Abstract
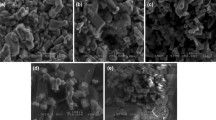
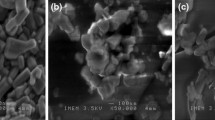
Low-temperature ZnO has been synthesized using a single-step composite hydroxide-mediated (CHM) technique. The prepared sample is characterized by X-ray diffraction (XRD) for structural confirmation, where average crystallite size is found to be around 15 nm. The obtained results are interpreted for the calculation of X-ray and dislocation densities. Field emission scanning electron microscopy (FE-SEM) results shows uniform spherical shape, narrow size distribution. Using Image J Software, an average grain and diameter sizes of 13–45 nm and 35 nm, respectively is measured. The dielectric behavior of the prepared sample reveals the high dielectric constant (ε′) > 103 at low frequency (∼100 Hz) with low dielectric loss caused due to the grain, grain boundary, and close intimate contact. The orientational and interfacial polarization of the (Zn2+-VO) dipoles boosted due to the interaction between ZnO granules; as a result, dielectric constant (ε′) increases with increasing temperature, meanwhile rise in frequency drops the dielectric loss. The improved dielectric constant due to the enhanced Maxwell–Wagner relaxation is because of the sintering technique which makes the ZnO a suitable material for high dielectric constant practical applications. This approach opens up a new horizon of exploring outstanding dielectric characteristics. The activation energy values of conductivity, 1.39 eV, 1.40 eV, and 1.68 eV, are calculated from the slope of linear regions on the SPH (Small Polaron Hopping Model) plot for the heating curve that corresponds to the total resistance, grain boundary resistance, and bulk resistance, respectively.









Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
Required data associated with submitted manuscript will be available, if required.
References
M.A. Javid, M. Rafi, I. Ali, F. Hussain, M. Imran, A. Nasir, Synthesis and study of structural properties of Sn doped ZnO nanoparticles. Mater. Sci-Pol. 34(4), 741–746 (2016)
Q. Chen, J. Shi, R. Zhao, X. Shen, Radiolytic syntheses of nanoparticles and Inorganic polymer hybrid microgels. (IAEA), IAEA-RC-11242. 46(6) (2010)
A. Moezzi, A.M. McDonagh, M.B. Cortie, Zinc oxide particles: synthesis, properties and applications. Chem. Eng. J. 185–186, 1–22 (2012)
C.C. Chen, P. Liu, C.H. Lu, Synthesis and characterization of nano-sized ZnO powders by direct precipitation method. Chem. Eng. J. 144(3), 509–513 (2008)
C. Hu, Y. Xi, H. Liu, Z.L. Wang, Composite-hydroxide-mediated approach as a general methodology for synthesizing nanostructures. J. Mater. Chem. 19(7), 858–869 (2009)
T. Shahid, M. Arfan, W. Ahmad, T. Bibi, T.M. Khan, Preparation and physical properties of functional barium carbonate nanostructures by a facile composite-hydroxide-mediated route. Nanomater. Nanotech. 8(7), 561–566 (2018)
Xu. Li, L. Lixin, Y. Wang, X. Cao, Y. Huang, C. Meng, Z. Wang, High pressure treated ZnO ceramics towards giant dielectric constants. J. Mater. Chem. A 2, 16740–16745 (2014)
T. Shahid, T.M. Khan, M. Zakria, R.I. Shakoor, M. Arfan, S. Khursheed, Synthesis of pyramid-shaped NiO nanostructures using low-temperature composite- hydroxide- mediated approach carbonate nanostructures by a facile composite-hydroxide-mediated route. J. Mater. Sci. Eng. (2016). https://doi.org/10.4172/2169-0022.1000287
O.R. Vasile, I. Serdaru, E. Andronescu, R. Truşcă, V.A. Surdu, O. Oprea, A. Ilie, B.S. Vasile, Influence of the size and the morphology of ZnO nanoparticles on cell viability. CR Chimie 18(12), 1335–1343 (2015)
Y. Kim, H.K. Kim, Application of pole figures to rietveld refinement. J. Mat. Sci. Lett. 19(140), 1251–1252 (2000)
A.S. Kermani, S. Miri, Synthesis, characterization and bactericidal property of chitosan-graft-polyaniline/ montmorillonite/ZnO nanocomposite. Korean J. Chem. Eng. 32, 1137–1141 (2015)
R. Ding, J. Liu, J. Jiang, Xi. Ji, Xi. Li., F. Wu., Xi. Huang, A, General solution synthesis route to ZnO-based nanorod arrays on ceramic/silicon/quartz glass/metal substrates. Sci. of Adv. Mat. 2(3), 396–401 (2010)
