Abstract
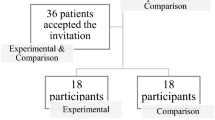
End-Stage Renal disease patients experience a drastic change in physical, psychological, emotional and quality of life after the diagnosis. Various psychotherapeutic interventions were found to be effective in reducing the singular anxiety, depressive, and sleep related issues, however, an integrated approach is required to cater the psychological distress in a collective fashion, and enhance the psychological well-being of end-stage renal disease patients. Rational Emotive Behavior Therapy has been found to be effective in catering to the needs of various chronic disease patients. Therefore, the current study aimed to find the efficacy of rational emotive behavior therapy on the psychological distress and well-being of end-stage renal disease patients. The participants for the study were selected using G*power analysis. Total 64 participants were selected then randomly allocated to experimental and waitlist control groups. Mental Health Inventory (MHI) was used for pre-post assessment. Application of rational emotive behavior therapy was distributed into eight sessions, and two follow-up sessions were provided after the post-assessment. The results suggested statistically significant effectiveness of rational emotive behavior therapy for the alleviation of psychological distress and amelioration of psychological wellbeing. The study suggested efficacy of Rational Emotive Behavior Therapy as an integrated approach to cater to the End-stage Renal Disease patients’ needs.



Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
The datasets generated during and/or analyzed during the current study are not publicly available due to the confidential information of the participants but are available from the corresponding author at reasonable request.
References
Artiran, M., & DiGiuseppe, R. (2022). Rational emotive behavior therapy compared to client-centered therapy for outpatients: A randomized clinical trial with a three months follow up. Journal of Rational-Emotive & Cognitive-Behavior Therapy, 40(2), 206–233.
DiGiuseppe, R. A., DiGiuseppe, R., Doyle, K. A., Dryden, W., & Backx, W. (2014). A practitioner’s guide to rational-emotive behavior therapy. Oxford University Press.
Ede, M. O., Adene, F. M., Okeke, C. I., Mezieobi, D. I., Isiwu, E. N., & Abdullahi, Y. (2022). The effect of rational emotive behaviour therapy on post-traumatic depression in flood victims. Journal of Rational-Emotive & Cognitive-Behavior Therapy, 40(1), 124–143.
Eswarappa, M., Prabhu, S. A. R. A. L., Chennabasappa, P., Siddaiah, G., Reddy, G., & Gangula, R., R (2023). WCN23-0946 Health Related Quality of Life (Hrqol) and its determinants in end stage kidney disease (end-stage renal disease) patients on Hemodialysis: A study from South India. Kidney International Reports, 8(3), S297–S298.
Fradelos, E. C. (2021). Spiritual well-being and associated factors in end-stage renal disease. The Scientific World Journal, 2021, 1–9.
Hashmi, M. F., Benjamin, O., & Lappin, S. L. (2022). End-Stage Renal Disease. StatPearls. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing.
Hopewell, S., Boutron, I., Chan, A. W., Collins, G. S., de Beyer, J. A., Hróbjartsson, A., & Moher, D. (2022). An update to SPIRIT and CONSORT reporting guidelines to enhance transparency in randomized trials. Nature Medicine, 28(9), 1740–1743.
Hwan, N. L., & Hussin, N. A. M. (2022). Volunteering experience among older adults with end-stage renal disease (END-STAGE RENAL DISEASE). Journal of Gerontological Social work, 65(3), 271–289.
Kang, H. (2021). Sample size determination and power analysis using the G* Power software. Journal of educational evaluation for health professions, 18.
Lee, H. J., & Son, Y. J. (2021). Prevalence and associated factors of frailty and mortality in patients with end-stage renal disease undergoing hemodialysis: A systematic review and meta-analysis. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 18(7), 3471.
Khan, M. J., Hanif, R., & Tariq, N. (2015). Translation and validation of mental health inventory. Pakistan Journal of Psychological Research, 30(1).
Liu, Y., Ni, X., Wang, R., Liu, H., & Guo, Z. (2022). Application of rational emotive behavior therapy in patients with colorectal cancer undergoing adjuvant chemotherapy. International Journal of Nursing Sciences, 9(2), 147–154.
Nair, N., Saurav, K. P., Yaacoub, R. M., Sandhu, J. M., Bhavaraju, S., & Raina, R. (2023). Challenges and Unique Considerations of Adolescents with Chronic Kidney Disease. Acta Paediatrica.
Nielsen, S. L., Abegg, D. D., Brown, B. T., Erekson, D. M., Hamilton, R. A., & Lindsey, S. E. (2023). Religiously accommodative and integrative rational emotive behavior therapy.
Qawaqzeh, D. T. A., Masa’deh, R., Hamaideh, S. H., Alkhawaldeh, A., & ALBashtawy, M. (2023). Factors affecting the levels of anxiety and depression among patients with end-stage renal disease undergoing hemodialysis. International Urology and Nephrology, 1–10.
Şahin, E. S., & Acar, N. V. (2019). Rational emotive behavior therapy from a new perspective. Journal of Human Sciences, 16(4), 894–906.
Samoudi, A. F., Marzouq, M. K., Samara, A. M., Zyoud, S. E. H., & Al-Jabi, S. W. (2021). The impact of pain on the quality of life of patients with end-stage renal disease undergoing hemodialysis: A multicenter cross-sectional study from Palestine. Health and Quality of life Outcomes, 19(1), 1–10.
Vasavada, A., Velastegui, J. L., & Singh, K. (2022). Comment on the effects of rational emotive behavior therapy for depressive symptoms in adults with congenital heart disease. Heart & Lung: The Journal of Cardiopulmonary and Acute Care, 56, 189.
Veit, C. T., & Ware, J. E. (1983). Mental health inventory. Psychological Assessment.
Wang, X., Shi, Q., Mo, Y., Liu, J., & Yuan, Y. (2022). Palliative care needs and symptom burden in younger and older patients with end-stage renal disease undergoing maintenance hemodialysis: A cross-sectional study. International Journal of Nursing Sciences, 9(4), 422–429.
Acknowledgements
We would like to thank the medical facility for allowing us to develop the project and conduct research.
Funding
No funds, grants, or other support were received.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethical Approval
Ethical approval was acquired from the ethics department of the medical facility for individual cases or case series concurrent with the Helsinki Declaration.
Conflict of interest
The authors have no conflicts of interest to declare that are relevant to the content of this article.
Informed Consent
Written informed consent was obtained from the patients for their. a. Participation in study. b. Anonymized information to be published in this article.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Aurooj, A., Zia, N., Nadeem Kirmani, S. et al. Efficacy of Rational Emotive Behavior Therapy for the Alleviation of Psychological Distress and Amelioration of Psychological Well-Being Among End-Stage Renal Disease Patients. J Contemp Psychother 54, 29–36 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10879-023-09596-5
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10879-023-09596-5