:12400–12404. https://doi.org/10.1002/ANIE.201805565
Soto CM, Ratna BR (2010) Virus hybrids as nanomaterials for biotechnology. Curr Opin Biotechnol 21:426–438. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.COPBIO.2010.07.004
Nunes ÁM, da Silva Filho RC, da Silva KR et al (2022) Gold nanoparticles with different shapes can cause distinct effect on mitochondria bioenergetics. J Nanoparticle Res 24:31. https://doi.org/10.1007/S11051-022-05410-W
Canini V, Bono F, Calzavacca P et al (2021) Cytopathology of bronchoalveolar lavages in COVID-19 pneumonia: a pilot study. Cancer Cytopathol 129:632–641. https://doi.org/10.1002/CNCY.22422
Chaibun T, Puenpa J, Ngamdee T et al (2021) Rapid electrochemical detection of coronavirus SARS-CoV-2. Nat Commun 12:802. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-021-21121-7
Krishnan S, ul Quasim SZ (2022) Colorimetric visual sensors for point-of-needs testing. Sensors Actuators Rep 4:100078. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.SNR.2022.100078
Saylan Y, Erdem Ö, Ünal S, Denizli A (2019) An alternative medical diagnosis method: biosensors for virus detection. Biosensors 9:65. https://doi.org/10.3390/BIOS9020065
Yang B, Fang X, Kong J (2019) In situ sampling and monitoring cell-free DNA of the Epstein-Barr virus from dermal interstitial fluid using wearable microneedle patches. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 11:38448–38458. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsami.9b12244
Toppings NB, Mohon AN, Lee Y et al (2021) A rapid near-patient detection system for SARS-CoV-2 using saliva. Sci Reports 11:13778. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-021-92677-z
Dixon RV, Skaria E, Lau WM et al (2021) Microneedle-based devices for point-of-care infectious disease diagnostics. Acta Pharm Sin B 11:2344–2361. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.APSB.2021.02.010
Zarubova J, Zhang X, Hoffman T et al (2021) Biomaterial-based immunoengineering to fight COVID-19 and infectious diseases. Matter 4:1528–1554. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.MATT.2021.02.025
Ménard-Moyon C, Bianco A, Kalantar-Zadeh K (2020) Two-dimensional material-based biosensors for virus detection. ACS Sensors 5:3739–3769. https://doi.org/10.1021/acssensors.0c01961
Bhardwaj N, Bhardwaj SK, Mehta J et al (2017) MOF-bacteriophage biosensor for highly sensitive and specific detection of staphylococcus aureus. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 9:33589–33598. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsami.7b07818
Li S, Dharmarwardana M, Welch RP et al (2018) Investigation of controlled growth of metal-organic frameworks on anisotropic virus particles. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 10:18161–18169. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsami.8b01369
Chauhan G, Madou MJ, Kalra S et al (2020) Nanotechnology for COVID-19: therapeutics and vaccine research. ACS Nano 14:7760–7782. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsnano.0c04006
Tamayo J, Kosaka PM, Ruz JJ et al (2013) Biosensors based on nanomechanical systems. Chem Soc Rev 42:1287–1311. https://doi.org/10.1039/c2cs35293a
Vermisoglou E, Panáček D, Jayaramulu K et al (2020) Human virus detection with graphene-based materials. Biosens Bioelectron 166:112436. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bios.2020.112436
Singh KRB, Rathee S, Nagpure G et al (2022) Smart and emerging nanomaterials-based biosensor for SARS-CoV-2 detection. Mater Lett 307:131092. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.MATLET.2021.131092
Saatçi E, Natarajan S (2021) State-of-the-art colloidal particles and unique interfaces-based SARS-CoV-2 detection methods and COVID-19 diagnosis. Curr Opin Colloid Interface Sci 55:101469. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.COCIS.2021.101469
Yang X, You J, Wei Y et al (2021) Emerging nanomaterials applied for tackling the COVID-19 cytokine storm. J Mater Chem B 9:8185–8201. https://doi.org/10.1039/D1TB01446C
