Abstract
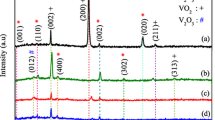
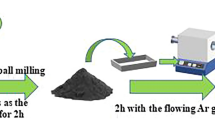
The daisy-like vanadium nitride powders were synthesized via solvothermal combined with ammonia reduction nitridation method. The results of XRD and XPS showed that the sample was mainly cubic vanadium nitride phase and also contained abundant valence states of V element. Moreover, the residual oxygen element still existed in daisy-like vanadium nitride powders due to the inadequate reduction nitriding reaction, which is positive to generate abundant defects in the samples and is conducive to impedance matching. Meanwhile, the defect-rich samples favored the interfacial polarization effect. The daisy-like structure produced a large number of interfaces and pores, which promoted conductivity loss, interface polarization, multiple reflections, and scattering of electromagnetic waves. Hence, the daisy-like vanadium nitride powders exhibit distinguished reflection loss (RL) performance with RL values of − 56.7 dB (1.38 mm) and the optimal effective absorption bandwidth (EAB) of 4.13 GHz (1.6 mm). Furthermore, the EAB covers the entire X and Ku bands by adjusting the thickness (1.3–2.5 mm).











Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
Not applicable.
Code availability
Not applicable.
References
P. Miao, R. Zhou, K. Chen, J. Liang, Q. Ban, J. Kong, Tunable electromagnetic wave absorption of supramolecular isomer-derived nanocomposites with different morphology. Adv. Mater. Interfaces. (2020). https://doi.org/10.1002/admi.201901820
B. Quan, W. Gu, J. Sheng, X. Lv, Y. Mao, L. Liu, X. Huang, Z. Tian, G. Ji, From intrinsic dielectric loss to geometry patterns: Dual-principles strategy for ultrabroad band microwave absorption. Nano Res. 14(5), 1495–1501 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12274-020-3208-8
J. Guo, X. Li, Z. Chen, J. Zhu, X. Mai, R. Wei, K. Sun, H. Liu, Y. Chen, N. Naik, Z. Guo, Magnetic NiFe2O4/polypyrrole nanocomposites with enhanced electromagnetic wave absorption. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Med. 108, 64–72 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmst.2021.08.049
I. Abdalla, A. Elhassan, J. Yu, Z. Li, B. Ding, A hybrid comprised of porous carbon nanofibers and rGO for efficient electromagnetic wave absorption. Carbon 157, 703–713 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbon.2019.11.004
J. Zhou, X. Wang, K. Ge, Z. Yang, H. Li, C. Guo, J. Wang, Q. Shan, L. Xia, Core-shell structured nanocomposites formed by silicon coated carbon nanotubes with anti-oxidation and electromagnetic wave absorption. J. Coll. Interface Sci. 607(Pt 1), 881–889 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcis.2021.09.022
T. Gao, H. Rong, K.H. Mahmoud, J. Ruan, S.M. El-Bahy, A.A. Faheim, Y. Li, M. Huang, M.A. Nassan, R. Zhao, Iron/silicon carbide composites with tunable high-frequency magnetic and dielectric properties for potential electromagnetic wave absorption. Adv. Compos. Hybrid Mater. 5(2), 1158–1167 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s42114-022-00507-1
J. Guo, Z. Chen, X. Xu, X. Li, H. Liu, S. Xi, W. Abdul, Q. Wu, P. Zhang, B.B. Xu, J. Zhu, Z. Guo, Enhanced electromagnetic wave absorption of engineered epoxy nanocomposites with the assistance of polyaniline fillers. Adv. Compos. Hybrid Mater. 5(3), 1769–1777 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s42114-022-00417-2
K. Peng, Y. Wu, C. Liu, A. Xiao, G. Xu, G. Fang, Y. Zhang, Y. Cao, Y. Zhang, Achievement of superior microwave absorption performance and ultra-wide regulation frequency range in Fe-Co-Nd via tuning the phase constitution and crystallinity. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmmm.2020.166561
P. Xu, J. Fang, H. He, X. Yue, In situ growth of globular MnO2 nanoflowers inside hierarchical porous mangosteen shells-derived carbon for efficient electromagnetic wave absorber. J. Alloys Compd. (2022). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2022.163826
