Abstract
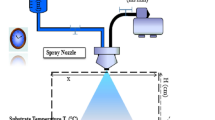
In the current study, CuO–ZnO coupled oxide thin films were deposited on glass substrates using the spray pyrolysis technique at different substrate temperatures of 250 °C, 300 °C, and 350 °C. The physical properties of the new CuO–ZnO nanocomposite material were investigated using various techniques, including X-ray diffraction analysis, Micro-Raman spectroscopy, Fourier-transform infrared spectroscopy, scanning electron microscopy, energy-dispersive X-ray analysis, UV–VIS–NIR spectrophotometry, photoluminescence spectra, and impedance spectroscopy. To incorporate new sensitive materials, the sensor response to ozone (O3) gas was measured at 100 ppb to assess air quality (poor or good) under different biasing voltages and temperatures. The gas sensor exhibited an acceptable response with high response and recovery times. The optimal working conditions were determined to be 260 °C and 0.5 V. The gas-sensing mechanism was also investigated in detail. Additionally, the CuO–ZnO coupled oxide demonstrated higher photocatalytic activity for the degradation of Methylene Blue. The photocatalytic activity and gas-sensing mechanisms were also investigated in detail.














Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The data and materials of this study are available from the corresponding author, HAJJI MOEZ on reasonable request.
References
G. Chatterjee, S. Chatterjee et al., Graphene-metal oxide nanohybrids for toxic gas sensor: a review. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 221, 1170–1181 (2015)
D. Zappa, V. Galstyanl et al., Metal oxide-based heterostructures for gas sensors—a review. Anal. Chim. Acta 1039, 1–23 (2018)
K. Krishna, S. Parnl et al., Nanostructured metal oxide semiconductor-based gas sensors: a comprehensive review. Sens. Actuators A: Phys. 341, 113587 (2022)
J. Cole, S. Sul et al., Radiolytic yield of ozone in air for low dose neutron and X-ray/gamma-ray radiation. Radiat. Phys. Chem. 106, 95–98 (2015)
D. Robert, C. Averyl et al., Ozone Gas: scientific justification and practical guidelines for improvised disinfection using consumer-grade ozone generators and plastic storage boxes. J. Sci. Med. (2020). https://doi.org/10.37714/JOSAM.V2I1.35
F. Panebianco, S. Rubiolal et al., The use of ozone as an eco-friendly strategy against microbial biofilm in dairy manufacturing plants: a review. Microorganism 10, 162 (2022)
R. Babaee, R. Osboo et al., Evaluation of the use of Ozone, UV-C and Citric acid in reducing aflatoxins in pistachio nut. J. Food Compos. Anal. 106, 104276 (2022)
T. Wu, Z. Lil et al., Advances in understanding mechanisms underlying mitochondrial structure and function damage by ozone. Sci. Total Environ. 861, 160598 (2023)
J. Petruci, D. Barretol et al., Analytical methods applied for ozone gas detection: a review. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 149, 116254 (2022)
N. Mohammed, A. Ramli, Ozone phytotoxicity evaluation and prediction of crops production in tropical region. Atmos. Environ. 68, 343 (2012)
N. Amin, Effect of ozone on the relative yield of rice crop in japan evaluated based on monitored concentrations. Water Air Soil Pollut. 225, 1–9 (2014)
Y. Wang, B. Hu, Characteristics of ozone and its precursors in northern china: a comparative study of three sites. Atmos. Res. 132, 450 (2013)
E. Epelle, A. Macfarlanel et al., Ozone application in different industries: a review of recent developments. Chem. Eng. J. 454, 140188 (2023)
G. Korotcenkov, V. Brinzaril et al., In2O3- and SnO2-based ozone sensors: design and characterization. Crit. Rev. Solid State Mater. Sci. 43, 83 (2017)
G. Lei, C. Lou, Thin films of tungsten oxide materials for advanced gas sensors. Sens. Actuators B: Chem. 341, 12996 (2022)
