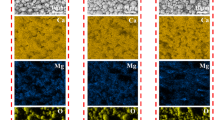
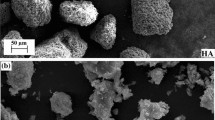
Abstract
Hydroxyapatite (HA) was coated onto pure magnesium (Mg) with an MgF2 interlayer in order to reduce the surface corrosion rate and enhance the biocompatibility. Both MgF2 and HA were successfully coated in sequence with good adhesion properties using the fluoride conversion coating and aerosol deposition techniques, respectively. In a simulated body fluid (SBF), the double layer coating remarkably enhanced the corrosion resistance of the coated Mg specimen. The in vitro cellular responses of the MC3T3-E1 pre-osteoblasts were examined using a cell proliferation assay and an alkaline phosphatase (ALP) assay, and these results demonstrated that the double coating layer also enhanced cell proliferation and differentiation levels. In the in vivo study, the HA/MgF2 coated Mg corroded less than the bare Mg and had a higher bone-to-implant contact (BIC) ratio in the cortical bone area of the rabbit femora 4 weeks after implantation. These in vitro and in vivo results suggested that the HA coated Mg with the MgF2 interlayer could be used as a potential candidate for biodegradable implant materials.













Similar content being viewed by others
References
Nair LS, Laurencin CT. Biodegradable polymers as biomaterials. Prog Polym Sci. 2007;32:762–98.
Gunatillake P, Mayadunne R, Adhikari R. Recent developments in biodegradable synthetic polymers. Biotechnol Annu Rev. 2006;12:301–47.
Chiu KY, Wong MH, Cheng FT, Man HC. Characterization and corrosion studies of fluoride conversion coating on degradable Mg implants. Surf Coat Tech. 2007;202:590–8.
Staiger MP, Pietak AM, Huadmai J, Dias G. Magnesium and its alloys as orthopedic biomaterials: a review. Biomaterials. 2006;27:1728–34.
Zreiqat H, Howlett CR, Zannettino A, Evans P, Schulze-Tanzil G, Knabe C, et al. Mechanisms of magnesium-stimulated adhesion of osteoblastic cells to commonly used orthopaedic implants. J Biomed Mater Res. 2002;62:175–84.
Zeng RC, Dietzel W, Witte F, Hort N, Blawert C. Progress and challenge for magnesium alloys as biomaterials. Adv Eng Mater. 2008;10:B3–14.
Song GL, Atrens A. Corrosion mechanisms of magnesium alloys. Adv Eng Mater. 1999;1:11–33.
Witte F, Kaese V, Haferkamp H, Switzer E, Meyer-Lindenberg A, Wirth CJ, et al. In vivo corrosion of four magnesium alloys and the associated bone response. Biomaterials. 2005;26:3557–63.
Witte F, Fischer J, Nellesen J, Crostack HA, Kaese V, Pisch A, et al. In vitro and in vivo corrosion measurements of magnesium alloys. Biomaterials. 2006;27:1013–8.
Song GL. Control of biodegradation of biocompatable magnesium alloys. Corros Sci. 2007;49:1696–701.
Wang H, Estrin Y, Fu H, Song G, Zuberova Z. The effect of pre-processing and grain structure on the bio-corrosion and fatigue resistance of magnesium alloy AZ31. Adv Eng Mater. 2007;9:967–72.
Xu LP, Yu GN, Zhang E, Pan F, Yang K. In vivo corrosion behavior of Mg-Mn-Zn alloy for bone implant application. J Biomed Mater Res A. 2007;83A:703–11.
Li ZJ, Gu XN, Lou SQ, Zheng YF. The development of binary Mg-Ca alloys for use as biodegradable materials within bone. Biomaterials. 2008;29:1329–44.
Pietak A, Mahoney P, Dias GJ, Staiger MP. Bone-like matrix formation on magnesium and magnesium alloys. J Mater Sci-Mater M. 2008;19:407–15.
Kannan MB, Raman RKS. In vitro degradation and mechanical integrity of calcium-containing magnesium alloys in modified-simulated body fluid. Biomaterials. 2008;29:2306–14.
Xu LP, Zhang EL, Yin DS, Zeng SY, Yang K. In vitro corrosion behaviour of Mg alloys in a phosphate buffered solution for bone implant application. J Mater Sci-Mater M. 2008;19:1017–25.
Gu XN, Zheng YF, Cheng Y, Zhong SP, Xi TF. In vitro corrosion and biocompatibility of binary magnesium alloys. Biomaterials. 2009;30:484–98.
Hanzi AC, Gunde P, Schinhammer M, Uggowitzer PJ. On the biodegradation performance of an Mg-Y-RE alloy with various surface conditions in simulated body fluid. Acta Biomater. 2009;5:162–71.
Zhang EL, Xu LP, Yu GN, Pan F, Yang K. In vivo evaluation of biodegradable magnesium alloy bone implant in the first 6 months implantation. J Biomed Mater Res A. 2009;90A:882–93.
Witte F, Hort N, Vogt C, Cohen S, Kainer KU, Willumeit R, et al. Degradable biomaterials based on magnesium corrosion. Curr Opin Solid St M. 2008;12:63–72.
Song GL, Song SZ. A possible biodegradable magnesium implant material. Adv Eng Mater. 2007;9:298–302.
Song YW, Shan DY, Han EH. Electrodeposition of hydroxyapatite coating on AZ91D magnesium alloy for biomaterial application. Mater Lett. 2008;62:3276–9.
