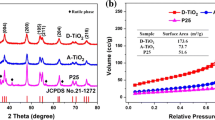
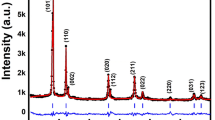
Abstract
The hydrogenation and introducing oxygen vacancies (VO) can lead to surface lattice disorder in TiO2, which is a new form of TiO2 named black TiO2, with excellent visible-light photocatalytic activity, but this TiO2 is easy to failure because oxidation makes the concentration of surface VO decrease rapidly in a short time. In this work, black TiO2 nanoparticles with VO almost concentrated inside nanoparticles were fabricated under ultrafast hydrogen flow. These bulk VO shortened the bandgaps of black TiO2, enhanced its visible light absorption, and meanwhile provided extremely strong stability. The location of VO in black TiO2 was evident from EPR, XPS with HRTEM investigation, and other characteristics of black TiO2 were obtained by XRD, UV-Vis, SEM, PL, and photocurrent techniques. The degradation experiments on Cr6+ or rhodamine B demonstrated the good visible-light photocatalytic performance of our material. After 18 months of natural aging treatment (in the air), our samples showed no discoloration and maintained 89.5% photocatalytic efficiency, and further study exhibited that this black TiO2 also contained excellent acid resistance and moderate alkaline resistance. This work could help design lattice disorder to obtain more stable and practical black TiO2.









Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
The source of the chemical, the process of the experiment, the handling of the data, etc., are transparent.
Code availability
The software application used in this work was also available on other computers.
References
A. Fujishima, K. Honda, Electrochemical photolysis of water at a semiconductor electrode. Nature 238, 37–38 (1972)
M. Altomare, M. Pozzi, M. Allieta, L.G. Bettini, E. Selli, H2 and O2 photocatalytic production on TiO2 nanotube arrays: effect of the anodization time on structural features and photoactivity. Appl. Catal. B-Environ. 136–137, 81–88 (2013)
F. Xu, Y. Le, B. Cheng, C. Jiang, Effect of calcination temperature on formaldehyde oxidation performance of Pt/TiO2 nanofiber composite at room temperature. Appl. Surf. Sci. 426, 333–341 (2017)
D.O. Scanlon, C.W. Dunnill, J. Buckeridge, S.A. Shevlin, A.J. Logsdail, S.M. Woodley, C.R.A. Catlow, M.J. Powell, R.G. Palgrave, I.P. Parkin, G.W. Watson, T.W. Keal, P. Sherwood, A. Walsh, A.A. Sokol, Band alignment of rutile and anatase TiO2. Nat. Mater. 12, 798–801 (2013)
N.K. Allam, M.A. El-Sayed, Photoelectrochemical water oxidation characteristics of anodically fabricated TiO2 nanotube arrays: structural and optical properties. J. Phys. Chem. C 114, 12024–12029 (2010)
L. Jiang, Z. Luo, Y. Li, W. Wang, J. Li, J. Li, Y. Ao, J. He, V.K. Sharma, J. Wang, Morphology- and phase-controlled synthesis of visible-light-activated S-doped TiO2 with tunable S4+/S6+ ratio. Chem. Eng. J. 402, 125549 (2020)
C.O. Amor, K. Elghniji, E. Elaloui, Improving charge separation, photocurrent and photocatalytic activities of Dy-doped TiO2 by surface modification with salicylic acid. J. Mater. Sci.: Mater. Electron. 31, 20919–20931 (2020)
X. Zheng, D. Li, X. Li, J. Chen, C. Cao, J. Fang, J. Wang, Y. He, Y. Zheng, Construction of ZnO/TiO2 photonic crystal heterostructures for enhanced photocatalytic properties. Appl. Catal. B-Environ. 168–169, 408–415 (2015)
X. Chen, L. Liu, P.Y. Yu, S.S. Mao, Increasing solar absorption for photocatalysis with black hydrogenated titanium dioxide nanocrystals. Science 331, 746–750 (2011)
N. Liu, C. Schneider, D. Freitag, M. Hartmann, U. Venkatesan, J. Müller, E. Spiecker, P. Schmuki, Black TiO2 nanotubes: cocatalyst-free open-circuit hydrogen generation. Nano Lett. 14, 3309–3313 (2014)
Z. Tian, H. Cui, G. Zhu, W. Zhao, J. Xu, F. Shao, J. He, F. Huang, Hydrogen plasma reduced black TiO2-B nanowires for enhanced photoelectrochemical water-splitting. J. Power Sources 325, 697–705 (2016)
K. Carlson, C. Elliott, S. Walker, M. Misra, S. Mohanty, An effective, point-of-use water disinfection device using immobilized black TiO2 nanotubes as an electrocatalyst. J. Electrochem. Soc. 163, H395–H401 (2016)
T. Jedsukontorn, T. Ueno, N. Saito, M. Hunsom, Facile preparation of defective black TiO2 through the solution plasma process: effect of parametric changes for plasma discharge on its structural and optical properties. J. Alloy. Compd. 726, 567–577 (2017)