Zhao J, Zhao F, Li H et al (2022) Magnet-assisted electrochemical immunosensor based on surface-clean Pd-Au nanosheets for sensitive detection of SARS-CoV-2 spike protein. Electrochim Acta 404:139766. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.ELECTACTA.2021.139766
Zhang T, Sun L, Zhang Y (2021) Highly sensitive electrochemical determination of the SARS-COV-2 antigen based on a gold/graphene imprinted poly-arginine sensor. Anal Methods 13:5772–5776. https://doi.org/10.1039/D1AY01478A
El-Awady M, Elmansi H, Belal F, Shabana RA (2022) Insights on the quantitative concurrent fluorescence-based analysis of anti-COVID-19 drugs remdesivir and favipiravir. J Fluoresc 32:1941–1948. https://doi.org/10.1007/S10895-022-02998-Z
Yousefi H, Mahmud A, Chang D et al (2021) Detection of SARS-CoV-2 viral particles using direct, reagent-free electrochemical sensing. J Am Chem Soc 143:1722–1727. https://doi.org/10.1021/JACS.0C10810
Acosta M, Fernández LP, Talio MC (2023) Sonochemical Synthesized Manganese Oxide Nanoparticles as Fluorescent Sensor for Selenium (IV) Quantification. Application to Food and Drink Samples. J Fluoresc 2023:1–10. https://doi.org/10.1007/S10895-023-03247-7
Bardajee GR, Zamani M, Sharifi M et al (2022) Rapid and highly sensitive detection of target DNA related to COVID-19 virus with a fluorescent bio-conjugated probe via a FRET mechanism. J Fluoresc 32:1959–1967. https://doi.org/10.1007/S10895-022-02992-5
Ashraf G, Chen W, Asif M et al (2022) Topical advancements in electrochemical and optical signal amplification for biomolecules detection: a comparison. Mater Today Chem 26:101119. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.MTCHEM.2022.101119
Sravani AB, Mathew EM, Ghate V, Lewis SA (2022) A Sensitive spectrofluorimetric method for curcumin analysis. J Fluoresc 32:1517–1527. https://doi.org/10.1007/S10895-022-02947-W
Elugoke SE, Fayemi OE, Adekunle AS et al (2023) Sensitive and selective neurotransmitter epinephrine detection at a carbon quantum dots/copper oxide nanocomposite. J Electroanal Chem 929:117120. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.JELECHEM.2022.117120
Ganesh PS, Kim SY (2022) A comparison of conventional and advanced electroanalytical methods to detect SARS-CoV-2 virus: a concise review. Chemosphere 307:135645. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.CHEMOSPHERE.2022.135645
Assi S, Abbas I, Arafat B et al (2023) Authentication of Covid-19 vaccines using synchronous fluorescence spectroscopy. J Fluoresc 33:1165–1174. https://doi.org/10.1007/S10895-022-03136-5
Chen C, Lai H, Liang H et al (2021) A new method for detection african swine fever virus: time-resolved fluorescence immunoassay. J Fluoresc 31:1291–1296. https://doi.org/10.1007/S10895-021-02754-9
Liu L, Bai Q, Zhang X et al (2022) Fluorescent biosensor based on hairpin DNA stabilized copper nanoclusters for chlamydia trachomatis detection. J Fluoresc 32:1651–1660. https://doi.org/10.1007/S10895-022-02961-Y
Ganesh PS, Kim SY, Kaya S, Salim R (2022) An experimental and theoretical approach to electrochemical sensing of environmentally hazardous dihydroxy benzene isomers at polysorbate modified carbon paste electrode. Sci Rep 12:2149. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-022-06207-6
Rane AV, Kanny K, Abitha VK, Thomas S (2018) Methods for synthesis of nanoparticles and fabrication of nanocomposites. Synthesis of inorganic nanomaterials. Woodhead Publishing, pp 121–139. https://doi.org/10.1016/B978-0-08-101975-7.00005-1
Dixit N, Singh SP (2022) Laser-Induced Graphene (LIG) as a smart and sustainable material to restrain pandemics and endemics: a perspective. ACS Omega 7:5112–5130. https://doi.org/10.1021/ACSOMEGA.1C06093
Liu J, Li R, Yang B (2020) Carbon dots: a new type of carbon-based nanomaterial with wide applications. ACS Cent Sci 6:2179–2195. https://doi.org/10.1021/ACSCENTSCI.0C01306
Soy S, Sharma SR, Nigam VK (2022) Bio-fabrication of thermozyme-based nano-biosensors: their components and present scenario. J Mater Sci Mater Electron 33:5523–5533. https://doi.org/10.1007/S10854-022-07741-9
Toppo AL, Jujjavarapu SE (2022) New insights for integration of nano particle with microfluidic systems for sensor applications. Biomed Microdevices 24:13. https://doi.org/10.1007/S10544-021-00598-5
