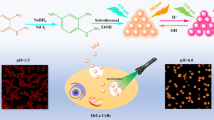
Abstract
Accurate monitoring of intracellular pH in living cells is critical for developing a better understanding of cellular activities. In the current study, label-free carbon dots (p-CDs), which were fabricated using a straightforward one-pot solvothermal treatment of p-phenylenediamine and urea, were employed to create a new ratiometric pH nanosensor. Under single-wavelength excitation (λex = 500 nm), the p-CDs gave dual emission bands at 525 and 623 nm. The fluorescent intensity ratio (I525/I623) was linearly related to pH over the range 4.0 to 8.8 in buffer solutions, indicating that the ratiometric fluorescence nanoprobe may be useful for pH sensing. In pH measurements, the p-CDs also demonstrated outstanding selectivity, reversibility, and photostability. Owing to the advantages outlined above, the nanoprobe was used to monitor the pH of HeLa cells effectively. The label-free CD-based ratiometric nanoprobe features comparatively easy manufacturing and longer excitation and emission wavelengths than the majority of previously reported CD-based ratiometric pH sensors, which is ultimately beneficial for applications in biological imaging.
Graphical Abstract










Similar content being viewed by others
Code Availability
Not applicable.
Data Availability
All data generated or analyzed of this study are available within the article.
References
Ohkuma S, Poole B (1978) Fluorescence probe measurement of the intralysosomal pH in living cells and the perturbation of pH by various agents. Proc Natl Acad Sci 75(7):3327–3331. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.75.7.3327
Kennedy RT, Huang L, Aspinwall CA (1996) Extracellular pH is required for rapid release of insulin from Zn-insulin precipitates in β-cell secretory vesicles during exocytosis. J Am Chem Soc 118(7):1795–1796. https://doi.org/10.1021/ja953271w
Wan SL, Zheng Y, Shen J, Yang WT, Yin MZ (2014) “On-off-on” switchable sensor: a fluorescent spiropyran responds to extreme pH conditions and its bioimaging applications. ACS Appl Mater Inter 6(22):19515–19519. https://doi.org/10.1021/am506641t
Chen Y (2021) Recent advances in fluorescent probes for extracellular pH detection and imaging. Anal Biochem 612:113900. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ab.2020.113900
Dangi V, Baral M, Kanungo BK (2020) Study on the development of a cyclohexane based tripodal molecular device as “off-on-off” pH sensor and fluorescent iron sensor. Curr Anal Chem 16(5):620–630. https://doi.org/10.2174/1573411015666-190314154126
Liu LY, Zhao YP, Zhang N, Wang KN, Tian MG, Pan QL, Lin WY (2021) Ratiometric fluorescence imaging for the distribution of nucleic acid content in living cells and human tissue sections. Anal Chem 93(3):1612–1619. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.analchem.0c04064
Li S, Li L, Tu HY, Zhang H, Silvester DS, Banks CE, Zou GQ, Hou HS, Ji XB (2021) The development of carbon dots: from the perspective of materials chemistry. Mater Today 51:188–207. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mattod.2021.07.028
Wareing TC, Gentile P, Phan AN (2021) Biomass-based carbon dots: current development and future perspectives. ACS Nano 15(10):15471–15501. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsnano.1c03886
Sk MP, Sailapu SK, Chattopadhyay A (2015) Luminescent carbon dots for logic operations in two phases. ChemPhysChem 16(4):723–727. https://doi.org/10.1002/cphc.201402747
Arshad F, Pal A, Alam T, Khan JA, Sk MP (2020) Luminescent carbogenic dots for the detection and determination of hemoglobin in real samples. New J Chem 44(16):6213–6221. https://doi.org/10.1039/D0NJ00401D
Arshad F, Sk MP (2019) Aggregation-induced red shift in N, S-doped chiral carbon dot emissions for moisture sensing. New J Chem 43(33):13240–13248. https://doi.org/10.1039/C9NJ03009C
Macairan JR, Zhang I, Clermont-Paquette A, Naccache R, Maysinger D (2020) Ratiometric pH sensing in living cells using carbon dots. Part Part Syst Char 37(1):2070002. https://doi.org/10.1002/ppsc.202070002
