Abstract
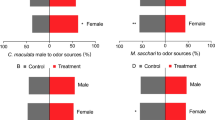
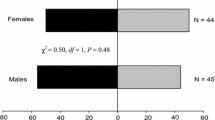
The role of two volatile sesquiterpenes, (E)-β-farnesene and (−)-β-caryophyllene, in the chemical ecology of the multicolored Asian lady beetle, Harmonia axyridis Pallas, was investigated by using both electrophysiological and behavioral techniques. (E)-β-Farnesene is the major component of the alarm pheromone of most aphid species, which are preyed on by H. axyridis. (−)-β-Caryophyllene was previously isolated from the headspace volatiles above overwintering and aggregated H. axyridis females. These sesquiterpenes elicited significant electroantennogram (EAG) activity from both H. axyridis male and female antennae. In a four-arm olfactometer, male and female H. axyridis were highly attracted toward (E)-β-farnesene, whereas only males were attracted to (−)-β-caryophyllene. In a bioassay technique that used a passively ventilated plastic box, both male and female H. axyridis aggregated in the (−)-β-caryophyllene-treated side of the box. These results support the potential usefulness of (E)-β-farnesene and (−)-β-caryophyllene in push–pull strategies that use H. axyridis as a biological control agent in aphid-infested sites or to control this new urban pest in residential structures.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Al Abassi, S. A., Birkett, M. A., Pettersson, J., Pickett, J. A., Wadhams, L. J., and Woodcock, C. M. 2000. Response of the seven-spot ladybird to an alarm pheromone and an alarm pheromone inhibitor is mediated by paired olfactory cells. J. Chem. Ecol. 26:1765–1771.
Acar, E. B., Medina, J. C., Lee, M. L., and Booth, G. M. 2001. Olfactory behavior of convergent lady beetles (Coleoptera: Coccinellidae) to alarm pheromone of green peach aphid (Hemiptera: Aphididae). Can. Entomol. 133:389–397.
Brown, A. E., Riddick, E. W., Aldrich, J. R., and Holmes, W. E. 2006. Identification of (−)-β-caryophyllene as a gender-specific terpene produced by the multicolored Asian lady beetle. J. Chem. Ecol. 32:2489–2499.
Cook, S. M., Khan, Z. R., and Pickett, J. A. 2007. The use of push–pull strategies in integrated pest management. Annu. Rev. Entomol. 52:375–400.
Dean, J. M., and De Moraes, C. M. 2006. Effects of genetic modification on herbivore-induced volatiles from maize. J. Chem. Ecol. 32:713–724.
Dawson, G. W., Griffiths, D. C., Pickett, J. A., Smith, M. C., and Woodcock, C. M. 1984. Natural inhibition of the aphid alarm pheromone. Entomol. Exp. Appl. 36:197–199.
Edwards, L. J., Siddball, J. B., Dunham, L. L., Uden, P., and Kislow, C. J. 1973. Trans-beta-farnesene, alarm pheromone of the green peach aphid, Myzus persicae (Sulzer). Nature 241:126–127.
Farag, M. A., and Paré, P. W. 2002. C6-Green leaf volatiles trigger local and systemic VOC emissions in tomato. Phytochemistry 61:545–554.
Francis, F., Lognay, G., Wathelet, J.-P., and Haubruge, E. 2001. Effect of allelochemicals from first (Brasicaceae) and second (Myzus persicae and Brevicoryne brassicae) trophic levels on Adalia bipunctata. J. Chem. Ecol. 27:243–256.
Francis, F., Lognay, G., and Haubruge, E. 2004. Olfactory responses to aphid and host plant volatile releases: E-β-Farnesene an effective kairomone for the predator Adalia bipunctata. J. Chem. Ecol. 30:741–755.
Francis, F., Vandermoten, S., Verheggen, F., Lognay, G., and Haubruge, E. 2005. Is the (E)-β-Farnesene only volatile terpenoid in aphids? J. Appl. Entomol. 129:6–11.
Han, B.-Y., and Chen, Z.-M. 2002. Composition of the volatiles from intact and tea aphid-damaged tea shoots and their allurement to several natural enemies of the tea aphid. J. Appl. Entomol. 126:497–500.
Hemptinne, J. L., Gaudin, M., Dixon, A. F. G., and Lognay, G. 2000. Social feeding in ladybird beetles: adaptive significance and mechanism. Chemoecology 10:149–152.