Hu X, Li Z, Yang Z et al (2022) Fabrication of functional polycatechol nanoparticles. ACS Macro Lett 11:251–256. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsmacrolett.1c00729
Lv J, Gao X, Han B et al (2022) Self-assembled inorganic chiral superstructures. Nat Rev Chem 62(6):125–145. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41570-021-00350-w
Salem SS (2022) Bio-fabrication of selenium nanoparticles using baker’s yeast extract and its antimicrobial efficacy on food borne pathogens. Appl Biochem Biotechnol 194:1898–1910. https://doi.org/10.1007/S12010-022-03809-8
Abbas M, Susapto HH, Hauser CAE (2022) Synthesis and organization of gold-peptide nanoparticles for catalytic activities. ACS Omega 7:2082–2090. https://doi.org/10.1021/ACSOMEGA.1C05546
He L, Mu J, Gang O, Chen X (2021) Rationally programming nanomaterials with DNA for biomedical applications. Adv Sci 8:2003775. https://doi.org/10.1002/ADVS.202003775
Oh JW, Lim DK, Kim GH et al (2014) Thiolated DNA-based chemistry and control in the structure and optical properties of plasmonic nanoparticles with ultrasmall interior nanogap. J Am Chem Soc 136:14052–14059. https://doi.org/10.1021/JA504270D
Zhang L, Gu C, Wen J et al (2020) Recent advances in nanomaterial-based biosensors for the detection of exosomes. Anal Bioanal Chem 413:83–102. https://doi.org/10.1007/S00216-020-03000-0
Zhao J, Liu C, Li Y et al (2020) Thermophoretic detection of exosomal microRNAs by nanoflares. J Am Chem Soc 142:4996–5001. https://doi.org/10.1021/JACS.9B13960
Singh YD, Ningthoujam R, Panda MK et al (2021) Insight from nanomaterials and nanotechnology towards COVID-19. Sensors Int 2:100099. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.SINTL.2021.100099
Srivastava M, Srivastava N, Mishra PK, Malhotra BD (2021) Prospects of nanomaterials-enabled biosensors for COVID-19 detection. Sci Total Environ 754:142363. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.SCITOTENV.2020.142363
Bisht A, Mishra A, Bisht H, Tripathi RM (2021) Nanomaterial based biosensors for detection of viruses including SARS-CoV-2: a review. J Anal Test 5:327–340. https://doi.org/10.1007/S41664-021-00200-0
Choi HK, Lee MJ, Lee SN et al (2021) Noble metal nanomaterial-based biosensors for electrochemical and optical detection of viruses causing respiratory illnesses. Front Chem 9:672739. https://doi.org/10.3389/FCHEM.2021.672739
Peng Y, Lin C, Long L et al (2021) Charge-transfer resonance and electromagnetic enhancement synergistically enabling MXenes with excellent SERS sensitivity for SARS-CoV-2 S protein detection. Nano-Micro Lett 13:52. https://doi.org/10.1007/S40820-020-00565-4
Balkourani G, Brouzgou A, Archonti M et al (2021) Emerging materials for the electrochemical detection of COVID-19. J Electroanal Chem (Lausanne Switz) 893:115289. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.JELECHEM.2021.115289
Wang M, Fu A, Hu B et al (2020) Nanopore targeted sequencing for the accurate and comprehensive detection of SARS-CoV-2 and other respiratory viruses. Small 16:2002169. https://doi.org/10.1002/SMLL.202002169
Rennick JJ, Johnston APR, Parton RG (2021) Key principles and methods for studying the endocytosis of biological and nanoparticle therapeutics. Nat Nanotechnol 16:266–276. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41565-021-00858-8
Kaur A, Kaur P, Ahuja S (2020) Förster resonance energy transfer (FRET) and applications thereof. Anal Methods 12:5532–5550. https://doi.org/10.1039/D0AY01961E
Viljoen A, Mathelié-Guinlet M, Ray A et al (2021) Force spectroscopy of single cells using atomic force microscopy. Nat Rev Methods Prim 1:63. https://doi.org/10.1038/s43586-021-00062-x
Leïchlé T, Nicu L, Alava T (2020) MEMS biosensors and COVID-19: missed opportunity. ACS Sensors 5:3297–3305. https://doi.org/10.1021/acssensors.0c01463
Li Q, Guan X, Wu P et al (2020) Early transmission dynamics in Wuhan, China, of novel coronavirus-infected pneumonia. N Engl J Med 382:1199–1207. https://doi.org/10.1056/nejmoa2001316
Narayan RJ (2016) Medical Biosensors for Point of Care (POC) Applications. Elsevier Inc
