Abstract
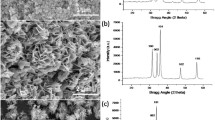
Iron oxide nanorods (NRs) possess excellent optoelectronic properties leading to potential UV photodetection and other sensing applications. A wet-chemical synthesis method was carried out to synthesize iron oxide NRs, which were then investigated for their physical and chemical properties. X-ray Diffraction (XRD) confirmed the formation of γ-FeOOH/γ-Fe2O3/α-FeOOH mixed phases of iron oxide. Transmission electron Microscope (TEM) analysis confirmed an average NR length of ∼ 62 ± 23 nm and average diameter of ∼ 10 ± 3 nm. Magnetic Force Microscopic (MFM) studies confirm the magnetic nature of the sample with magnetization degree of ∼ 76 ± 22°. The bandgap of the as-synthesized NRs was estimated to be 2.06 eV by Ultraviolet-visible (UV) spectroscopy. A thin film of the as-synthesized samples was cast on the screen-printed electrodes for measuring the photocurrent in dark and UV illumination at 365 nm wavelength. The NRs exhibited a quick UV photoresponse and recovery times of ∼ 8 ± 3 s at the minimal applied bias of 0.5 V. The synthesis resulted in iron oxide nanorods with impressive response and recovery times. As compared to existing literature reports, this is the first time undoped and multi-phase oxides of iron have been used for UV photodetection application.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
B.R. Tak, V. Gupta, A.K. Kapoor, Y.-H. Chu, R. Singh, ACS Appl. Electron. Mater. 1, 2463 (2019)
Y.-L. Chu, S.-J. Young, L.-W. Ji, I.-T. Tang, T.-T. Chu, Sensors. 20, 3861 (2020)
K. Suganthi, S. Rani, J. Mater. Res. 38, 1919 (2023)
H. Bae, A. Charnas, X. Sun, J. Noh, M. Si, W. Chung, G. Qiu, X. Lyu, S. Alghamdi, H. Wang, ACS Omega. 4, 20756 (2019)
B.R. Tak, S. Kumar, D. Wang, X. Li, H. Sun, R. Singh, J. Phys. D: Appl. Phys. 54, 453002 (2021)
Y. El Mendili, J.-F. Bardeau, N. Randrianantoandro, J.-M. Greneche, F. Grasset, Sci. Technol. Adv. Mater. 17, 597 (2016)
J.C. Souza, R.A. Ribeiro, L. c., G. da Trindade, R.C. Oliveira, L.D. Costa, M.C. de Oliveira, S.R. De Lazaro, J.R. Sambrano, C.R. Mendonça, L. De Boni, ACS Omega. 6, 28049 (2021)
S. Sakurai, K. Tomita, K. Hashimoto, H. Yashiro, S.-. Ohkoshi, J. Phys. Chem. C 112, 20212 (2008)
N.M.S. Kaawash, D.I. Halge, V.N. Narwade, P.S. Alegaonkar, K.A. Bogle, Mater. Chem. Phys. 300, 127546 (2023)
R.M. Cornell, U. Schwertmann, The iron oxides (Wiley, Hoboken, 1996)
S. Liu, J. Wu, P. Yu, Q. Ding, Z. Zhou, H. Li, C.-. Lai, Y.-L. Chueh, Z.M. Wang, Nanoscale Res. Lett. 9, 1 (2014)
Y.-Y. Zheng, Q. Sun, Y.-H. Duan, J. Zhai, L.-L. Zhang, J.-X. Wang, Mater. Chem. Phys. 252, 123431 (2020)
A.D. Nusseif, A.M. Abdul-Majeed, N.S. Hameed, Silicon. 14, 1817 (2022)
A.K. Mondal, S. Chen, D. Su, K. Kretschmer, H. Liu, G. Wang, J. Alloys Compd. 648, 732 (2015)
G. Liu, X. Gao, K. Wang, D. He, J. Li, Nano Res. 10, 2096 (2096)
L.P. Mona, S.P. Songca, P.A. Ajibade, Nanatechnol. Rev. 11, 176 (2021)
J. Liu, Z. Wu, Q. Tian, W. Wu, X. Xiao, Cryst. Eng. Comm. 18, 6303 (2016)
J. Qin, M. Liu, Z. Wang, L. Pei, M. Zhao, Q. Zhou, B. Wu, R. Liu, Mater. Res. Express. 9, 075005 (2022)
D. Kumar, H. Singh, S. Jouen, B. Hannoyer, S. Banerjee, RSC Adv. 5, 7138 (2015)
W.H. Eisa, N. Okasha, J. Sci. Res. Sci. 37, 73 (2020)
C. Chircov, B. Vasile, IntechOpen (2022). https://doi.org/10.5772/intechopen.101784
Z. Wei, X. Wei, S. Wang, D. He, Mater. Lett. 118, 107 (2014)
F.N. Sayed, V. Polshettiwar, Sci. Rep. 5, 9733 (2015)
A. Lassoued, B. Dkhil, A. Gadri, S. Ammar, Results Phys. 7, 3007 (2017)
S. Hei, Y. Jin, F. Zhang, Ed. A Mudhoo, Hindawi J. Chem. 2014, 546956 (2014)
E.C. Nnadozie, P.A. Ajibade, J Int. J. Electrochem. Sci. 17, 22124 (2022)
Z. Bazhan, F. Ghodsi, Mazloom, J. Mater. Sci.: Mater. Electron. 29, 11489 (2018)
J. Lewandowska, M. Staszewska, M. Kepczynski, M. Szuwarzyński, A. Łatkiewicz, Z. Olejniczak, M. Nowakowska, J. Solgel Sci. Technol. 64, 67 (2012)
Acknowledgements
The author would like to acknowledge Symbiosis Center for Research and Innovation, Symbiosis International (Deemed University) for their infrastructure and RSF SIU, for their funding support. The authors extend gratitude to the Semiconducting Oxide Materials, Nanostructured and Tailored Heterojunction Lab, Physics Dept. of Physics, IIT Madras, for facilitating UV photosensing measurements.
Funding
Authors acknowledge Symbiosis Centre for Research and Innovations (SCRI) for funding support toward the student. RN is thankful to Symbiosis International (Deemed University) for Research Support Funds (RSF). Authors would further like to acknowledge SAIF/CRNTS, IIT Bombay for providing HRTEM 200 analytical facility.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All author contributed to the study conception and design. Material preparation was performed by VEK, AM. Data collection, analysis were performed by VEK, SR and RN. The first draft of the manuscript was written by VEK and all authors commented on previous version of the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors have no relevant financial or non-financial interest to disclose.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Kalokhe, V.E., Mahajan, A., Rani, S. et al. Facile synthesis of photosensitive iron oxide nanorods and their application as UV photodetectors. J Mater Sci: Mater Electron 35, 117 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-023-11874-w
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-023-11874-w