Xu LP, Zhang EL, Yang K. Phosphating treatment and corrosion properties of Mg-Mn-Zn alloy for biomedical application. J Mater Sci-Mater M. 2009;20:859–67.
Zhang E, Xu LP, Yang K. Formation by ion plating of Ti-coating on pure Mg for biomedical applications. Scripta Mater. 2005;53:523–7.
Gray-Munro JE, Seguin C, Strong M. Influence of surface modification on the in vitro corrosion rate of magnesium alloy AZ31. J Biomed Mater Res A. 2009;91A:221–30.
Wen CL, Guan SK, Peng L, Ren CX, Wang X, Hu ZH. Characterization and degradation behavior of AZ31 alloy surface modified by bone-like hydroxyapatite for implant applications. Appl Surf Sci. 2009;255:6433–8.
Geng F, Tan LL, Jin XX, Yang JY, Yang K. The preparation, cytocompatibility, and in vitro biodegradation study of pure beta-TCP on magnesium. J Mater Sci-Mater M. 2009;20:1149–57.
Zhang YJ, Zhang GZ, Wei M. Controlling the biodegradation rate of magnesium using biomimetic apatite coating. J Biomed Mater Res B. 2009;89B:408–14.
Wang Y, Wei M, Gao JC. Improve corrosion resistance of magnesium in simulated body fluid by dicalcium phosphate dihydrate coating. Mat Sci Eng C-Bio S. 2009;29:1311–6.
Xu LP, Pan F, Yu GN, Yang L, Zhang EL, Yang K. In vitro and in vivo evaluation of the surface bioactivity of a calcium phosphate coated magnesium alloy. Biomaterials. 2009;30:1512–23.
Lakstein D, Kopelovitch W, Barkay Z, Bahaa M, Hendel D, Eliaz N. Enhanced osseointegration of grit-blasted, NaOH-treated and electrochemically hydroxyapatite-coated Ti-6Al-4V implants in rabbits. Acta Biomater. 2009;5:2258–69.
Bigi A, Fini M, Bracci B, Boanini E, Torricelli P, GiavareSi G, et al. The response of bone to nanocrystalline hydroxyapatite-coated Ti13Nb11Zr alloy in an animal model. Biomaterials. 2008;29:1730–6.
Akedo J. Aerosol deposition of ceramic thick films at room temperature: densification mechanism of ceramic layers. J Am Ceram Soc. 2006;89:1834–9.
Hahn BD, Park DS, Choi JJ, Ryu J, Yoon WH, Kim KH, et al. Dense nanostructured hydroxyapatite coating on titanium by aerosol deposition. J Am Ceram Soc. 2009;92:683–7.
Kokubo T, Takadama H. How useful is SBF in predicting in vivo bone bioactivity? Biomaterials. 2006;27:2907–15.
Hahn BD, Lee JM, Park DS, Choi JJ, Ryu J, Yoon WH, et al. Aerosol deposition of silicon-substituted hydroxyapatite coatings for biomedical applications. Thin Solid Films. 2010;518:2194–9.
Gineste L, Gineste M, Ranz X, Ellefterion A, Guilhem A, Rouquet N, et al. Degradation of hydroxylapatite, fluorapatite, and fluorhydroxyapatite coatings of dental implants in dogs. J Biomed Mater Res. 1999;48:224–34.
Guo XX, Xu SL, Zhao LL, Lu W, Zhang FZ, Evans DG, et al. One-step hydrothermal crystallization of a layered double hydroxide/alumina bilayer film on aluminum and its corrosion resistance properties. Langmuir. 2009;25:9894–7.
Dearnley PA. A brief review of test methodologies for surface-engineered biomedical implant alloys. Surf Coat Tech. 2005;198:483–90.
Meyer U, Buchter A, Wiesmann HP, Joos U, Jones DB. Basic reactions of osteoblasts on structured material surfaces. Eur Cell Mater. 2005;9:39–49.
Kim HW, Koh YH, Li LH, Lee S, Kim HE. Hydroxyapatite coating on titanium substrate with Titania buffer layer processed by sol-gel method. Biomaterials. 2004;25:2533–8.
Hahn BD, Lee JM, Park DS, Choi JJ, Ryu J, Yoon WH, et al. Mechanical and in vitro biological performances of hydroxyapatite-carbon nanotube composite coatings deposited on Ti by aerosol deposition. Acta Biomater. 2009;5:3205–14.
Ramires PA, Wennerberg A, Johansson CB, Cosentino F, Tundo S, Milella E. Biological behavior of sol-gel coated dental implants. J Mater Sci-Mater M. 2003;14:539–45.
Faeda RS, Tavares HS, Sartori R, Guastaldi AC, Marcantonio E. Biological performance of chemical hydroxyapatite coating associated with implant surface modification by laser beam: biomechanical study in rabbit tibias. J Oral Maxil Surg. 2009;67:1706–15.
Acknowledgments
This research was supported by WCU (World Class University) project through National Research Foundation of Korea funded by the Ministry of Education, Science and Technology (R31-2008-000-10075-0) and by the Fundamental R&D Program for Core Technology of Materials funded by the Ministry of Knowledge Economy, Republic of Korea.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jo, JH., Kang, BG., Shin, KS. et al. Hydroxyapatite coating on magnesium with MgF2 interlayer for enhanced corrosion resistance and biocompatibility. J Mater Sci: Mater Med 22, 2437–2447 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10856-011-4431-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10856-011-4431-3