Sultangaziyev A, Bukasov R (2020) Review: applications of surface-enhanced fluorescence (SEF) spectroscopy in bio-detection and biosensing. Sens Bio-Sensing Res 30:100382. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.sbsr.2020.100382
Imani M, Mohajeri N, Rastegar M, Zarghami N (2021) Recent advances in FRET-Based biosensors for biomedical applications. Anal Biochem 630:114323. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.AB.2021.114323
Liu L, He F, Yu Y, Wang Y (2020) Application of FRET Biosensors in Mechanobiology and Mechanopharmacological Screening. Front Bioeng Biotechnol 8:595497. https://doi.org/10.3389/FBIOE.2020.595497
Pazos MD, Hu Y, Elani Y et al (2021) Tattoo Inks for optical biosensing in interstitial fluid. Adv Healthc Mater 10:2101238. https://doi.org/10.1002/ADHM.202101238
Yang M, Liu M, Cheng J, Wang H (2021) A movable type bioelectronics printing technology for modular fabrication of biosensors. Sci Rep 11:22323. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-021-01741-1
Wu K, Liu J, Saha R et al (2020) Magnetic particle spectroscopy for detection of influenza A virus subtype H1N1. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 12:13686–13697. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsami.0c00815
Ganganboina AB, Khoris IM, Chowdhury AD et al (2020) Ultrasensitive detection of the hepatitis E virus by electrocatalytic water oxidation using Pt-Co3O4 hollow cages. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 12:50212–50221. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsami.0c13247
Mak WC, Cheung KY, Orban J et al (2015) Surface-engineered contact lens as an advanced theranostic platform for modulation and detection of viral infection. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 7:25487–25494. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsami.5b08644
Dong S, Zhao R, Zhu J et al (2015) Electrochemical DNA biosensor based on a tetrahedral nanostructure probe for the detection of avian influenza A (H7N9) virus. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 7:8834–8842. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsami.5b01438
Zang F, Gerasopoulos K, Brown AD et al (2017) Capillary microfluidics-assembled virus-like particle bionanoreceptor interfaces for label-free biosensing. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 9:8471–8479. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsami.6b14045
Oh S, Kim J, Tran VT et al (2018) Magnetic nanozyme-linked immunosorbent assay for ultrasensitive influenza A virus detection. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 10:12534–12543. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsami.8b02735
Li J, Yang K, Wu Z et al (2019) Nitrogen-doped porous carbon-based fluorescence sensor for the detection of ZIKV RNA sequences: fluorescence image analysis. Talanta 205:120091. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.talanta.2019.06.091
Hideshima S, Hayashi H, Hinou H et al (2019) Glycan-immobilized dual-channel field effect transistor biosensor for the rapid identification of pandemic influenza viral particles. Sci Rep 9:11616. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-019-48076-6
Wang C, Wang C, Wang X et al (2019) Magnetic SERS strip for sensitive and simultaneous detection of respiratory viruses. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 11:19495–19505. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsami.9b03920
Nidzworski D, Siuzdak K, Niedziałkowski P et al (2017) A rapid-response ultrasensitive biosensor for influenza virus detection using antibody modified boron-doped diamond. Sci Rep 7:15707. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-017-15806-7
Udugama B, Kadhiresan P, Kozlowski HN et al (2020) Diagnosing COVID-19: the disease and tools for detection. ACS Nano 14:3822–3835. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsnano.0c02624
Lu R, Zhao X, Li J et al (2020) Genomic characterisation and epidemiology of 2019 novel coronavirus: implications for virus origins and receptor binding. Lancet 395:565–574. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0140-6736(20)30251-8