R. Tang, P. Xu, J. Dong, H. Gui, T. Zhang, Y. Ding, V. Murugadoss, N. Naik, D. Pan, M. Huang, Z. Guo, Carbon foams derived from emulsion-templated porous polymeric composites for electromagnetic interference shielding. Carbon 188, 492–502 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbon.2021.12.026
B. Dai, Y. Ma, F. Dong, J. Yu, M. Ma, H.K. Thabet, S.M. El-Bahy, M.M. Ibrahim, M. Huang, I. Seok, G. Roymahapatra, N. Naik, B.B. Xu, J. Ding, T. Li, Overview of MXene and conducting polymer matrix composites for electromagnetic wave absorption. Adv. Compos. Hybrid Mater. 5(2), 704–754 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s42114-022-00510-6
R. Liu, N. Lun, Y.X. Qi, Y.J. Bai, H.L. Zhu, F.D. Han, X.L. Meng, J.Q. Bi, R.H. Fan, Microwave absorption properties of TiN nanoparticles. J. Alloys Compd. 509(41), 10032–10035 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2011.08.022
B. Zhu, Y. Cui, D. Lv, K. Xu, Y. Chen, Y. Wei, H. Wei, J. Bu, Synthesis of setaria viridis-like TiN fibers for efficient broadband electromagnetic wave absorption in the whole X and Ku bands. Appl. Surf. Sci. (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsusc.2020.147439
J. Kuang, T. Xiao, X. Hou, Q. Zheng, Q. Wang, P. Jiang, W. Cao, Microwave synthesis of worm-like SiC nanowires for thin electromagnetic wave absorbing materials. Ceram. Int. 45(9), 11660–11667 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ceramint.2019.03.040
Y. Cui, K. Xu, B. Zhu, S. Hu, Y. Chen, D. Lv, Y. Yu, J. Bu, H. Wei, B. Liang, Synthesis of niobium nitride porous nanofibers with excellent microwave absorption properties via reduction nitridation of electrospinning precursor nanofibers with ammonia gas. J. Alloys Compd. (2022). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2022.164453
P.J. Hanumantha, M.K. Datta, K. Kadakia, C. Okoli, P. Patel, P.N. Kumta, Vanadium nitride supercapacitors: Effect of Processing Parameters on electrochemical charge storage behavior. Electrochim. Acta. 207, 37–47 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.electacta.2016.04.058
Z. Hou, K. Guo, H. Li, T. Zhai, Facile synthesis and electrochemical properties of nanoflake VN for supercapacitors. CrystEngComm 18(17), 3040–3047 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1039/c6ce00333h
X. Yuan, R. Wang, S. Huang, A. Sha, S. Guo, Vanadium nitride@carbon nanowires with inner porous structure for high-efficient microwave absorption. Mater. Sci. Eng. B. (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mseb.2021.115156
X. Tong, B. Zhai, X. Gao, Multiple dielectric resonance behaviors and microwave attenuation in vanadium nitride/vanadium sesquioxide nanowires. J. Alloys Compd. (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2020.156393
X. Yuan, R. Wang, W. Huang, L. Kong, S. Guo, L. Cheng, Morphology Design of Co-electrospinning MnO-VN/C Nanofibers for Enhancing the Microwave Absorption Performances. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces. 12(11), 13208–13216 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1021/acsami.9b23310
X. Yuan, R. Wang, W. Huang, Y. Liu, L. Zhang, L. Kong, S. Guo, Lamellar vanadium nitride nanowires encapsulated in graphene for electromagnetic wave absorption. Chem. Eng. J. (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2019.122203
R. Li, C. Li, F. Zhang, Y. Cui, D. Lv, Y. Chen, Y. Wei, H. Wei, J. Bu, Synthesis and microwave absorption properties of porous vanadium nitride microspheres. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 33(21), 17306–17321 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-022-08608-9
X. Zeng, X. Cheng, R. Yu, G.D. Stucky, Electromagnetic microwave absorption theory and recent achievements in microwave absorbers. Carbon 168, 606–623 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbon.2020.07.028