Huelsman, M. F., Kovach, J., Jasinski, J., Young, C., and Eisley, B. 2002. Multicolored Asian lady beetle (Harmonia axyridis) as a nuisance pest in households in Ohio, pp. 243–250, in S. C. Jones, J. Zhai, and W. H. Robinson (eds.). Proceedings of the 4th International Conference on Urban Pests, 7–10 July, 2002, Charleston, SC, USA.
Koch, R. L. 2003. The multicolored Asian lady beetle, Harmonia axyridis: A review of its biology, uses in biological control, and non target impacts. J. Insect Sci. 3:16.
Magnan, E. M., Sanchez, H., Luskin, A. T., and Bush, R. K. 2002. Multicolored Asian lady beetle (Harmonia axyridis) sensitivity. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 109:205.
Mondor, E. B., and Roitberg, B. D. 2000. Has the attraction of predatory coccinellids to cornicle droplets constrained aphid alarm signalling behavior? J. Insect Behav. 13:321–329.
Nakamuta, K. 1991. Aphid alarm pheromone component, (E)-beta-farnesene, and local search by a predatory lady beetle, Coccinella septempunctata Bruckii mulsant (Coleoptera: Coccinellidae). Appl. Entomol. Zool. 26:1–7.
Nalepa, C. A., Kidd, K. A., and Hopkins, D. I. 2000. The multicolored Asian lady beetle (Coleoptera: Coccinellidae): Orientation to aggregation sites. J. Entomol. Sci. 35:150–157.
Ninkovic, V., Abassi, S. A., and Pettersson, J. 2001. The influence of aphid-induced plant volatiles on ladybird beetle searching behavior. Biol. Control 21:191–195.
Osawa, N. 2000. Population field studies on the aphidophagous ladybird beetle Harmonia axyridis (Coleoptera: Coccinellidae): resource tracking and population characteristics. Popul. Ecol. 42:115–127.
Rohloff, J., and Bones, A. M. 2005. Volatile profiling of Arabidopsis thaliana—Putative olfactory compounds in plant communication. Phytochemistry 66:1941–1955
Sato, S., Yasuda, H., and Evans, E. W. 2005. Dropping behaviour of larvae of aphidophagous ladybirds and its effects on incidence of intraguild predation: Interactions between the intraguild prey, Adalia bipunctata (L.) and Coccinella septempunctata (L.), and the intraguild predator, Harmonia axyridis Pallas. Ecol. Entomol. 30:220–224.
Tanaka, S., Yasuda, A., Yamamoto, H., and Nozaki, H. 1975. A general method for the synthesis of 1,3-dienes. Simple syntheses of β- and trans-α-farnesene from farnesol. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 97:3252–3254.
Tumlinson, J. H., Turlings, T. C. J., and Lewis, W. J. 1992. The semiochemical complexes that mediate insect parasitoid foraging. Agric. Zool. Rev. 5:221–252.
Verheggen, F., Ryne, C., Olsson, P. O. C., Arnaud, L., Lognay, G., Högberg, H. E., Persson, D., Haubruge, E., and Löfstedt, C. 2007. Electrophysiological and behavioral activity of secondary metabolites in the confused flour beetle, Tribolium confusum. J. Chem. Ecol. 33:525–539.
Vet, L. E. M., Lenteren, J. C. V., Heymans, M., and Meelis, E. 1983. An airflow olfactometer for measuring olfactory responses of hymenopterous parasitoids and other small insects. Physiol. Entomol. 8:97–106.
Zhu, J., Cossé, A. A., Obrycki, J. J., Boo, K. S., and Baker, T. C. 1999. Olfactory reactions of the twelve-spotted lady beetle, Coleomegilla maculata and the green lacewing, Chrysoperla to semiochemicals released from their prey and host plant: Electroantennogram and behavioral responses. J. Chem. Ecol. 5:1163–1177.
Acknowledgments
The authors are grateful to Dr. Bartram, from Max Planck Institute for Chemical Ecology, for the synthesis of (E)-β-farnesene. We also thank Dr. Yves Brostaux and Adeline Gillet, from Gembloux Agricultural University, for advice on statistical analysis. This work was supported by the Fonds National pour la Recherche Scientifique (grant M 2.4.586.04.F).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Verheggen, F.J., Fagel, Q., Heuskin, S. et al. Electrophysiological and Behavioral Responses of the Multicolored Asian Lady Beetle, Harmonia axyridis Pallas, to Sesquiterpene Semiochemicals. J Chem Ecol 33, 2148–2155 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10886-007-9370-6
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10886-007-9370-6