Naqvi AAT, Fatima K, Mohammad T et al (2020) Insights into SARS-CoV-2 genome, structure, evolution, pathogenesis and therapies: Structural genomics approach. Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Basis Dis 1866:165878. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.BBADIS.2020.165878
Emrani J, Ahmed M, Jeffers-Francis L et al (2021) SARS-COV-2, infection, transmission, transcription, translation, proteins, and treatment: a review. Int J Biol Macromol 193:1249–1273. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.IJBIOMAC.2021.10.172
Peacock TP, Goldhill DH, Zhou J et al (2021) The furin cleavage site in the SARS-CoV-2 spike protein is required for transmission in ferrets. Nat Microbiol 6:899–909. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41564-021-00908-w
Finkel Y, Mizrahi O, Nachshon A et al (2020) The coding capacity of SARS-CoV-2. Nature 589:125–130. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41586-020-2739-1
Tang YD, Fang QQ, Liu JT et al (2016) Open reading frames 1a and 1b of the porcine reproductive and respiratory syndrome virus (PRRSV) collaboratively initiate viral minus-strand RNA synthesis. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 477:927–931. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.BBRC.2016.06.161
Feng W, Newbigging AM, Le C et al (2020) Molecular diagnosis of COVID-19: challenges and research needs. Anal Chem 92:10196–10209. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.analchem.0c02060
Wrapp D, Wang N, Corbett KS et al (2020) Cryo-EM structure of the 2019-nCoV spike in the prefusion conformation. bioRxiv 1263:1260–1263. https://doi.org/10.1101/2020.02.11.944462
Ning S, Yu B, Wang Y, Wang F (2021) SARS-CoV-2: origin, evolution, and targeting inhibition. Front Cell Infect Microbiol 11:676451. https://doi.org/10.3389/FCIMB.2021.676451
Sohail A, Nutini A (2020) Forecasting the timeframe of 2019-nCoV and human cells interaction with reverse engineering. Prog Biophys Mol Biol 155:29–35. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.PBIOMOLBIO.2020.04.002
Callaway E (2022) Scientists deliberately gave people COVID — here’s what they learnt. Nature 602:191–192. https://doi.org/10.1038/D41586-022-00319-9
Leung NHL (2021) Transmissibility and transmission of respiratory viruses. Nat Rev Microbiol 19:528–545. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41579-021-00535-6
Kames J, Holcomb DD, Kimchi O et al (2020) Sequence analysis of SARS-CoV-2 genome reveals features important for vaccine design. Sci Rep 10:15643. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-020-72533-2
Mohamadian M, Chiti H, Shoghli A et al (2021) COVID-19: Virology, biology and novel laboratory diagnosis. J Gene Med 23:e3303. https://doi.org/10.1002/JGM.3303
Lasserre P, Balansethupathy B, Vezza VJ et al (2022) SARS-CoV-2 aptasensors based on electrochemical impedance spectroscopy and low-cost gold electrode substrates. Anal Chem 94:2126–2133. https://doi.org/10.1021/ACS.ANALCHEM.1C04456
Weiss C, Carriere M, Fusco L et al (2020) Toward nanotechnology-enabled approaches against the COVID-19 pandemic. ACS Nano 14:6383–6406. https://doi.org/10.1021/ACSNANO.0C03697
Flerlage T, Boyd DF, Meliopoulos V et al (2021) Influenza virus and SARS-CoV-2: pathogenesis and host responses in the respiratory tract. Nat Rev Microbiol 19:425–441. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41579-021-00542-7
Medeiros IG, Khayat AS, Stransky B et al (2021) A small interfering RNA (siRNA) database for SARS-CoV-2. Sci Rep 11:8849. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-021-88310-8
Georgiou PG, Guy CS, Hasan M et al (2022) Plasmonic detection of SARS-CoV-2 spike protein with polymer-stabilized glycosylated gold nanorods. ACS Macro Lett 47:317–322. https://doi.org/10.1021/ACSMACROLETT.1C00716
Erdem Ö, Derin E, Sagdic K et al (2021) Smart materials-integrated sensor technologies for COVID-19 diagnosis. Emergent Mater 4:169–185. https://doi.org/10.1007/s42247-020-00150-w
