Abstract
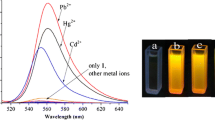
We reported here the unique ability of a Rhodamine 6G-based probe (3) to detect discriminately several targets, including H+, HO−, Cu2+, Hg2+, Fe3+, Co2+, Cd2+, Zn2+, Sn2+, Ni2+, Al3+, Pb2+, Ce3+and Ag+, by unambiguously colorimetric and fluorimetric outcomes. In aqueous solutions, the presence of proton induced the ring-opening of rhodamine moiety but the presence of hydroxide induced the conversion of 2-hydroxyphenyl hydrazone moiety from the non-fluorescent benzenoid form into the fluorescent quinoid form. The probe could to distinguish between different cations in DMF and to work like an artificial tongue at molecular level. Several logic gates including OR, INHIBIT and TRANSFER, were performed by the probe. Moreover, the probe is able to execute three INHIBIT logic gates by two inputs, which was exploited to execute a digital molecular comparator.















Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- HEPES :
-
4-(2-hydroxyethyl)-1-piperazineethanesulfonic acid
- DMF :
-
Dimethylformamide
- NMR :
-
Nuclear magnetic resonance
- FT-IR :
-
Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy
- UV-VIS :
-
Ultraviolet Visible Spectroscopy
References
Jin W, Jiang J, Wang X, Zhu X, Wang G, Song Y, Bai C (2011) Continuous intra-arterial blood pH monitoring in rabbits with acid-base disorders. Respir Physiol Neurobiol 177:183–188
Grant S, Bettencourt K, Krulevitch P, Hamilton J, Glass R (2001) In vitro and in vivo measurements of fiber optic and electrochemical sensors to monitor brain tissue pH. Sensors Actuators B Chem 72:174–719
Georgiev N, Said A, Toshkova R, Tzoneva R, Bojinov V (2019) A novel water-soluble perylenetetracarboxylic diimide as a fluorescent pH probe: chemosensing, biocompatibility and cell imaging. Dyes Pigments 160:28–36
Young O, Thomson R, Merhtens V, Loeffen M (2014) Industrial application to cattle of a method for the early determination of meat ultimate pH. Meat Sci 67:107–112
Zhang X, Jiang H, Jin J, Xu X, Zhang Q (2012) Analysis of acid rain patterns in northeastern China using a decision tree method. Atmos Environ 46:590–596
Han J, Burgess K (2011) Fluorescent indicators for intracellular pH. Chem Rev 52:2709–2728
Kim N, Swamy KMK, Yoon J (2011) Study on various fluorescein derivatives as pH sensors. Tetrahedron Lett 52:2340–2343
Aigner D, Borisov SM, Fernández FJ, Fernández Sánchez JF, Saf R, Klimant I (2012) New fluorescent pH sensors based on covalently linkable PET rhodamines. Talanta 99:194–201
Li CY, Zhou Y, Xu F, Li YF, Zou CX, Weng C (2012) A fluorescent pH chemosensor based on functionalized naphthalimide in aqueous solution. Anal Sci 28:743–747
Georgiev N, Bryaskova R, Tzoneva R, Ugrinova I, Detrembleur C, Miloshev S, Asiri A, Qusti A, Bojinov V (2013) A novel pH sensitive water soluble fluorescent nanomicellar sensor for potential biomedical applications. Bioorg Med Chem 21:6292–6302
Aigner D, Ungerböck B, Mayr T, Saf R, Klimant I, Borisov SM (2013) Fluorescent materials for pH sensing and imaging based on novel 1,4-diketopyrrolo-[3,4-c]pyrrole dyes. J Mater Chem C 1:5685–5693
Dimov S, Georgiev N, Asiri A, Bojinov V (2014) Synthesis and sensor activity of a PET-based 1,8-naphthalimide probe for Zn2+ and pH determination. J Fluoresc 24:1621–1628
Alamry K, Georgiev N, El-Daly SA, Taib L, Bojinov V (2015) A highly selective ratiometric fluorescent pH probe based on a PAMAM wavelength-shifting bichromophoric system. Spectrochim Acta Part A Mol Biomol Spectrosc 135:792–800
Georgiev N, Dimitrova M, Todorova Y, Bojinov V (2016) Synthesis, chemosensing properties and logic behaviour of a novel ratiometric 1,8-naphthalimide probe based on ICT and PET. Dyes Pigments 131:9–17
McRae R, Bagchi P, Sumalekshmy S, Fahrni C (2019) In situ imaging of metals in cells and tissues. Chem Rev 109:4780–4827
Que EL, Domaille DW, Chang C (2018) Metals in neurobiology: probing their chemistry and biology with molecular imaging. Chem Rev 108:1517–1549