W. Zhou, L. Long, P. Xiao, Y. Li, H. Luo, W.-D. Hu, R.-M. Yin, Silicon carbide nano-fibers in-situ grown on carbon fibers for enhanced microwave absorption properties. Ceram. Int. 43(7), 5628–5634 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ceramint.2017.01.095
J. Liu, Z. Zhao, L. Zhang, Toward the application of electromagnetic wave absorption by two-dimension materials. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 32(21), 25562–25576 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-020-03800-1
C. Chen, J. Xi, E. Zhou, L. Peng, Z. Chen, C. Gao, Porous graphene microflowers for high-performance microwave absorption. Nanomicro Lett. 10(2), 26 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40820-017-0179-8
B. Zhao, G. Shao, B. Fan, W. Zhao, Y. Xie, R. Zhang, Synthesis of flower-like CuS hollow microspheres based on nanoflakes self-assembly and their microwave absorption properties. J. Mater. Chem. A. 3(19), 10345–10352 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1039/c5ta00086f
X. Su, J. Ning, Y. Jia, Y. Liu, Flower-like MoS2 nanospheres: a promising material with good microwave absorption property in the frequency range of 8.2–12.4 GHz. NANO (2018). https://doi.org/10.1142/s1793292018500844
Y. Li, J. Zhang, Z. Liu, M. Liu, H. Lin, R. Che, Morphology-dominant microwave absorption enhancement and electron tomography characterization of CoO self-assembly 3D nano-flowers. J. Mater. Chem. C. (2014). https://doi.org/10.1039/c4tc00739e
B. Zhao, G. Shao, B. Fan, B. Sun, K. Guan, R. Zhang, Facile synthesis and novel microwave electromagnetic properties of flower-like Ni structures by a solvothermal method. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 25(8), 3614–3621 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-014-2064-2
Q. Zhang, X. Wang, Z. Pan, J. Sun, J. Zhao, J. Zhang, C. Zhang, L. Tang, J. Luo, B. Song, Z. Zhang, W. Lu, Q. Li, Y. Zhang, Y. Yao, Wrapping aligned carbon nanotube composite sheets around vanadium nitride nanowire arrays for asymmetric coaxial fiber-shaped supercapacitors with ultrahigh energy density. Nano Lett. 17(4), 2719–2726 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.nanolett.7b00854
A.M. Glushenkov, D. Hulicova-Jurcakova, D. Llewellyn, G.Q. Lu, Y. Chen, Structure and capacitive properties of porous nanocrystalline VN prepared by temperature-programmed ammonia reduction of V2O5. Chem. Mater. 22(3), 914–921 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1021/cm901729x
D. Zhang, J. Li, Z. Su, S. Hu, H. Li, Y. Yan, Electrospun polyporous VN nanofibers for symmetric all-solid-state supercapacitors. J. Adv. Ceram. 7(3), 246–255 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40145-018-0276-2
S. Liu, X. Meng, Z. Wang, Z. Li, K. Yang, Enhancing microwave absorption by constructing core/shell TiN@TiO2 heterostructures through post-oxidation annealing. Mater. Lett. (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matlet.2019.126677
X. Mao, Y. Bai, J. Yu, B. Ding, Insights into the flexibility of ZrMxOy (M = Na, Mg, Al) nanofibrous membranes as promising infrared stealth materials. Dalton Trans. 45(15), 6660–6666 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1039/c6dt00319b
S. Gao, Q. An, Z. Xiao, S. Zhai, Z. Shi, Significant promotion of porous architecture and magnetic Fe3O4 NPs inside honeycomb-like carbonaceous composites for enhanced microwave absorption. RSC Adv. 8(34), 19011–19023 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1039/c8ra00913a
H. Lin, B.W. Tao, Q. Li, Y.R. Li, Rapid preparation of V2O3 and VN nanocrystals by ammonolysis of the precursor VOC2O4·H2O. Adv. Mater. Res. 194–196, 660–664 (2011). https://doi.org/10.4028/www.scientific.net/AMR.194-196.660
H. Li, P. He, Y. Wang, E. Hosono, H. Zhou, High-surface vanadium oxides with large capacities for lithium-ion batteries: from hydrated aerogel to nanocrystalline VO2(B), V6O13 and V2O5. J. Mater. Chem. (2011). https://doi.org/10.1039/c1jm11523e