Yang Y, Peng Y, Lin C et al (2021) Human ACE2-functionalized gold “virus-trap” nanostructures for accurate capture of SARS-CoV-2 and single-virus SERS detection. Nano-Micro Lett 13:109. https://doi.org/10.1007/S40820-021-00620-8
Yang J (2021) Real nano “light vaccine” will benefit to COVID-19 pandemic control. Nano-Micro Lett 13:185. https://doi.org/10.1007/S40820-021-00723-2
Orooji Y, Sohrabi H, Hemmat N et al (2021) An overview on SARS-CoV-2 (COVID-19) and other human coronaviruses and their detection capability via amplification assay, chemical sensing, biosensing, immunosensing, and clinical assays. Nano-Micro Lett 13:18. https://doi.org/10.1007/S40820-020-00533-Y
Wang Q, Wang X, Tang PS et al (2017) Targeted sequencing of both DNA strands barcoded and captured individually by RNA probes to identify genome-wide ultra-rare mutations. Sci Rep 7:3356. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-017-03448-8
Wang Y, Zou Q, Li F et al (2021) Identification of the cross-strand chimeric RNAs generated by fusions of bi-directional transcripts. Nat Commun 12:4645. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-021-24910-2
Yoon J, Shin M, Lee JY et al (2022) RNA interference (RNAi)-based plasmonic nanomaterials for cancer diagnosis and therapy. J Control Release 342:228–240. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.JCONREL.2022.01.012
Qiu G, Gai Z, Tao Y et al (2020) Dual-functional plasmonic photothermal biosensors for highly accurate severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 detection. ACS Nano 14:5268–5277. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsnano.0c02439
Torrente-Rodríguez RM, Lukas H, Tu J et al (2020) SARS-CoV-2 RapidPlex: a graphene-based multiplexed telemedicine platform for rapid and low-cost COVID-19 diagnosis and monitoring. Matter 3:1981–1998. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matt.2020.09.027
Ali MA, Hu C, Jahan S et al (2021) Sensing of COVID-19 antibodies in seconds via aerosol jet nanoprinted reduced-graphene-oxide-coated 3D electrodes. Adv Mater 33:2006647. https://doi.org/10.1002/adma.202006647
Makela M, Lin PT (2021) Detection of SARS-CoV-2 DNA targets using femtoliter optofluidic waveguides. Anal Chem 93:4154–4159. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.analchem.0c02971
Pang B, Xu J, Liu Y et al (2020) Isothermal amplification and ambient visualization in a single tube for the detection of SARS-CoV-2 using loop-mediated amplification and CRISPR technology. Anal Chem 92:16204–16212. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.analchem.0c04047
Yuan X, Yang C, He Q et al (2020) Current and perspective diagnostic techniques for COVID-19. ACS Infect Dis 6:1998–2016. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsinfecdis.0c00365
Li Y, Li S, Wang J, Liu G (2019) CRISPR/Cas systems towards next-generation biosensing. Trends Biotechnol 37:730–743. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tibtech.2018.12.005
Zhu X, Wang X, Li S et al (2021) Rapid, ultrasensitive, and highly specific diagnosis of COVID-19 by CRISPR-based detection. ACS Sens 6:881–888. https://doi.org/10.1021/acssensors.0c01984
Rahimi H, Salehiabar M, Barsbay M et al (2021) CRISPR systems for COVID-19 diagnosis. ACS Sensors 6:1430–1445. https://doi.org/10.1021/acssensors.0c02312
Lagopati N, Tsioli P, Mourkioti I et al (2021) Sample pooling strategies for SARS-CoV-2 detection. J Virol Methods 289:114044. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jviromet.2020.114044
Huang Z, Tian D, Liu Y et al (2020) Ultra-sensitive and high-throughput CRISPR-p owered COVID-19 diagnosis. Biosens Bioelectron 164:112316. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bios.2020.112316
Fresco-Taboada A, García-Durán M, Aira C et al (2022) Diagnostic performance of two serological assays for the detection of SARS-CoV-2 specific antibodies: surveillance after vaccination. Diagn Microbiol Infect Dis 102:115650. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.DIAGMICROBIO.2022.115650
Bontempi E (2021) The europe second wave of COVID-19 infection and the Italy “strange” situation. Environ Res 193:110476. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.ENVRES.2020.110476