Bargossi C, Fiorini MC, Montalti M, Prodi L, Zaccheroni N (2000) Recent developments in transition metal ion detection by luminescent chemosensors. Coord Chem Rev 208:17–32
Eisenstein R (2000) Iron regulatory proteins and the molecular control of mammallan iron metabolism. Annu Rev Nutr 20:627–662
Tang L, Zhou P, Zhang Q, Huang Z, Zhao J, Cai M (2013) A simple quinoline derivatized thiosemicarbazone as a colorimetic and fluorescent sensor for relay recognition of Cu2+ and sulfide in aqueous solution. Inorg Chem Commun 36:100–104
Ahamed B, Ghosh P (2011) An integrated system of pyrene and rhodamine-6G for selective colorimetric and fluorometric sensing of mercury(II). Inorg Chim Acta 372:100–107
Winder C, Carmichael N, Lewis P (1982) Effects of chronic low level lead exposure on brain development and function. Trends Neurosci 4:207–209
Bernardo-Filho M, da Conceicão CM, de Oliveira VJ, Caldeira de Araujo A, Pereira da Silva FC, de Sousa da Fonseca A (1994) Evaluation of potential genotoxity of stannous chloride: inactivation, filamentation and lysogenic induction of Escherichia coli. Food Chem Toxicol 32:477–479
Lee HN, Xu ZC, Kim SK, Swamy KMK, Kim Y, Kim SJ, Yoon JY (2007) Pyrophosphate-selective fluorescent chemosensor at physiological pH: formation of a unique excimer upon addition of pyrophosphate. J Am Chem Soc 129:3828–3829
Wang JB, Qian XH (2006) Two regioisomeric and exclusively selective Hg(II) sensor molecules composed of a naphthalimide fluorophore and an o-phenylenediamine derived triamide receptor. Chem Commun 2006:109–111
Komatsu K, Urano Y, Kojima P, Nagano TJ (2007) Development of an iminocoumarin-based zinc sensor suitable for ratiometric fluorescence imaging of neuronal zinc. J Am Chem Soc 129:13447–13454
Butler O, Cook J, Harrington C, Hill S, Rieuwerts J, Miles D (2006) Atomic spectrometry update. Environmental analysis J Anal At Spectrom 21:217–243
Li Y, Chen C, Li B, Sun J, Wang J, Gao Y, Zhao Y, Chai Z (2006) Elimination efficiency of different reagents for the memory effect of mercury using ICP-MS. J Anal At Spectrom 21:94–96
Leermakers M, Baeyens W, Quevauviller P, Horvat M (2005) Mercury in environmental samples: speciation, artifacts and validation. Trends Anal Chem 24:383–393
Georgiev N, Bakov V, Bojinov V (2019) A solid-state-emissive 1,8-naphthalimide probe based on photoinduced electron transfer and aggregation-induced emission. ChemistrySelect 4:4163–4167
Czarnik A (1993) Fluorescent chemosensors for ion and molecule recognition. American Chemical Society, Washington
Said A, Georgiev N, Bojinov V (2019) A smart chemosensor: discriminative multidetection and various logic operations in aqueous solution at biological pH. Spectrochim Acta Part A Mol Biomol Spectrosc 223:117304
Lakowicz J (1983) Principles of fluorescence spectroscopy. Plenum Press, New York
Said A, Georgiev N, Bojinov V (2018) Synthesis of a single 1,8-naphthalimide fluorophore as a molecular logic lab for simultaneously detecting of Fe3+, Hg2+ and Cu2+. Spectrochim Acta Part A Mol Biomol Spectrosc 196:76–82
Goswami S, Sen D, Das N, Hazra G (2010) Highly selective colorimetric fluorescence sensor for Cu2+: cation-induced ‘switching on’ of fluorescence due to excited state internal charge transfer in the red/near-infrared region of emission spectra. Tetrahedron Lett 51:5563–5566
Bojinov V, Panova I, Simeonov D, Georgiev N (2010) Synthesis and sensor activity of photostable blue emitting 1,8-naphthalimides containing s-triazine UV absorber and HALS fragments. J Photochem Photobiol A Chem 210:89–99
Kim J, Morozumi T, Kurumatani N, Nakamura H (2008) Novel chemosensor for alkaline earth metal ion based on 9-anthryl aromatic amide using a naphthalene as a TICT control site and intramolecular energy transfer donor. Tetrahedron Lett 49:1984–1987
Georgiev N, Sakr A, Bojinov V (2015) Design and synthesis of a novel PET and ICT based 1,8-naphthalimide FRET bichromophore as a four-input disabled-enabled-OR logic gate. Sensors Actuators B Chem 221:625–634