Du FK, Ming YH, Zeng F, Yu CM, Wu SZ (2013) A low cytotoxic and ratiometric fluorescent nanosensor based on carbon-dots for intracellular pH sensing and mapping. Nanotechnology 24(36):365101. https://doi.org/10.1088/0957-4484/24/36/365101
Hu SL, Meng X, Tian F, Yang WL, Li N, Xue CR, Yang JL, Chang Q (2017) Dual photoluminescence centers from inorganic-salt-functionalized carbon dots for ratiometric pH sensing. J Mater Chem C 5(38):9849–9853. https://doi.org/10.1039/C7TC03266H
Lesani P, Singh G, Lu Z, Mirkhalaf M, New EJ, Zreiqat H (2022) Two-photon ratiometric carbon dot-based probe for real-time intracellular pH monitoring in 3D environment. Chem Eng J 433(3):133668. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2021. 133668
Long RQ, Tang C, Li T, Tong X, Tong CY, Guo Y, Gao QP, Wu LH, Shi SY (2020) Dual-emissive carbon dots for dual-channel ratiometric fluorometric determination of pH and mercury ion and intracellular imaging. Microchim Acta 187(5):307. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-020-04287-7
Pal A, Ahmad K, Dutta D, Chattopadhyay A (2019) Boron doped carbon dots with unusually high photoluminescence quantum yield for ratiometric intracellular pH sensing. ChemPhysChem 20(8):1018–1027. https://doi.org/10.1002/cphc.201900140
Wang X, Zhao L, Hu JS, Wei H, Liu XY, Li E, Yang SH (2022) Rational design of novel carbon-oxygen quantum dots for ratiometrically mapping pH and reactive oxygen species scavenging. Carbon 190:115–124. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbon.2022.01.006
Shi W, Li XH, Ma HM (2012) A tunable ratiometric pH sensor based on carbon nanodots for the quantitative measurement of the intracellular pH of whole cells. Angew Chem Int Edit 51(26):6432–6435. https://doi.org/10.1002/anie.201202533
Zhu XX, Jin H, Gao CL, Gui RJ, Wang ZH (2017) Ratiometric, visual, dual-signal fluorescent sensing and imaging of pH/copper ions in real samples based on carbon dots-fluorescein isothiocyanate composites. Talanta 162(1):65–71. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.talanta.2016.10.015
Xu SM, He X, Huang YB, Liu X, Zhao LH, Wang XH, Sun Y, Ma PY, Song DQ (2020) Lysosome-targeted ratiometric fluorescent sensor for monitoring pH in living cells based on one-pot-synthesized carbon dots. Microchim Acta 187:478. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-020-04462-w
Xia C, Cao MM, Xia JF, Zhou GH, Jiang DY, Zhang DF, Wang J, Li HL (2019) An ultrafast responsive and sensitive ratiometric fluorescent pH nanoprobe based on label-free dual-emission carbon dots. J Mater Chem C 7:2563–2569. https://doi.org/10.1039/C8TC05693E
Hamd-Ghadareh S, Salimi A, Fathi F, Soleimani F (2019) Dual-emission carbon dots as biocompatible nanocarrier for in vitro/in vivo cell microenvironment ratiometric pH sensing in broad range. J Iran Chem Soc 16(10):2081–2092. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13738-019-01678-3
Chang D, Zhao ZH, Shi H, Feng JY, Yang YX, Shi LH (2022) Ratiometric fluorescent carbon dots for enantioselective sensing of L-lysine and pH discrimination in vivo and in vitro. Sens Actuat B-Chem 362:131792. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.snb.2022.131792
Li SR, Song XR, Wang YH, Hu ZR, Yan F, Feng GD (2021) Developed a ratiometric fluorescence pH nanosensor based on label-free carbon dots for intracellular lysosome imaging and water pH monitoring with a smartphone. Dyes Pigm 193:109490. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.dyepig.2021.109490
He C, Xu P, Zhang XH, Long WJ (2022) The synthetic strategies, photoluminescence mechanisms and promising applications of carbon dots: current state and future perspective. Carbon 186:91–127. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbon.2021.10.002
Das P, Maruthapandi M, Saravanan A, Natan M, Jacobi G, Banin E, Gedanken A (2020) Carbon dots for heavy-metal sensing, pH-sensitive cargo delivery, and antibacterial applications. ACS Appl Nano Mater 3(12):11777–11790. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsanm.0c02305
Lesani P, Lu Z, Singh G, Mursi M, Mirkhalaf M, New EJ, Zreiqat H (2021) Influence of carbon dot synthetic parameters on photophysical and biological properties. Nanoscale 13(25):11138–11149. https://doi.org/10.1039/D1NR01389K