Yakoh A, Pimpitak U, Rengpipat S et al (2021) Paper-based electrochemical biosensor for diagnosing COVID-19: Detection of SARS-CoV-2 antibodies and antigen. Biosens Bioelectron 176:112912. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bios.2020.112912
Trivedi SU, Miao C, Sanchez JE et al (2019) development and evaluation of a multiplexed immunoassay for simultaneous detection of serum IgG antibodies to six human coronaviruses. Sci Rep 9:1390. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-018-37747-5
Chen R, Ren C, Liu M et al (2021) Early detection of SARS-CoV-2 seroconversion in humans with aggregation-induced near-infrared emission nanoparticle-labeled lateral flow immunoassay. ACS Nano 15:8996–9004. https://doi.org/10.1021/ACSNANO.1C01932
Li Z, Yi Y, Luo X et al (2020) Development and clinical application of a rapid IgM-IgG combined antibody test for SARS-CoV-2 infection diagnosis. J Med Virol 92:1518–1524. https://doi.org/10.1002/jmv.25727
Ahn DG, Jeon IJ, Kim JD et al (2009) RNA aptamer-based sensitive detection of SARS coronavirus nucleocapsid protein. Analyst 134:1896–1901. https://doi.org/10.1039/b906788d
Seo G, Lee G, Kim MJ et al (2020) Rapid detection of COVID-19 causative virus (SARS-CoV-2) in human nasopharyngeal swab specimens using field-effect transistor-based biosensor. ACS Nano 14:5135–5142. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsnano.0c02823
Li J, Lillehoj PB (2021) Microfluidic magneto immunosensor for rapid, high sensitivity measurements of SARS-CoV-2 nucleocapsid protein in serum. ACS Sensors 6:1270–1278. https://doi.org/10.1021/acssensors.0c02561
Guo L, Sun X, Wang X et al (2020) SARS-CoV-2 detection with CRISPR diagnostics. Cell Discov 6:34. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41421-020-0174-y
Ding X, Yin K, Li Z et al (2020) Ultrasensitive and visual detection of SARS-CoV-2 using all-in-one dual CRISPR-Cas12a assay. Nat Commun 11:4711. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-020-18575-6
Xiong Y, Zhang J, Yang Z et al (2020) Functional DNA regulated CRISPR-Cas12a sensors for point-of-care diagnostics of non-nucleic-acid targets. J Am Chem Soc 142:207–213. https://doi.org/10.1021/jacs.9b09211
Tian T, Shu B, Jiang Y et al (2021) An ultralocalized Cas13a assay enables universal and nucleic acid amplification-free single-molecule RNA diagnostics. ACS Nano 15:1167–1178. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsnano.0c08165
Chandra S, Bharadwaj R, Mukherji S (2017) Label free ultrasensitive optical sensor decorated with polyaniline nanofibers: Characterization and immunosensing application. Sensors Actuators B Chem 240:443–450. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.snb.2016.08.103
Li D, Chen H, Gao X et al (2021) Development of general methods for detection of virus by engineering fluorescent silver nanoclusters. ACS Sensors 6:613–627. https://doi.org/10.1021/acssensors.0c02322
Jiang Y, Hu M, Liu AA et al (2021) Detection of SARS-CoV-2 by CRISPR/Cas12a-enhanced colorimetry. ACS Sensors 6:1086–1093. https://doi.org/10.1021/acssensors.0c02365
Zhang WS, Pan J, Li F et al (2021) Reverse transcription recombinase polymerase amplification coupled with CRISPR-Cas12a for facile and highly sensitive colorimetric SARS-CoV-2 detection. Anal Chem 93:4126–4133. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.analchem.1c00013
Marston DJ, Vilela M, Huh J et al (2020) Multiplexed GTPase and GEF biosensor imaging enables network connectivity analysis. Nat Chem Biol 16:826–833. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41589-020-0542-9
Yang SP, Chen SR, Liu SW et al (2015) Platforms formed from a three-dimensional Cu-based zwitterionic metal-organic framework and probe ss-DNA: selective fluorescent biosensors for human immunodeficiency virus 1 ds-DNA and sudan virus RNA sequences. Anal Chem 87:12206–12214. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.analchem.5b03084
Zhang Y, Shi F, Zhang C et al (2023) Detection of avian influenza virus H9N2 based on self-driving and self-sensing microcantilever piezoelectric sensor. Chinese Chem Lett 34:107700. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cclet.2022.07.043
