Abstract
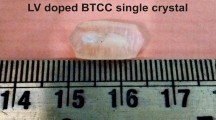
Pure and l-valine (LV)-doped bis(thiourea) cadmium chloride (BTCC) crystals have been grown by slow evaporation technique at room temperature. l-valine has been used as a dopant to tune the optical (linear and nonlinear) and electrical properties of BTCC crystal, which are vital to different optoelectronic devices such as photodiodes and solar cells. The composition of the crystals was confirmed by CHNS analysis, FTIR spectroscopy, EDAX analysis, and LIBS. The lattice parameters were determined by single-crystal XRD, by which the orthorhombic structure of BTCC and LV-doped crystals were confirmed. UV–visible spectrum analysis, photoluminescence spectroscopy, and Raman spectroscopy were used to determine the optical transparencies of the produced crystals, and it was discovered that the optical band gap increases as the l-valine doping concentration in the BTCC increases. Also, the decomposition temperature of the sample increases with an increasing percentage of l-valine, according to thermogravimetric analysis (TGA) and derivative thermogravimetric analysis (DTG). Electric properties such as dielectric constant and dielectric loss were calculated. At room temperature, the dielectric constant rises from 18.2 to 75.4 as the concentration of l-valine increases. It was also discovered that increasing the l-valine concentration resulted in considerable increases in the sample's AC conductivity and dielectric loss at room temperature. The electrochemical characteristics of the crystal were investigated using cyclic voltammetry and galvanostatic charge–discharge.























Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The data of this work will be available on reasonable request.
References
S. Chenthamarai, D. Jayaraman, C. Subramanian, P. Ramasamy, Mechanical and optical studies on pure and nitro doped 4-hydroxyacetophenone. Mater. Lett. 47(4–5), 247–251 (2001)
K. Ambujam, K. Rajarajan, S. Selvakumar, I.V. Potheher, G.P. Joseph, P. Sagayaraj, Growth and characterization of a novel NLO crystal bis-glycine hydrogen chloride (BGHC). J. Cryst. Growth 286(2), 440–444 (2006)
S.S. Hussaini, N.R. Dhumane, G. Rabbani, P. Karmuse, V.G. Dongre, M.D. Shirsat, Growth and high frequency dielectric study of pure and thiourea doped KDP crystals. Cryst. Res. Technol. J. Exp. Ind. Crystallogr. 42(11), 1110–1116 (2007)
V. Kannan, N.P. Rajesh, R.B. Ganesh, P. Ramasamy, Growth and characterization of bisthiourea–zinc acetate, a new nonlinear optical material. J. Cryst. Growth 269(2–4), 565–569 (2004)
K. Meera, R. Muralidharan, R. Dhanasekaran, P. Manyum, P. Ramasamy, Growth of nonlinear optical material: l-arginine hydrochloride and its characterisation. J. Cryst. Growth 263(1–4), 510–516 (2004)
R. Sankar, C.M. Raghavan, R. Jayavel, Nucleation kinetics and growth aspects of semi organic non-linear optical bisthiourea cadmium acetate single crystals. Cryst. Res. Technol. J. Exp. Ind. Crystallogr. 41(9), 919–924 (2006)
V. Venkataramanan, S. Maheswaran, J.N. Sherwood, H.L. Bhat, Crystal growth and physical characterization of the semiorganic bis (thiourea) cadmium chloride. J. Cryst. Growth 179(3–4), 605–610 (1997)
M.H. Jiang, Q. Fang, Organic and semiorganic nonlinear optical materials. Adv. Mater. 11(13), 1147–1151 (1999)
J. Ramajothi, S. Dhanuskodi, K. Nagarajan, Crystal growth, thermal, optical and microhardness studies of tris (thiourea) zinc sulphate—a semiorganic NLO material. Cryst. Res. Technol. J. Exp. Ind. Crystallogr. 39(5), 414–420 (2004)
S. Ariponnammal, S. Radhika, R.S. Vennila, N.V. Jeya, High pressure electrical resistivity study on nonlinear single crystal zinc thioureasulphate (ZTS). Cryst. Res. Technol. J. Exp. Ind. Crystallogr. 40(8), 786–788 (2005)
M.J. Rosker, P. Cunningham, M.D. Ewbank, H.O. Marcy, F.R. Vachss, L.F. Warren et al., Salt-based approach for frequency conversion materials. Pure Appl. Opt. J. Eur. Opt. Soc. A 5(5), 667 (1996)
M. Anis, R.N. Shaikh, M.D. Shirsat, S.S. Hussaini, Investigation of optical and electrical properties of l-cysteine doped zinc thiourea chloride (ZTC) crystal for nonlinear optical (NLO) applications. Opt. Laser Technol. 60, 124–129 (2014)
M. Anis, G.G. Muley, G. Rabbani, M.D. Shirsat, S.S. Hussaini, Optical, photoconductivity, dielectric and thermal studies of l-arginine doped zinc thiourea chloride crystal for photonics applications. Mater. Technol. 30(3), 129–133 (2015)
Y. Zhang, X. Xu, Machine learning optical band gaps of doped-ZnO films. Optik 217, 164808 (2020)
Y. Zhang, X. Xu, Machine learning band gaps of doped-TiO2 photocatalysts from structural and morphological parameters. ACS Omega 5(25), 15344–15352 (2020)
Y. Zhang, X. Xu, Machine learning lattice constants for cubic perovskite A22+BB′O6 compounds. CrystEngComm 22(38), 6385–6397 (2020)