Wang Q, Tang ZH, Li L, Guo JX, Jin LX, Lu JF, Huang P, Zhang SR, Jiao (2022) Highly efficient red-emitting carbon dots as a “turn-on” temperature probe in living cells. Spectrochim Acta A 280:121538. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.saa.2022.121538
Ji YY, Zou X, Wang WJ, Wang TF, Zhang SL, Gong ZJ (2021) Co-doped S, N-Carbon dots and its fluorescent film sensors for rapid detection of cr (VI) and ascorbic aci. Microchem J 167:106284. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.microc.2021.106284
Wang Q, Zhang SR, Zhong YG, Yang XF, Li Z, Li H (2017) Preparation of yellow-green-emissive carbon dots and their application in constructing a fluorescent turn-on nanoprobe for imaging of selenol in living cells. Anal Chem 89(3):1734–1741. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.analchem.6b03983
Jia J, Lu WJ, Li L, Gao YF, Jiao Y, Han H, Dong C, Shuang SM (2020) Orange-emitting N-doped carbon dots as fluorescent and colorimetric dual-mode probes for nitrite detection and cellular imaging. J Mater Chem B 8(10):2123–2127. https://doi.org/10.1039/C9TB02934F
Lu S, Sui L, Liu J, Zhu SJ, Chen A, Jin MX, Yang B (2017) Near-infrared photoluminescent polymer-carbon nanodots with two-photon fluorescence. Adv Mater 29(15):1603443. https://doi.org/10.1002/adma.201603443
Espina-Casado J, Fontanil T, Fernández-González A, Cal S, Obaya ÁJ, Díaz-García ME, Badía-Laíño R (2021) Carbon dots as multifunctional platform for intracellular pH sensing and bioimaging. In vitro and in vivo studies. Sens Actuators B 346:130555. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.snb.2021.130555
Yang Y, Wang CF, Shu Q, Xu N, Qi SQ, Zhuo SJ, Zhu CQ, Du JY (2022) Facile one-step fabrication of Cu-doped carbon dots as a dual-selective biosensor for detection of pyrophosphate ions and measurement of pH. Spectrochim Acta A 268:120681. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.saa.2021.120681
Huo XM, Shen HL, Xu YJ, Shao J, Liu R, Zhang ZY (2022) Fluorescence properties of carbon dots synthesized by different solvents for pH detector. Opt Mater 123:111889. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.optmat.2021.111889
Bhati A, Anand SR, Gunture, Garg AK, Khare P, Sonkar SK (2018) Sunlight-induced photocatalytic degradation of pollutant dye by highly fluorescent red-emitting Mg-N-embedded carbon dots. ACS Sustain Chem Eng 6(7):9246–9256. https://doi.org/10.1021/acssuschemeng.8b01559
Liu JJ, Li DW, Zhang K, Yang MX, Sun HC, Yang B (2018) One-step hydrothermal synthesis of nitrogen-doped conjugated carbonized polymer dots with 31% efficient red emission for in vivo imaging. Small 14(15):1703919. https://doi.org/10.1002/smll.201703919
Zou GY, Chen S, Liu NZ, Yu YL (2021) A ratiometric fluorescent probe based on carbon dots assembly for intracellular lysosomal polarity imaging with wide range response. Chin Chem Lett 33(2):778–782. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cclet.202108.076
Ge JC, Jia QY, Liu WM, Guo L, Liu QY, Lan MH, Zhang HY, Meng XM, Wang PF (2015) Red-emissive carbon dots for fluorescent, photoacoustic, and thermal theranostics in living mice. Adv Mater 27(28):4169–4177. https://doi.org/10.1002/adma.201500323
Xu HB, Zhou SH, Xiao L, Wang HH, Li SZ, Yuan QH (2015) Fabrication of a nitrogen-doped graphene quantum dot from MOF-derived porous carbon and its application for highly selective fluorescence detection of Fe3+. J Mater Chem 3(2):291–297. https://doi.org/10.1039/C4TC01991A
Shi BF, Su YB, Zhang LL, Liu RJ, Huang MJ, Zhao SL (2016) Nitrogen-rich functional groups carbon nanoparticles based fluorescent pH sensor with broad-range responding for environmental and live cells applications. Biosens Bioelectron 82:233–239. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bios.2016.04.003
Liu XX, Liu JR, Zheng BZ, Yan L, Dai JY, Zhuang ZJ, Du J, Guo Y, Xiao D (2017) N-doped carbon dots: green and efficient synthesis on a large-scale and their application in fluorescent pH sensing. New J Chem 41(19):10607–10612. https://doi.org/10.1039/C7NJ01889D