B.C. Sertel, N.A. Sonmez, Development of MgO:TiO2 thin films for gas sensor applications. Ceram. Int. 45, 2917–2921 (2019)
S. Kim, H. Kiml et al., High-performance, transparent thin film hydrogen gas sensor using 2D electron gas at interface of oxide thin film heterostructure grown by atomic layer deposition. Adv. Funct. Mater. (2018). https://doi.org/10.1002/adfm.201807760
M. Wu, Recent progress in chemical gas sensors based on organic thin film transistors. J. Mater. Chem. C (2020). https://doi.org/10.1039/D0TC03132A
L. Liua, T. Lib, Conductometric ozone sensor based on mesoporous ultrafine Co3O4 nanobricks. Sens. Actuators B: Chem. 297, 126815 (2019)
S.S. Shendage, L.P. Vithoba, Characterization and gas sensing properties of spin coated WO3 thin films. Zeitschrift für Physikalische Chemie 234, 1819 (2018)
N. Sui, P. Zhang, Selective ppb-level ozone gas sensor based on hierarchical branch-like In2O3 nanostructure. Sens. Actuators B: Chem. 336, 129612 (2021)
W.A. dos Santos Silva, B.S. de Lima, Enhancement of the ozone-sensing properties of ZnO through chemical-etched surface texturing. J. Nanopart. Res. (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11051-022-05479-3
M.A.M. Akhir, S.A. Rezan, Synthesis of SnO2 nanoparticles via hydrothermal method and their gas sensing applications for ethylene detection. Mater. Today Proc. 17, 810–819 (2019)
A. Mejda, N.T. Kamoun, Structural and optoelectronic studies of CuO, In2−xAlxS3 and SnO2: F sprayed thin films for solar cell application: Au/CuO (p)/In2−xAlxS3 (n)/SnO2: F. Optik 229, 166222 (2021)
A. Bougharouat et al., Hydrophobic properties of cuo thin films obtained by sol–gel spin coating technique-annealing temperature effect. ACSM 45, 439 (2021)
J. Lillo-Ramiro et al., Optical and microstructural characteristics of CuO thin films by sol gel process and introducing in non-enzymatic glucose biosensor applications. Optik 229, 166238 (2021)
A. Djelloul, M.S. Aida, J. Bougdira, Photoluminescence, FTIR and X-ray diffraction studies on undoped and Al-doped ZnO thin films grown on polycrystalline α-alumina substrates by ultrasonic spray pyrolysis. J. Lumin. 130(11), 2113–2117 (2010)
Z.R. Khan et al., Optical and structural properties of ZnO thin films fabricated by sol–gel method. Mater. Sci. Appl. 2(5), 340–345 (2011)
D. Upadhaya, D.D. Purkayastha, Self-cleaning activity of CuO/ZnO heterostructure: a synergy of photocatalysis and hydrophilicity. J. Taiwan Inst. Chem. Eng. 132, 104216 (2022)
K. Mageshwari, R. Sathyamoorthy, Physical properties of nanocrystalline CuO thin films prepared by the SILAR method. Mater. Sci. Semicond. Process. 16(2), 337–343 (2013)
R. Shabu et al., Assessment of CuO thin films for its suitablity as window absorbing layer in solar cell fabrications. Mater. Res. Bull. 68, 1–8 (2015)
S.B. Yahia et al., Raman study of oriented ZnO thin films deposited by sol–gel method. Spectrochim. Acta Part A: Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 71(4), 1234–1238 (2008)
M. Koyano et al., Photoluminescence and Raman spectra of ZnO thin films by charged liquid cluster beam technique. Phys. Status Solidi 193(1), 125–131 (2002)
C. Bundesmann et al., Raman scattering in ZnO thin films doped with Fe, Sb, Al, Ga, and Li. Appl. Phys. Lett. 83(10), 1974–1976 (2003)
B.A. Anandh et al., Structural, morphological and optical properties of aluminium doped ZnO thin film by dip-coating method. Orient. J. Chem. 34(3), 1619–1624 (2018)
D.P. Dubal et al., Surfactant-assisted morphological tuning of hierarchical CuO thin films for electrochemical supercapacitors. Dalton Trans. 42(18), 6459–6467 (2013)
M. Abdel-Wahab, A.R. Wassel, A.H. Hammad, Characterization of CuZnO nanocomposite thin films prepared from CuO–ZnO sputtered films. J. Electron. Mater. 49(12), 7179–7186 (2020)