S. Milošević, I. Stojković, S. Kurko, J.G. Novaković, N. Cvjetićanin, The simple one-step solvothermal synthesis of nanostructurated VO2(B). Ceram. Int. 38(3), 2313–2317 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ceramint.2011.11.001
A. Pan, H.B. Wu, L. Yu, T. Zhu, X.W. Lou, Synthesis of hierarchical three-dimensional vanadium oxide microstructures as high-capacity cathode materials for lithium-ion batteries. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces. 4(8), 3874–3879 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1021/am3012593
N.A. Chernova, M. Roppolo, A.C. Dillon, M.S. Whittingham, Layered vanadium and molybdenum oxides: batteries and electrochromics. J. Mater. Chem. (2009). https://doi.org/10.1039/b819629j
B. Zhao, B. Fan, Y. Xu, G. Shao, X. Wang, W. Zhao, R. Zhang, Preparation of honeycomb SnO(2) foams and configuration-dependent microwave absorption features. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces. 7(47), 26217–26225 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1021/acsami.5b08383
X. Sun, J. He, G. Li, J. Tang, T. Wang, Y. Guo, H. Xue, Laminated magnetic graphene with enhanced electromagnetic wave absorption properties. J. Mater. Chem. C. 1(4), 765–777 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1039/c2tc00159d
D. Zhao, Z. Cui, S. Wang, J. Qin, M. Cao, VN hollow spheres assembled from porous nanosheets for high-performance lithium storage and the oxygen reduction reaction. J. Mater. Chem. A. 4(20), 7914–7923 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1039/c6ta01707j
Z. Sun, J. Zhang, L. Yin, G. Hu, R. Fang, H.M. Cheng, F. Li, Conductive porous vanadium nitride/graphene composite as chemical anchor of polysulfides for lithium-sulfur batteries. Nat. Commun. 8, 14627 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1038/ncomms14627
W. Gu, X. Cui, J. Zheng, J. Yu, Y. Zhao, G. Ji, Heterostructure design of Fe3N alloy/porous carbon nanosheet composites for efficient microwave attenuation. J. Mater. Sci. Technol. 67, 265–272 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmst.2020.06.054
J.P. Chen, H. Jia, Z. Liu, Q.Q. Kong, Z.H. Hou, L.J. Xie, G.H. Sun, S.C. Zhang, C.M. Chen, Construction of C-Si heterojunction interface in SiC whisker/reduced graphene oxide aerogels for improving microwave absorption. Carbon 164, 59–68 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbon.2020.03.049
J. Zhou, B. Wei, Z. Yao, H. Lin, R. Tan, W. Chen, X. Guo, Preparation of hollow SiC spheres with biological template and research on its wave absorption properties. J. Alloys Compd. (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2019.153021
Y. Wei, Y. Shi, X. Zhang, Z. Jiang, Y. Zhang, L. Zhang, J. Zhang, C. Gong, Electrospinning of lightweight TiN fibers with superior microwave absorption. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 30(15), 14519–14527 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-019-01823-x
S. Xie, Z. Ji, L. Zhu, J. Zhang, Y. Cao, J. Chen, R. Liu, J. Wang, Recent progress in electromagnetic wave absorption building materials. J. Alloys Compd. (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jobe.2019.100963
Z. Ren, W. Zhou, Y. Qing, S. Duan, H. Pan, Y. Zhou, Improved mechanical and microwave absorption properties of SiCf/SiC composites with SiO2 filler. Ceram. Int. 47(10), 14455–14463 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ceramint.2021.02.024
J. Cheng, H. Zhang, Y. Xiong, L. Gao, B. Wen, H. Raza, H. Wang, G. Zheng, D. Zhang, H. Zhang, Construction of multiple interfaces and dielectric/magnetic heterostructures in electromagnetic wave absorbers with enhanced absorption performance: a review. J. Materiomics. 7(6), 1233–1263 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmat.2021.02.017
