Abstract
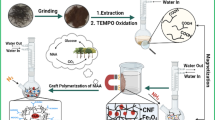
Developing a green adsorbent to deal with Congo red dyes from wastewater was a significative exploration. In the work, we prepared an ionic liquid modified magnetic cellulose/sepiolite composite FSCS-cl-p(MBA-co-BVI) via a simple method, the process including the magnetic sepiolite/cellulose complex grafting the polymer of MBA and BVI. The high specific surface area of sepiolite and cellulose, the electropositivity of ionic liquids [Bvim][Br] and magnetic response of Fe3O4@SiO2 nanoparticles jointly promoted the adsorption performance of adsorbents. The composites were characterized by SEM, XRD, EDS, FTIR, BET, TGA and VSM, the adsorption performances were evaluated containing the influence factors, adsorption kinetics, isotherm and thermodynamics. In brief, the adsorbents were suitable within the pH range of 3–9 and reach adsorption equilibrium during 120 min. Meanwhile, the maximum adsorption capacity for CR was up to 1374.10 mg/g at 45 ℃. Furthermore, the adsorption kinetics and isotherm models were well-fitted to pseudo-second-order model and Langmuir isotherm model, respectively. The adsorption mechanisms of FSCS-cl-p(MBA-co-BVI) for CR could be interpreted as electrostatic attraction, hydrogen bonding and π-π stacking interaction. Based on results, the as-obtained adsorbents were effective, inexpensive and expected to be applied to the treatment of dyestuff.














Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The data supporting this study are available from the corresponding author upon reasonable request.
References
A.A. Ramírez-Ortega, M.M. -Llamas, R.J. Da Silva et al., Synthesis of a maghemite-polypyrene nanocomposite for the removal of Congo red dye from aqueous solutions. Environ. Nanatechnol. Monit. Manage. 16, 100597 (2021)
R. Ozola-Davidane, J. Burlakovs, T. Tamm et al., Bentonite-ionic liquid composites for Congo red removal from aqueous solutions. J. Mol. Liq. 337, 116373 (2021)
M. Das, P.G. Ray, S. Dhara, S. Roy, Symbiotically augmented removal of Congo red by polyaniline/cobalt sulfide/graphite composites. Mater. Chem. Phys. 278, 125487 (2022)
K. Alsamhary, N.M. Al-Enazi, E. Alhomaidi, S. Alwakeel, Spirulina platensis mediated biosynthesis of CuO NPs and photocatalytic degradation of toxic azo dye Congo red and kinetic studies. Environ. Res. 207, 112–172 (2022)
J. Dutta, N. Devi, Preparation, optimization, and characterization of chitosan-sepiolite nanocomposite films for wound healing. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 186, 244–254 (2021)
X. Hu, X. Feng, M. Fei et al., Preparation of Acid Red73 adsorbed on chitosan-modified sepiolite with SiO2 coating as a highly stable hybrid pigment. Dyes Pigm. 185, 108938 (2021)
F. Largo, R. Haounati, S. Akhouairi et al., Adsorptive removal of both cationic and anionic dyes by using sepiolite clay mineral as adsorbent: experimental and molecular dynamic simulation studies. J. Mol. Liq. 318, 114247 (2020)
Y. Pang, Z. Yu, L. Chen, H. Chen, Superhydrophobic polyurethane sponges modified by sepiolite for efficient oil-water separation. Colloids Surf, a 627, 127175 (2021)
D. Killeen, M. Frydrych, B. Chen, Porous poly(vinyl alcohol)/sepiolite bone scaffolds: preparation, structure and mechanical properties. Mater. Sci. Eng.: C 32, 749–757 (2012)
W. Jiang, Y. Han, Y. Jiang et al., Preparation and electrochemical properties of sepiolite supported Co3O4 nanoparticles. Appl. Clay Sci. 203, 106020 (2021)
M. Frydrych, C. Wan, R. Stengler, K.U. O’Kelly, B. Chen, Structure and mechanical properties of gelatin/sepiolite nanocomposite foams. J. Mater. Chem. 21, 9103 (2011)