Wang K, Wang XY, Liu XY, Li ES, Zhao RS, Yang SH (2022) Facile synthesis of dual emission carbon dots for the ratiometric fluorescent detection of 2, 4, 6-trinitrophenol and cell imaging. J Mol Struct 1263(2022)133167. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molstruc.2022.133167
Luo X, Yang HT, Wang HL, Ye ZW, Zhou ZN, Gu LY, Chen JQ, Xiao Y, Liang XW, Qian XH, Yang YJ (2018) Highly sensitive hill-type small-molecule pH probe that recognizes the reversed pH gradient of cancer cells. Anal Chem 90(9):5803–5809. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.analchem.8b00218
Chen YC, Zhu CC, Cen JJ, Bai Y, He WJ, Guo ZJ (2015) Ratiometric detection of pH fluctuation in mitochondria with a new fluorescein/cyanine hybrid sensor. Chem Sci 6:3187–3194. https://doi.org/10.1039/C4SC04021J
Li B, Ma H, Zhang B, Qian J, Cao T, Feng HT, Li W, Dong YP, Qin WW (2019) Dually emitting carbon dots as fluorescent probes for ratiometric fluorescent sensing of pH values, mercury (II), chloride and cr (VI) via different mechanisms. Microchim Acta 186(6):1–10. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-019-3437-2
Lei XX, Fu YY, Wu Y, Chen L, Liang JG (2020) A ratiometric fluorescent probe for pH detection based on Ag2S quantum dots-carbon dots nanohybrids. Roy Soc Open Sci 7(7):200482. https://doi.org/10.1098/rsos.200482
Wang XY, Wang YS, Pan W, Wang JP, Sun XB (2021) Carbon-dot-based probe designed to detect intracellular pH in fungal cells for building its relationship with intracellular polysaccharide. ACS Sustain Chem Eng 9(10):3718–3726. https://doi.org/10.1021/acssuschemeng.0c08160
Shangguan JF, He DG, He XX, Wang K, Xu FZ, Liu JQ, Tang JL, Yang X, Huang J (2016) Label-free carbon-dots-based ratiometric fluorescence pH nanoprobes for intracellular pH sensing. Anal Chem 88(15):7837–7843. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.analchem.6b01932
Chen YY, Zhao CX, Wang YY, Rao HB, Lu ZW, Lu CF, Shan Z, Ren B, Wu W, Wang XX (2020) Green and high-yield synthesis of carbon dots for ratiometric fluorescent determination of pH and enzyme reactions. Mat Sci Eng C 117(1–2):111264. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.msec.2020.111264
Song JQ, Zhao N, Qu Y, Zhao LS (2021) Natural deep eutectic solvent-assisted preparation of nitrogen-doped carbon dots for ratiometric determination of pirimicarb and pH. Dyes Pigm 193:109564. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.dyepig2021.109564
Li SR, Song XR, Hu ZR, Feng GD (2021) A carbon dots-based ratiometric fluorescence probe for monitoring intracellular pH and bioimaging. J Photoch Photobio A 409:113129. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jphotochem.2021.113129
Funding
The authors acknowledge financial support from the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Nos. 22177066), Innovation Capability Support Program of Shaanxi (No. 2021KJXX-51), Coconstruction Project of Hanzhong city and Shaanxi University of Technology (SXJ-2103, SXJ-2105) and Open Foundation of Key Laboratory of Synthetic and Natural Functional Molecule Chemistry of Ministry of Education (KLSNFM2020007).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Yanli Sun contributed to the methodology, investigations, probe preparation, data collection and curation, and writing-original draft preparation. Jin Liu, Zuoping Zhao, Lihua Li, and Zhifeng Liu contributed to methodology development, data collection, and sample pretreatment. Jiufu Lu and Lingxia Jin contributed to the formal analyses and validation. Qin Wang and Shengrui Zhang performed conceptualization, supervision, writing-reviewing and editing. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Ethics Approval
Not applicable.
Consent to Participate
Not applicable.
Consent for Publication
Not applicable.
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that they have no competing.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic Supplementary Material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Sun, Y., Wang, Q., Liu, J. et al. Ratiometric Sensing of Intracellular pH Based on Dual Emissive Carbon Dots. J Fluoresc 33, 653–661 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10895-022-03107-w
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10895-022-03107-w