Y. Huo, K. Zhao, P. Miao, J. Kong, Z. Xu, K. Wang, F. Li, Y. Tang, Microwave absorption performance of SiC/ZrC/SiZrOC hybrid nanofibers with enhanced high-temperature oxidation resistance. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 8(28), 10490–10501 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1021/acssuschemeng.0c02789
Y. Wang, J. Yang, Z. Chen, Y. Hu, A new flexible and ultralight carbon foam/Ti3C2T X MXene hybrid for high-performance electromagnetic wave absorption. RSC Adv. 9(70), 41038–41049 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1039/c9ra09817h
Y. Cheng, Y. Zhao, H. Zhao, H. Lv, X. Qi, J. Cao, G. Ji, Y. Du, Engineering morphology configurations of hierarchical flower-like MoSe2 spheres enable excellent low-frequency and selective microwave response properties. Chem. Eng. J. 372, 390–398 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2019.04.174
C. Liu, S. Liu, L. Wang, Z. Bai, Y. Huang, X. Liu, In situ fabrication of flower-like metallopolymeric superstructure on Nd2Fe14B template for enhanced microwave absorption. J. Phys. Chem. Solids. (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jpcs.2020.109755
M. Qin, D. Lan, G. Wu, X. Qiao, H. Wu, Sodium citrate assisted hydrothermal synthesis of nickel cobaltate absorbers with tunable morphology and complex dielectric parameters toward efficient electromagnetic wave absorption. Appl. Surf. Sci. (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsusc.2019.144480
M. Green, X. Chen, Recent progress of nanomaterials for microwave absorption. J. Materiomics. 5(4), 503–541 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmat.2019.07.003
H. Yang, Z. Shen, H. Peng, Z. Xiong, C. Liu, Y. Xie, 1D–3D mixed-dimensional MnO2@nanoporous carbon composites derived from Mn-metal organic framework with full-band ultra-strong microwave absorption response. Chem. Eng. J. (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2020.128087
Z. Shen, J. Chen, B. Li, G. Li, Z. Zhang, X. Hou, Recent progress in SiC nanowires as electromagnetic microwaves absorbing materials. J. Alloys Compd. (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2019.152388
Acknowledgements
The work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant Numbers 51472072) and the Hebei Natural Science Foundation (Grant Numbers E2021209120 and E2022209067).
Funding
The work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant Numbers 51472072) and the Hebei Natural Science Foundation (Grant Numbers E2021209120 and E2022209067).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
RL participated in the conceptualization, synthesis, performance testing, and writing of the original draft. FZ participated in the synthesis, performance testing, and writing, reviewing, and editing of the manuscript. CL participated in the investigation, methodology, and synthesis. JW participated in the investigation, methodology, and synthesis. YC participated in the idea and design of this research, writing of the original draft & writing, reviewing, & editing of the manuscript, investigation, synthesis, and performance testing. DL participated in the formal analysis and performance testing. YC participated in the methodology and performance testing. YW participated in the resources and formal analysis. HW participated in the investigation, synthesis, and performance testing. JB participated in the resources and formal analysis.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Research involving human participants and/or animals
This article does not contain any studies with human participants performed by any of the authors.
Informed consent
Informed consent was obtained from all individual participants included in the study.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Li, R., Zhang, F., Li, C. et al. Synthesis of daisy-like vanadium nitride powders with excellent microwave absorption properties. J Mater Sci: Mater Electron 34, 293 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-022-09727-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-022-09727-z