R.R. Palem, K.M. Rao, G. Shimoga et al., Physicochemical characterization, drug release, and biocompatibility evaluation of carboxymethyl cellulose-based hydrogels reinforced with sepiolite nanoclay. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 178, 464–476 (2021)
C. Feng, P. Ren, M. Huo et al., Facile synthesis of trimethylammonium grafted cellulose foams with high capacity for selective adsorption of anionic dyes from water. Carbohydr. Polym. 241, 116369 (2020)
X. Jiang, S. Wang, L. Ge et al., Development of organic–inorganic hybrid beads from sepiolite and cellulose for effective adsorption of malachite green. RSC Adv 7, 38965–38972 (2017)
A. Sanguanwong, A.E. Flood, M. Ogawa et al., Hydrophobic composite foams based on nanocellulose-sepiolite for oil sorption applications. J. Hazard Mater. 417, 126068 (2021)
J. Lin, T. Su, J. Chen et al., Efficient adsorption removal of anionic dyes by an imidazolium-based mesoporous poly(ionic liquid) including the continuous column adsorption-desorption process. Chemosphere 272, 129640 (2021)
A. Ayati, S. Ranjbari, B. Tanhaei, M. Sillanpää, Ionic liquid-modified composites for the adsorptive removal of emerging water contaminants: a review. J. Mol. Liq. 275, 71–83 (2019)
G. Zhu, G. Cheng, T. Lu et al., An ionic liquid functionalized polymer for simultaneous removal of four phenolic pollutants in real environmental samples. J. Hazard Mater. 373, 347–358 (2019)
Y. Jiang, F. Li, G. Ding et al., Synthesis of a novel ionic liquid modified copolymer hydrogel and its rapid removal of cr (VI) from aqueous solution. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 455, 125–133 (2015)
X. Peng, Z. Yan, L. Hu et al., Adsorption behavior of hexavalent chromium in aqueous solution by polyvinylimidazole modified cellulose. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 155, 1184–1193 (2020)
X. Peng, L. Chen, S. Liu et al., Insights into the interfacial interaction mechanisms of p-arsanilic acid adsorption on ionic liquid modified porous cellulose. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 9, 105225 (2021)
S. Jana, J. Ray, B. Mondal, S.S. Pradhan, T. Tripathy, pH responsive adsorption/desorption studies of organic dyes from their aqueous solutions by katira gum-cl-poly(acrylic acid-co-N-vinyl imidazole) hydrogel. Colloids Surf, a 553, 472–486 (2018)
R. Zhao, T. Han, D. Sun et al., Poly(ionic liquid)-Modified magnetic Janus particles for dye degradation. Langmuir 35, 11435–11442 (2019)
J. Ding, C. Zhou, Z. Wu et al., Core-shell magnetic nanomaterial grafted spongy-structured poly (ionic liquid): a recyclable brönsted acid catalyst for biodiesel production. Appl. Catal. A 616, 118080 (2021)
M. Maruthupandy, T. Muneeswaran, T. Vennila et al., Development of chitosan decorated Fe3O4 nanospheres for potential enhancement of photocatalytic degradation of Congo red dye molecules. Spectrochim. Acta A Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 267, 120511 (2022)
D. Liu, Y. Dai, S. Wang et al., Facile synthesis of layered core-shell structure Fe3O4 magnetic composites and its application for the Co2+ removal. J. Mol. Liq. 325, 114–517 (2021)
M.M. González del Campo, M. Darder, P. Aranda et al., Functional hybrid nanopaper by assembling nanofibers of cellulose and sepiolite. Adv. Funct. Mater. 28, 1703048 (2018)
M.M. González, del B. Campo, M. Caja-Munoz, Darder et al., Ultrasound-assisted preparation of nanocomposites based on fibrous clay minerals and nanocellulose from microcrystalline cellulose. Appl. Clay Sci. 189, 105538 (2020)
H.R. Yang, S.S. Li, Q.D. An et al., Facile transformation of carboxymethyl cellulose beads into hollow composites for dye adsorption. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 190, 919–926 (2021)