Y. Zhang, X. Xu, Machine learning lattice constants of zircon-group minerals MXO4. Struct. Chem. 32, 1311–1326 (2021)
K. Selvaraju, R. Valluvan, K. Kirubavathi, S. Kumararaman, l-cysteine hydrochloride: a novel semi-organic nonlinear optical material for optical devices. Opt. Commun. 269(1), 230–234 (2007)
S. Selvakumar, J.P. Julius, S.A. Rajasekar, A. Ramanand, P. Sagayaraj, Microhardness, FTIR and transmission spectral studies of Mg2+ and Zn2+ doped nonlinear optical BTCC single crystals. Mater. Chem. Phys. 89(2–3), 244–248 (2005)
M.I. Baig, S.S. Hussaini, H.E. Ali, M. Anis, Analyzing l-valine effect on structural, mechanical, optical and electrical traits of bis-thiourea cadmium chloride (BTCC) crystal. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron.Sci. Mater. Electron. 33(10), 8218–8225 (2022)
S. Krishnan, C.J. Raj, S. Dinakaran, S.J. Das, Investigation of optical band gap in potassium acid phthalate single crystal. Cryst. Res. Technol. J. Exp. Ind. Crystallogr. 43(6), 670–673 (2008)
S. Selvasekarapandian, K. Vivekanandan, P. Kolandaivel, T.K. Gundurao, Vibrational studies of bis (thiourea) cadmium chloride and tris (thiourea) zinc sulphate semiorganic non-linear optical crystals. Cryst. Res. Technol. 32(2), 299–309 (1997)
K.S. Cole, R.H. Cole, Dispersion and absorption in dielectrics I. Alternating current characteristics. J. Chem. Phys. 9(4), 341–351 (1941)
D.W. Davidson, R.H. Cole, Dielectric relaxation in glycerine. J. Chem. Phys. 18(10), 1417–1417 (1950)
G. Williams, D.C. Watts, Non-symmetrical dielectric relaxation behaviour arising from a simple empirical decay function. Trans. Faraday Soc. 66, 80–85 (1970)
A.K. Jonscher, The ‘universal’ dielectric response. Nature 267(5613), 673–679 (1977)
A.K. Jonscher, A new understanding of the dielectric relaxation of solids. J. Mater. Sci. 16, 2037–2060 (1981)
M. Roy, J.K. Nelson, R.K. MacCrone, L.S. Schadler, C.W. Reed, R. Keefe, Polymer nanocomposite dielectrics—the role of the interface. IEEE Trans. Dielectr. Electr. Insulation 12(4), 629–643 (2005)
A. Bhaskaran, C.M. Raghavan, R. MohanKumar, R. Jayavel, Studies on the structural, optical, dielectric and mechanical properties of non-linear optical manganese mercury tetrathiocyanate glycol mono methyl ether (MMTG) single crystal. Curr. Appl. Phys. 10(5), 1261–1266 (2010)
Acknowledgements
One of the authors acknowledges Council of Scientific and Industrial Research (CSIR), Government of India [Order No. 03 (1363)/16/EMR-II dated 11.05.2016] for funding this Research Project. One of the authors is also thankful for the support of Science Engineering Research Board (SERB), New Delhi, Government of India (YSS/2014/000649 dated 20 November 2015), for funding the project. We are grateful to STIC, Cochin University of Science and Technology for the CHNS analysis, Single XRD analysis and EDAX analysis; Dr. Alex Joseph, Department of Chemistry, Newman College Thodupuzha for the FTIR and UV–visible spectral analysis and Electrochemical workstation; Dr. A. Santhosh Kumar, Technical Officer, School of Pure and Applied Physics, MG University Kottayam for the dielectric studies; and Dr. Gijo Jose, HOD, Department of Physics, SB College Changanassery for the TGA–DTG studies.
Funding
This work was supported by Council of Scientific and Industrial Research (CSIR) Govt. of India [Order No. 03 (1363)/16/EMR-II dated 11.05.2016] by funding the research project. Also the project was supported by Science Engineering Research Board (SERB), New Delhi, Govt. of India (YSS/2014/000649 dated 20 November 2015) for funding the project. Dr. Ginson P Joseph received research support from both of the above organizations.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
BJ: Methodology, Investigation, Data Analysis, and Writing—Original Draft. GJ: Investigation and Data Curation. AG: Methodology and Validation. MKG: Formal analysis. AKT: Conceptualization and Review. NS: Validation and Data Curation. GPJ: Supervision and Writing—review and editing. The final version of the manuscript has been approved by all authors.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
All authors certify that they have no links with or involvement in any organization or entity that has a financial or nonfinancial interest in the subject matter or materials covered in this manuscript. The authors state that they have no known competing financial interests or personal ties that could have seemed to affect the work reported in this study.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
John, B., Joseph, G., G., A. et al. l-valine refines bis(thiourea) cadmium chloride single crystals for optoelectronic applications. J Mater Sci: Mater Electron 35, 135 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-023-11786-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-023-11786-9