Z. Wang, C. Yang, T. Lin, H. Yin, P. Chen, D. Wan, F. Xu, F. Huang, J. Lin, X. Xie, M. Jiang, Visible-light photocatalytic, solar thermal and photoelectrochemical properties of aluminium-reduced black titania. Energy Environ. Sci. 6, 3007–3014 (2013)
H. Choi, S.I. Moon, T. Song, S. Kim, Hydrogen-free defects in hydrogenated black TiO2. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 20, 19871–19876 (2018)
L.B. Mo, Y. Bai, Q.Y. Xiang, Q. Li, J.O. Wang, K. Ibrahim, J.L. Cao, Band gap engineering of TiO2 through hydrogenation. Appl. Phys. Lett. 105, 202114 (2014)
A. Naldoni, M. Allieta, S. Santangelo, M. Marelli, F. Fabbri, S. Cappelli, C.L. Bianchi, R. Psaro, V.D. Santo, Effect of nature and location of defects on bandgap narrowing in black TiO2 nanoparticles. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 134, 7600–7603 (2012)
F. Teng, M. Li, C. Gao, G. Zhang, P. Zhang, Y. Wang, L. Chen, E. Xie, Preparation of black TiO2 by hydrogen plasma assisted chemical vapor deposition and its photocatalytic activity. Appl. Catal. B-Environ. 148–149, 339–343 (2014)
S. Selcuk, X. Zhao, A. Selloni, Structural evolution of titanium dioxide during reduction in high-pressure hydrogen. Nat. Mater. 17, 923–928 (2018)
P. Deák, J. Kullgren, T. Frauenheim, Polarons and oxygen vacancies at the surface of anatase TiO2. Phys. Status Solidi-Rapid Res. Lett. 8, 583–586 (2014)
X. Yuan, X. Wang, X. Liu, H. Ge, G. Yin, C. Dong, F. Huang, Ti3+-promoted high oxygen-reduction activity of Pd nanodots supported by black titania nanobelts. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 8, 27654–27660 (2016)
R. Katal, M. Salehi, M.H.D.A. Farahani, S. Masudy-Panah, S.L. Ong, J. Hu, Preparation of a new type of black TiO2 under a vacuum atmosphere for sunlight photocatalysis. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 10, 35316–35326 (2018)
K. Lan, R. Wang, Q. Wei, Y. Wang, A. Hong, P. Feng, D. Zhao, Stable Ti3+ defects in oriented mesoporous titania frameworks for efficient photocatalysis. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 59, 17676–17683 (2020)
J. Li, M. Zhang, Z. Guan, Q. Li, C. He, J. Yang, Synergistic effect of surface and bulk single-electron-trapped oxygen vacancy of TiO2 in the photocatalytic reduction of CO2. Appl. Catal. B-Environ. 206, 300–307 (2017)
D.V. Zyabkin, H.P. Gunnlaugsson, J.N. Goncalves, K. Bharuth-Ram, B. Qi, I. Unzueta, D. Naidoo, R. Mantovan, H. Masenda, S. Ólafsson, G. Peters, J. Schell, U. Vetter, A. Dimitrova, S. Krischok, P. Schaaf, Experimental and theoretical study of electronic and hyperfine properties of hydrogenated anatase (TiO2): defect interplay and thermal stability. J. Phys. Chem. C 124, 7511–7522 (2020)
E. Ioannidou, A. Ioannidi, Z. Frontistis, M. Antonopoulou, C. Tselios, D. Tsikritzis, I. Konstantinou, S. Kennou, D.I. Kondarides, D. Mantzavinos, Correlating the properties of hydrogenated titania to reaction kinetics and mechanism for the photocatalytic degradation of bisphenol A under solar irradiation. Appl. Catal. B-Environ. 188, 65–76 (2016)
J. Mao, X. An, Z. Gu, J. Zhou, H. Liu, J. Qu, Visualizing the interfacial charge transfer between photoactive microcystis aeruginosa and hydrogenated TiO2. Environ. Sci. Technol. 54, 10323–10332 (2020)
W. Lin, H. Cheng, Q. Wu, C. Zhang, M. Arai, F. Zhao, Selective N–methylation of N–methylaniline with CO2 and H2 over TiO2–supported PdZn catalyst. ACS Catal. 10, 3285–3296 (2020)
O. Warschkow, Y. Wang, A. Subramanian, M. Asta, L.D. Marks, Structure and local-equilibrium thermodynamics of the c (2 × 2) reconstruction of rutile TiO2 (100). Phys. Rev. Lett. 100, 086102 (2008)
K.T. Park, M.H. Pan, V. Meunier, E.W. Plummer, Surface reconstructions of TiO2(110) driven by suboxides. Phys. Rev. Lett. 96, 226105 (2006)
J. Singh, A.K. Manna, R.K. Soni, Bifunctional Au–TiO2 thin films with enhanced photocatalytic activity and SERS based multiplexed detection of organic pollutant. J. Mater. Sci.: Mater. Electron. 30, 16478–16493 (2019)
Y.X. Li, X. Wang, C.C. Wang, H. Fu, Y. Liu, P. Wang, C. Zhao, S-TiO2/UiO-66-NH2 composite for boosted photocatalytic Cr (VI) reduction and bisphenol A degradation under LED visible light. J. Hazard. Mater. 399, 123085 (2020)