Y. Wang, W. Jie, C. Yang, X. Wei, J. Hao, Colossal permittivity materials as superior dielectrics for diverse applications. Adv. Funct. Mater. (2019). https://doi.org/10.1002/adfm.201808118
D. Chen, G.S. Wang, S. He, J. Liu, L. Guo, M.S. Cao, Controllable fabrication of mono-dispersed RGO– hematite nanocomposites and their enhanced wave absorption properties. J. Mater. Chem. A. 1, 5996 (2013)
J.J. Wu, S.C. Liu, Low-temperature growth of well-aligned ZnO nanorods by chemical vapor deposition. Adv. Mater. 14(3), 215–218 (2002)
S. Ibadat, M. Younas, S. Shahzada, M. Nadeem, T. Ali, M.J. Akhtar, S. Pollastri, U. Rehman, I. Yousef, R.T.A. Khan, Realistic dielectric response of high temperature sintered ZnO ceramic: a microscopic and spectroscopic approach. RSC Adv. 10(51), 30451–30462 (2020)
Z.M. Dang, J.K. Yuan, S.H. Yao, R.J. Liao, Flexible nano dielectric materials with high permittivity for power energy storage. Adv. Mater. (2013). https://doi.org/10.1002/adma.201301752
G. Wang, Y. Deng, L. Guo, Single-Crystalline ZnO nanowire bundles: synthesis, mechanism and their application in dielectric composites. Chem. A Eur. J. 16, 10220–10225 (2010)
A. Ray, P. Maji, A. Roy, S. Saha, P. Sadukhan, S. Das, Temperature and frequency dependent dielectric relaxation of Ni-Fe-Oxide nanocomposites. Mat. Res. Exp. 6(12), 1250h4 (2019)
J.K. Yuan, W.L. Li, S.H. Yao, Y.Q. Lin, A. Sylvester, J. Bai, High dielectric permittivity and low percolation threshold in polymer composites based on SiC-carbon nanotubes micro/nano hybrid. Appl. Phys. Lett. 98, 072912 (2011)
G.S. Wang, X.J. Zhang, Y.Z. Wei, S. He, L. Guo, M.S. Cao, Polymer composites with enhanced wave absorption properties based on modified graphite and polyvinylidene fluoride. J. Mater. Chem. A 1, 7031–7036 (2013)
F. Ahmad, A. Maqsood, Influence of nickel dopant on impedance, dielectric, and optical properties of ZnO nanoparticles at low temperatures. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Elec. 33, 12674–12700 (2022)
M. Younas, C. Xu, M. Arshad, L.P. Ho, S. Zhou, F. Azad, M.J. Akhtar, S. Su, W. Azeem, F.C. Ling, Reversible tuning of ferromagnetism and resistive switching in ZnO/Cu thin films. ACS Omega 2(12), 8810–8817 (2017)
D. Huang, W.L. Li, Z.F. Liu, Y.X. Li, C.T. That, J. Cheng, W.C.H. Choy, F.C.C. Ling, Electron-pinned defect dipoles in (Li, Al) co-doped ZnO ceramics with colossal dielectric permittivity. J. Mater. Chem. A 8, 4764–4774 (2020)
D. Chandra, N. Mukherjee, A. Mondal, A. Bhaumik, Design and synthesis of nanostructured porous SnO2 with high surface areas and their optical and dielectric properties. J. Phys. Chem. C 112(23), 8668–8674 (2008)
M. Younas, M. Nadeem, M. Idrees, M.J. Akhtar, Jahn-Teller assisted polaronic hole hopping as a charge transport mechanism in CuO nanograins. Appl. Phys. Lett. 100, 152103 (2012)
M. Nadeem, A. Farooq, T.J. Shin, Metal-insulator transition in ZnO nanopowder during thermal cycling by impedance spectroscopy. Appl. Phys. Lett. 96, 212104 (2010)
Acknowledgements
Authors acknowledge the support of Department of Physics, University of Wah, Wah Cantt, Pakistan, and Polymer Composite Group (PCG), PINSTECH Islamabad, Pakistan.
Funding
The authors declare that no funds, grants, or other support is received during the preparation of this manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
MR contributed to investigation, experimentation, and writing the original draft. GU contributed to Envision and Supervision, resources, review, and editing. MA contributed to methodology, validation, and formal analysis. RR contributed to resources and formal analysis. ZA contributed to resources and reviews validation. MN contributed to conceptualization, resources, review, and editing.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors have no relevant financial or non-financial interests to disclose.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Rafi, M., Uzma, G., Arfan, M. et al. Low-temperature composite hydroxide-mediated (CHM) novel approach toward ZnO ceramic: investigation of structural and dielectric properties. J Mater Sci: Mater Electron 34, 578 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-023-09940-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-023-09940-4