Said A, Georgiev N, Bojinov V (2015) Sensor activity and logic behavior of dihydroxyphenyl hydrazone derivative as a chemosensor for Cu2+ determination in alkaline aqueous solutions. J Photochem Photobiol A Chem 311:16–24
Andréasson J, Pischel U (2010) Smart molecules at work-mimicking advanced logic operations. Chem Soc Rev 39:174–188
de Silva AP, McClenaghan N (2004) Molecular-scale logic gates. Chem Eur J 10:574–586
Bojinov V, Georgiev N (2011) Molecular sensors and molecular logic gates. J Univ Chem Tech Metall 46:3–26
Andréasson J, Straight S, Kodis G, Park CD, Hambourger M, Gervaldo M, Albinsson B, Moore T, Moore A, Gust D (2006) All-photonic molecular half-adder. J Am Chem Soc 128:16259–16265
Georgiev N, Lyulev M, Bojinov V (2012) Sensor activity and logic behavior of PET based dihydroimidazonaphthalimide diester. Spectrochim Acta Part A Mol Biomol Spectrosc 97:512–520
Margulies D, Melman G, Shanzer A (2006) A molecular full-adder and full-subtractor, an additional step toward a moleculator. J Am Chem Soc 128:4865–4871
Li Q, Yue Y, Guo Y, Shao S (2012) Fluoride anions triggered “OFF–ON” fluorescent sensor for hydrogen sulfate anions based on a BODIPY scaffold that works as a molecular keypad lock. Sensors Actuators B Chem 173:797–801
Suresh M, Jose D, Das A (2007) [2,2‘-Bipyridyl]-3,3′-diol as a molecular half-subtractor. Org Lett 9:441–444
Ceroni P, Bergamini G, Balzani V (2009) Old molecules, new concepts: [Ru(bpy)3]2+ as a molecular encoder-decoder. Angew Chem Int Ed 48:8516–8518
Georgiev N, Lyulev M, Alamry K, El-Daly SA, Taib L, Bojinov V (2014) Synthesis, sensor activity and logic behavior of a highly water-soluble 9,10-dihydro-7H-imidazo[1,2-b]benz[d,e]isoqionolin-7-one dicarboxylic acid. J Photochem Photobiol A Chem 297:31–38
Jiang W, Zhang H, Liu Y (2009) Unimolecular half-adders and half-subtractors based on acid-base reaction. Front Chem China 4:292–298
Georgiev N, Yaneva I, Surleva A, Asiri A, Bojinov V (2013) Synthesis, sensor activity and logic behavior of a highly water-solublenaphthalimide derivative. Sensors Actuators B Chem 184:54–63
Said A, Georgiev N, Bojinov V (2019) A fluorescent bichromophoric “off-on-off” pH probe as a molecular logic device (half-subtractor and digital comparator) operating by controlled PET and ICT processes. Dyes Pigments 162:377–384
Macdonald J, Li Y, Sutovic M, Lederman H, Pendri K, Lu W, Andrews B, Stefanovic D, Stojanovic M (2006) Medium scale integration of molecular logic gates in an automaton. Nano Lett 6:2598–2603
Pais V, Remon P, Collado D, Andréasson J, Perez-Inestrosa E, Pischel U (2011) OFF-ON-OFF fluorescence switch with T-latch function. Org Lett 13:5572–5575
Pu F, Ju E, Ren J, Qu X (2014) Multiconfigurable logic gates based on fluorescence switching in adaptive coordination polymer nanoparticles. Adv Mater 26:1111–1117
Kim YS, Park GJ, Lee JJ, Lee SY, Lee SY, Kim C (2015) Multiple target chemosensor: a fluorescent sensor for Zn(II) and Al(III) and a chromogenic sensor for Fe(II) and Fe(III). RSC Adv 5:11229–11239
Alam R, Bhowmick R, Islam ASM, Katarkar A, Chaudhuri K, Ali M (2017) A rhodamine based fluorescent trivalent sensor (Fe3+, Al3+, Cr3+) with potential applications for live cell imaging and combinational logic circuits and memory devices. New J Chem 41:8359–8369
Wan X, Liu T, Liu H, Gu L, Yao Y (2014) Cascade OFF-ON-OFF fluorescent probe: dual detection of trivalent ions and phosphate ions. RSC Adv 4:29479–29484
Udhayakumari D, Suganya S, Velmathi S, MubarakAli D (2014) Naked eye sensing of toxic metal ions in aqueous medium using thiophene-based ligands and its application in living cells. J Mol Recognit 27:151–159
Behera N, Manivannan V (2018) A probe for multi detection of Al3+, Zn2+ and Cd2+ ions via turn-on fluorescence responses. J Photochem Photobiol A Chem 353:77–85