P. Makuła, M. Pacia, W. Macyk, How to correctly determine the band gap energy of modified semiconductor photocatalysts based on UV–Vis spectra. J. Phys. Chem. Lett. 9, 6814–6817 (2018)
M. Harb, P. Sautet, E. Nurlaela, P. Raybaud, L. Cavallo, K. Domen, J.M. Basset, K. Takanabe, Tuning the properties of visible-light-responsive tantalum (oxy)nitride photocatalysts by non-stoichiometric compositions: a first-principles viewpoint. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 16, 20548–20560 (2014)
N. Liu, H.G. Steinrück, A. Osvet, Y. Yang, P. Schmuki, Noble metal free photocatalytic H2 generation on black TiO2: on the influence of crystal facets vs. crystal damage. Appl. Phys. Lett. 110, 072102 (2017)
J. Zhang, P. Liu, Z. Lu, G. Xu, X. Wang, L. Qian, H. Wang, E. Zhang, J. Xi, Z. Ji, One-step synthesis of rutile nano-TiO2 with exposed {1 1 1} facets for high photocatalytic activity. J. Alloy. Compd. 632, 133–139 (2015)
H. Zhang, Y. Zhang, J. Yin, Z. Li, Q. Zhu, Z. Xing, In-situ N-doped mesoporous black TiO2 with enhanced visible-light-driven photocatalytic performance. Chem. Phys. 513, 86–93 (2018)
X. Chen, D. Zhao, K. Liu, C. Wang, L. Liu, B. Li, Z. Zhang, D. Shen, Laser-modified black titanium oxide nanospheres and their photocatalytic activities under visible light. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 7, 16070–16077 (2015)
H. Li, Z. Chen, C.K. Tsang, Z. Li, X. Ran, C. Lee, B. Nie, L. Zheng, T. Hung, J. Lu, B. Pan, Y.Y. Li, Electrochemical doping of anatase TiO2 in organic electrolytes for high-performance supercapacitors and photocatalysts. J. Mater. Chem. A 2, 229–236 (2014)
S. Shao, J. Yu, J.B. Love, X. Fan, An economic approach to produce iron doped TiO2 nanorods from ilmenite for photocatalytic applications. J. Alloy. Compd. 858, 158388 (2021)
M. Mondal, H. Dutta, S.K. Pradhan, Enhanced photocatalysis performance of mechano-synthesized V2O5–TiO2 nanocomposite for wastewater treatment: correlation of structure with photocatalytic performance. Mater. Chem. Phys. 248, 122947 (2020)
J. Singh, S. Juneja, R.K. Soni, J. Bhattacharya, Sunlight mediated enhanced photocatalytic activity of TiO2 nanoparticles functionalized CuO-Cu2O nanorods for removal of methylene blue and oxytetracycline hydrochloride. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 590, 60–71 (2021)
J. Singh, S. Palsaniya, R.K. Soni, Mesoporous dark brown TiO2 spheres for pollutant removal and energy storage applications. Appl. Surf. Sci. 527, 146796 (2020)
J. Singh, R.K. Soni, Two-dimensional MoS2 nanosheet-modified oxygen defect-rich TiO2 nanoparticles for light emission and photocatalytic applications. New J. Chem. 44, 14936–14946 (2020)
X. Deng, H. Zhang, R. Guo, X. Cheng, Q. Cheng, Construction of AgBr nano-cakes decorated Ti3+ self-doped TiO2 nanorods/nanosheets photoelectrode and its enhanced visible light driven photocatalytic and photoelectrochemical properties. Appl. Surf. Sci. 441, 420–428 (2018)
S. Wu, X. Li, Y. Tian, Y. Lin, Y.H. Hu, Excellent photocatalytic degradation of tetracycline over black anatase-TiO2 under visible light. Chem. Eng. J. 406, 126747 (2021)
J. Chen, Y. Fu, F. Sun, Z. Hu, X. Wang, T. Zhang, F. Zhang, X. Wu, H. Chen, G. Cheng, R. Zheng, Oxygen vacancies and phase tuning of self-supported black TiO2 – X nanotube arrays for enhanced sodium storage. Chem. Eng. J. 400, 125784 (2020)
J.P. Fitts, M.L. Machesky, D.J. Wesolowski, X. Shang, J.D. Kubicki, G.W. Flynn, T.F. Heinz, K.B. Eisenthal, Second-harmonic generation and theoretical studies of protonation at the water/α-TiO2 (110) interface. Chem. Phys. Lett. 411, 399–403 (2005)
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Nos. 61771327), NSFC (Nos. U1730138 and U1930123), Science and Technology Project of Sichuan Province (19ZDYF2180), and the Fundamental Research Funds for Central Universities.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
There is no conflict of interest or competing interests to declare that are relevant to the content of this article.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gao, J., Zhang, J., Huang, W. et al. Highly stable visible‐light photocatalytic properties of black rutile TiO2 hydrogenated in ultrafast flow. J Mater Sci: Mater Electron 32, 14665–14676 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-021-06024-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-021-06024-z