H. Geng, Preparation and characterization of cellulose/N,N’-methylene bisacrylamide/graphene oxide hybrid hydrogels and aerogels. Carbohydr. Polym. 196, 289–298 (2018)
G. Su, L. Liu, Q. Kuang et al., Enhanced visible-light photocatalytic activity and recyclability of magnetic core-shell Fe3O4@SiO2@BiFeO3–sepiolite microspheres for organic pollutants degradation. J. Mol. Liq. 335, 116566 (2021)
R. Nayebi, G. Daneshvar Tarigh, F. Shemirani, Porous ionic liquid polymer: a reusable adsorbent with broad operating pH range for speciation of nitrate and nitrite. Sci. Rep. 9, 11130 (2019)
G. Su, L. Liu, X. Liu, L. Zhang, J. Xue, A. Tang, Magnetic Fe3O4@SiO2@BiFeO3/rGO composite for the enhanced visible-light catalytic degradation activity of organic pollutants. Ceram. Int. 47, 5374–5538 (2021)
Y.Z. Dong, W.J. Han, H.J. Choi, Additive effect of rod-like magnetite/sepiolite composite particles on magnetorheology. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 93, 210–215 (2021)
L. Chen, Y. Dai, Q. Lu et al., Novel high-efficiency adsorbent consisting of magnetic cellulose-based ionic liquid for removal of anionic dyes. J. Mol. Liq. 353, 118723 (2022)
Y. Wu, Z. Jia, C. Bo, X. Dai, Preparation of magnetic β-cyclodextrin ionic liquid composite material with different ionic liquid functional group substitution contents and evaluation of adsorption performance for anionic dyes. Colloids Surf, a 614, 126147 (2021)
H. Gan, G. Zhang, Y. Zhang, Y. Guo, Adsorption of rhodamine B from aqueous solution onto sepiolite modified by cetyltrimethylammonium bromide. Desalin. Water Treat. 45, 112–119 (2012)
Acknowledgements
The authors greatly acknowledge the financial support provided by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (52106002), the Hunan Provincial Natural Science Foundation of China (2019JJ40310), Changsha City Key Research and Development Program Project (kq2004064), Research Fund of Science and Technology Innovation Platform of Key Laboratory of Dongting Lake Aquatic Eco-Environmental Control and Restoration of Hunan Province (2020DT008).
Funding
This work was supported by National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant Number: 52106002), the Hunan Provincial Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant Number: 2019JJ40310) and Changsha City Key Research and Development Program Project (Grant Number: kq2004064)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
LY - Methodology, software, investigation, formal analysis, writing—original draft, data curation, visualization. CL - Conceptualization, formal analysis, data curation, writing—original draft, validation. DY - Conceptualization, funding acquisition, resources, supervision, writing—review & editing, supervision. LQ - Visualization. FC - Visualization, formal analysis. WZ - Supervision. CL - Supervision. LB - Supervision. ZYF - Resources, supervision, writing—review & editing. LY - Resources, supervision, writing—review & editing. WL - Resources, supervision, writing—review & editing.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest. This article does not contain any studies with human participants or animals performed by any of the authors. Informed consent was obtained from all individual participants included in the study.
Ethical approval
The authors declare that there are no ethics problems.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Yaqi, L., Ling, C., Yimin, D. et al. Fabrication of ionic liquids-based magnetite-cellulose-sepiolite nanocomposite for the removal of Congo red. J Mater Sci: Mater Electron 35, 215 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-024-11961-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-024-11961-6