Toubanaki DK, Margaroni M, Prapas A, Karagouni E (2020) Development of a nanoparticle-based lateral flow strip biosensor for visual detection of whole nervous necrosis virus particles. Sci Rep 10:6529. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-020-63553-z
Rizvi AS, Murtaza G, Zhang W et al (2023) Aptamer-linked photonic crystal hydrogel sensor for rapid point-of-care detection of human immuno-deficiency virus-1 (HIV-1). J Pharm Biomed Anal 227:115104. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jpba.2022.115104
Yuan R, Wei J, Geng R et al (2023) Sensitive detection of African swine fever virus p54 based on in-situ amplification of disposable electrochemical sensor chip. Sensors Actuators B Chem 380:133363. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.snb.2023.133363
Antipchik M, Reut J, Ayankojo AG et al (2022) MIP-based electrochemical sensor for direct detection of hepatitis C virus via E2 envelope protein. Talanta 250:123737. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.talanta.2022.123737
Khan RR, Ibrahim H, Rawal G et al (2023) Multichannel microfluidic virus sensor for rapid detection of respiratory viruses using virus-imprinted polymer for digital livestock farming. Sensors Actuators B Chem 389:133920. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.snb.2023.133920
Wang L, Yang J, He S et al (2022) A mild and safe gas-responsive molecularly imprinted sensor for highly specific recognition of hepatitis B virus. Sensors Actuators B Chem 366:131990. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.snb.2022.131990
Kumar AVP, Dubey SK, Tiwari S et al (2021) Recent advances in nanoparticles mediated photothermal therapy induced tumor regression. Int J Pharm 606:120848. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.IJPHARM.2021.120848
Justino CIL, Rocha-Santos TAP, Cardoso S et al (2013) Strategies for enhancing the analytical performance of nanomaterial-based sensors. TrAC Trends Anal Chem 47:27–36. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.TRAC.2013.02.004
Esteves E, Karina Mendes A, BarrosID M et al (2022) Population wide testing pooling strategy for SARS-CoV-2 detection using saliva. PLoS ONE 17:e0263033. https://doi.org/10.1371/JOURNAL.PONE.0263033
Baharfar M, Rahbar M, Tajik M, Liu G (2020) Engineering strategies for enhancing the performance of electrochemical paper-based analytical devices. Biosens Bioelectron 167:112506. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.BIOS.2020.112506
Wang C, Wang L, Tadepalli S et al (2018) Ultrarobust biochips with metal-organic framework coating for point-of-care diagnosis. ACS Sensors 3:342–351. https://doi.org/10.1021/acssensors.7b00762
Chan WCW (2020) Nano research for COVID-19. ACS Nano 14:3719–3720. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsnano.0c02540
Acknowledgements
The authors gratefully acknowledge Instituto Superior Técnico, Universidade de Lisboa, Av. RoviscoPais, 1049-001 Lisboa, Portugal, Panjab University, Chandigarh-160014, India and Kurukshetra University Kurukshetra-136119, India, for providing a research platform.
Funding
Fundação para a Ciência e Tecnologia (FCT), Portugal, for the Centro de Química Estrutural, Institute of Molecular Sciences projects UIDB/00100/2020, UIDP/00100/2020 and LA/P/0056/2020 projects.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Priyanka & Brij Mohan have performed the literature search and drafted and critically revised the work. Ekta Poonia, Sandeep Kumar, Virender, Charan Singh, Jichuan Xiong, Xuefeng Liu, Armando J. L. Pombeiro, Gurjaspreet Singh: contributed to the critical revision of the work. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Ethical Approval
Not Applicable.
Consent to Participate
Not applicable.
Competing Interests
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Priyanka, Mohan, B., Poonia, E. et al. COVID-19 Virus Structural Details: Optical and Electrochemical Detection. J Fluoresc 34, 479–500 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10895-023-03307-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10895-023-03307-y