García-Gutiérrez Y, Huerta-Aguilar C, Thangarasu P, Vázquez-Ramos J (2017) Ciprofloxacin as chemosensor for simultaneous recognition of Al3+ and Cu2+ by logic gates supported fluorescence: application to bio-imaging for living cells. Sensors Actuators B Chem 248:447–459
Liu H, Cui S, Shi F, Pu S (2019) A diarylethene based multi-functional sensor for fluorescent detection of Cd2+ and colorimetric detection of Cu2+. Dyes Pigments 161:34–43
Xiang Y, Li Z, Chen X, Tong A (2008) Highly sensitive and selective optical chemosensor for determination of Cu2+ in aqueous solution. Talanta 74:1148–1153
Bojinov V, Venkova A, Georgiev N (2009) Synthesis and energy-transfer properties of fluorescence sensing bichromophoric system based on Rhodamine 6G and 1,8-naphthalimide. Sensors Actuators B Chem 143:42–49
Lakowicz JR (1991) Topics in fluorescence spectroscopy, Principles, vol 2. Plenum Press, New York
Lakowicz JR (1991) Topics in fluorescence spectroscopy, Application, vol 3. Plenum Press, New York
Lakowicz JR (1991) Topics in fluorescence spectroscopy, Techniques, vol 4. Plenum Press, New York
Irvine DJ, Purbhoo MA, Krogsgaard M, Davis MM (2002) Direct observation of ligand recognition by T cells. Nature 419:845–849
Pope AJ, Haupts UM, Moore KJ (1999) Homogeneous fluorescence readouts for miniaturized high-throughput screening: theory and practice. Drug Discov Today 4:350–362
Georgiev N, Asiri A, Qusti A, Alamry K, Bojinov V (2014) A pH sensitive and selective ratiometric PAMAM wavelength-shifting bichromophoric system based on PET, FRET and ICT. Dyes Pigments 102:35–45
Saleem M, Abdullah R, Ali A, Park B, Choi E, Hong I, Lee K (2014) Synthesis, cytotoxicity and bioimaging of novel Hg2+ selective fluorogenic chemosensor. Anal Methods 6:3588–3597
Georgiev N, Dimitrova M, Asiri A, Alamry K, Bojinov V (2015) Synthesis, sensor activity and logic behaviour of a novel bichromophoric system based on rhodamine 6G and 1,8-naphthalimide. Dyes Pigments 115:172–180
Fabbrizzi L, Licchelli M, Pallavicini P, Perotti A, Taglietti A, Sacchi D (1996) Fluorescent sensors for transition metals based on electron-transfer and energy-transfer mechanisms. Chem Eur J 2:75–92
Dougherty T, Hicks C, Maletta A, Fan J, Rutenberg I, Gafney HD (1998) Excited-state coordination chemistry: a new quenching mechanism. J Am Chem Soc 120:4226–4227
Crutchley R, Kress N, Lever ABP (1983) Protonation equilibria in excited-state tris(bipyrazine)ruthenium(II). J Am Chem Soc 105:1170–1178
Giordano PJ, Randolph Bock C, Wrighton MS, Interrante LV, Williams RFX (1977) Excited state proton transfer of a metal complex: determination of the acid dissociation constant for a metal-to-ligand charge transfer state of a ruthenium(II) complex. J Am Chem Soc 99:3187–3189
Lei Y, Buranda T, Endicott JF (1990) Photoinduced energy transfer in multinuclear transition-metal complexes. Reversible and irreversible energy flow between charge-transfer and ligand field excited states of cyanide-bridged ruthenium(II)-chromium(III) and ruthenium(II)-rhodium(III) complexes. J Am Chem Soc 112:8820–8833
Said A, Georgiev N, Bojinov V (2019) The simplest molecular chemosensor for detecting pH, Cu2+ and S2− in aqueous environment and executing various logic gates. J Photochem Photobiol A Chem 371:395–406
Pu F, Ran X, Ren J, Qu X (2016) Artificial tongue based on metal–biomolecule coordination polymer nanoparticles. Chem Commun 52:3410–3413
Acknowledgements
The Science Foundation at the University of Chemical Technology and Metallurgy (Sofia, Bulgaria) supported this work. Authors also acknowledge the Science foundation of Assiut University (Assiut, Egypt).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Said, A.I., Georgiev, N.I., Hamdan, S.A. et al. A chemosensoring molecular lab for various analytes and its ability to execute a molecular logical digital comparator. J Fluoresc 29, 1431–1443 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10895-019-02464-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10895-019-02464-3