M. Hajji et al., Photocatalytic performance and solar cell applications of coupled semiconductor CuO–ZnO sprayed thin films: coupling effect between oxides. Opt. Mater. 140, 113798 (2023)
N.M. Shah et al., Structural, electrical, and optical properties of copper indium diselenide thin film prepared by thermal evaporation method. Thin Solid Films 517(13), 3639–3644 (2009)
G.H. Yue et al., Structure and optical properties of SnS thin film prepared by pulse electrodeposition. J. Alloys Compd. 468(1–2), 254–257 (2009)
A.S. Hassanien, A.A. Akl, Effect of Se addition on optical and electrical properties of chalcogenide CdSSe thin films. Superlattices Microstruct. 89, 153–169 (2016)
M. Ajili, M. Castagné, N.K. Turki, Study on the doping effect of Sn-doped ZnO thin films. Superlattices Microstruct. 53, 213–222 (2013)
K. Mubeen et al., Band structure tuning of ZnO/CuO composites for enhanced photocatalytic activity. J. Saudi Chem. Soc. 27(3), 101639 (2023)
C. Li et al., Tetragonal multil ayered ZnO/CuO composites derived from Zn-and Cu-containing metal-organic framework: effect of calcination temperature on physicochemical properties and photocatalytic activity. Ceram. Int. 48(13), 18460–18467 (2022)
X. Liu et al., Sensitive room temperature photoluminescence-based sensing of H2S with novel CuO–ZnO nanorods. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 8(25), 16379–16385 (2016)
L. Zhu, W. Zeng, Room-temperature gas sensing of ZnO-based gas sensor: a review. Sens. Actuators, A Phys. 267, 242–261 (2017)
M. Akbari-Saatlu et al., Silicon nanowires for gas sensing: a review. Nanomaterials 10(11), 2215 (2020)
S.-J. Jung, H. Yanagida, The characterization of a CuO/ZnO heterocontact-type gas sensor having selectivity for CO gas. Sens. Actuators, B Chem. 37(1–2), 55–60 (1996)
M. Poloju, N. Jayababu, M.V. Ramana, Reddy., Improved gas sensing performance of Al doped ZnO/CuO nanocomposite based ammonia gas sensor. Mater. Sci. Eng.: B 227, 61–67 (2018)
A. Bejaoui et al., Theoretical and experimental study of the response of CuO gas sensor under ozone. Sens. Actuators, B Chem. 190, 8–15 (2014)
A. Paralikis et al., Study on the ozone gas sensing properties of rf-sputtered Al-doped NiO films. Appl. Sci. 11(7), 3104 (2021)
V.R. Mastelaro et al., Ozone gas sensor based on nanocrystalline SrTi1−xFexO3 thin films. Sens. Actuators B: Chem. 181, 919–924 (2013)
A.A. Al-Ghamdi et al., RF sputtered CuO thin films: structural, optical and photo-catalytic behavior. Phys. E: Low-Dimens. Syst. Nanostruct. 81, 83–90 (2016)
S. Das, V.C. Srivastava, An overview of the synthesis of CuO–ZnO nanocomposite for environmental and other applications. Nanotechnol. Rev. 7(3), 267–282 (2018)
Funding
The authors have not disclosed any funding.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All authors contributed to the study conception and design. Material preparation, data collection and analysis were performed by HM, SD, MA, NJ, AGL and NK. The first draft of the manuscript was written by MH and all authors commented on previous versions of the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors have no relevant financial or non-financial interests to disclose.
Ethical approval
The authors agree with Compliance with Ethical Standards of Journal of Materials Science: Materials in Electronics. The authors declare that this article is conforming to ethical standards and does not contain any studies with human or animal subjects.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Hajji, M., Dabbabi, S., Ajili, M. et al. Investigations on physical properties of CuO–ZnO couple oxide sprayed thin films for environmental applications (ozone gas sensing and MB degradation). J Mater Sci: Mater Electron 35, 663 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-024-12427-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-024-12427-5