Abstract
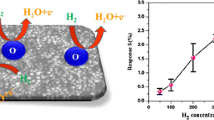
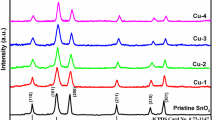
Cost-effective H2 detection sensors based on pure and CeO2 (0.5 at%, 1 at%, 1.5 at%, 2 at%, 3 at%, 4 at%)-doped SnO2 semiconductor oxides with both high moisture resistance and low operation temperature were prepared by a simple method. The crystal phase, morphology, and chemical composition of the obtained CeO2-doped SnO2 sample were analyzed and related with the sensing properties. The results show that the H2 sensing performance of pure SnO2 gas sensor can be improved a lot by CeO2 doping. In particular, gas sensors based on 2 at% CeO2/SnO2 exhibited the greatest performance: high responsiveness at 160 °C (23.7 for 50 ppm hydrogen), about 3 times higher than pure SnO2 sensor (6.9); short response and recovery time (2 and 9 s); good repeatability and long-term stability without any change after 30 days (23.7 for 50 ppm hydrogen), good selectivity, and moisture resistance. Finally, the function of CeO2 on SnO2 gas sensor for H2 detection is discussed.











Similar content being viewed by others
References
T. Abbasi, S.A. Abbasi, ‘Renewable’ hydrogen: prospects and challenges. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 15, 3034–3040 (2011)
J. Hord, Is hydrogen a safe fuel. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy. 3, 157–176 (1978)
R.G. Reddy, Fuel cell and hydrogen economy. J. Mater Eng. Perform. 15, 474–483 (2006)
X. Cheng, Z. Shi, N. Glass, L. Zhang, J.J. Zhang, D.T. Song, A review of PEM hydrogen fuel cell contamination: impacts, mechanisms, and mitigation. J. Power Sources. 165, 739–756 (2007)
K.J. Yoon, S.I. Lee, H. An, J. Kim, J.W. Son, J.H. Lee, H.J. Je, H.W. Lee, B.K. Kim, Gas-transport in hydrogen electrode of solid oxide regenerative fuel cells for power generation and hydrogen production. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy. 39, 3868–3878 (2014)
M.H. Yacob, M.Z. Ahmad, A.Z. Sadek, J.Z. Ou, J. Campbell, K. Kalantarzadeh, Optical response of WO3 nanostructured thin films sputtered on different transparent substrates towards hydrogen of low concentration. Sens. Actuators B. 177, 981–988 (2013)
X. Gao, T. Zhang, An overview: facet-dependent metal oxide semiconductor gas sensors. Sens. Actuators: B. 277, 604–633 (2018)
J.W. Shin, S.J. Choi, I.K. Lee, D.Y. Youn, C.O. Park, J.H. Lee, H.L. Tuller, I.D. Kim, Thin-wall assembled SnO2 fibers functionalized by catalytic Pt nanoparticles and their superior exhaled-breath-sensing properties for the diagnosis of diabetes. Adv. Funct. Mater. 23, 2357–2367 (2013)
L.L. Wang, T. Fei, J.N. Deng, Z. Lou, R. Wang, T. Zhang, Synthesis of rattle-type SnO2 structures with porous shells. J. Mater. Chem. 22, 18111–18114 (2012)
L.L. Wang, H.M. Dou, Z. Lou, T. Zhang, En-capsuled nano-reactors (Au@SnO2): a new sensing material for chemical sensors. Nanoscale. 5, 2686–2691 (2013)
Z.H. Jing, J.H. Zhan, Fabrication and gas-sensing properties of porous ZnO nanoplates. Adv. Mater. 20, 4547–4551 (2008)
S.H. Park, S.Y. An, H.S. Ko, C.H. Jin, C.M. Lee, Synthesis of nano-grained ZnO nanowires and their enhanced gas sensing properties. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces. 4, 3650–3656 (2012)
S.Q. Tian, F. Yang, D.W. Zeng, C.S. Xie, Solution-processed gas sensors based on ZnO nanorods array with an exposed (001) facet for enhanced gas-sensing properties. J. Phys. Chem. C. 116, 10586–10591 (2012)
J. Bai, B.X. Zhou, Titanium dioxide nanomaterials for sensor applications. Chem. Rev. 114, 10131–10176 (2014)
P.G. Hu, G.J. Du, W.J. Zhou, J.J. Cui, J.J. Lin, H. Liu, D. Liu, J.Y. Wang, S.W. Chen, Enhancement of ethanol vapor sensing of TiO2 nanobelts by surface engineering. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2, 3263–3269 (2010)
C.X. Wang, L.W. Yin, L.Y. Zhang, Y.X. Qi, N. Lun, N.N. Liu, Large scale synthesis and gas-sensing properties of anatase TiO2 three-dimensional hierarchical nanostructures. Langmuir 26, 12841–12848 (2010)
E. Rossinyol, A. Prim, E. Pellicer, J. Arbiol, F. Hernández-Ramírez, F. Peiró, A. Cornet, J.R. Morante, L.A. Solovyov, B. Tian, T. Bo, D. Zhao, Synthesis and characterization of chromium-doped mesoporous tungsten oxide for gas sensing applications. Adv. Funct. Mater. 17, 2801–2806 (2007)
S.S. Shendage, V.L. Patil, S.A. Vanalakar, S.P. Patil, N.S. Harale, J.L. Bhosale, J.H. Kim, P.S. Patil, Sensitive and selective NO2 gas sensor based on WO3 nanoplates. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 240, 426–433 (2017)
S.J. Choi, S. Chattopadhyay, J.J. Kim, S.J. Kim, H.L. Tuller, G.C. Rutledge, I.D. Kim, Coaxial electrospinning of WO3 nanotubes functionalized with bio-inspired Pd catalysts and their superior hydrogen sensing performance. Nanoscale 8, 9159–9166 (2016)
X.X. Xu, J. Zhuang, X. Wang, SnO2 quantum dots and quantum wires: controllable synthesis, self-assembled 2D architectures, and gas-sensing properties. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 130, 12527–12535 (2008)
X.G. Han, M.S. Jin, S.F. Xie, Q. Kuang, Z.Y. Jiang, Y.Q. Jiang, Z.X. Xie, L.S. Zheng, Synthesis of tin dioxide octahedral nanoparticles with exposed high-energy 221 facets and enhanced gas-sensing properties. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 48, 9180–9183 (2009)
J.Y. Liu, M.J. Dai, T.S. Wang, P. Sun, X.S. Liang, G.Y. Lu, K. Shimanoe, N. Yamazoe, Enhanced gas sensing properties of SnO2 hollow spheres decorated with CeO2 nanoparticles hetero-structure composite materials. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces. 8, 6669–6677 (2016)
J. Hu, Y.J. Sun, Y. Xue, Highly sensitive and ultra-fast gas sensor based on CeO2-loaded In2O3 hollow spheres for ppb-level hydrogen detection. Sens. Actuators B. 257, 124–135 (2018)
K. Katsuki, K. Fukui, H2 selective gas sensor based on SnO2. Sens. Actuators B 52, 30–37 (1998)
R. Huck, U. Bcttger, D. Kohl, G. Heiland, Spillover effects in the detection of H2 and CH4 by sputtered SnO2 films with Pd and PdO deposits. Sens. Actuators B 17, 355–359 (1989)
N. V. Toan, N. V. Chien, N. V. Duy, Hong. S. H, H. Nguyen, et al. Fabrication of highly sensitive and selective H2 gas sensor based on SnO2 thin film sensitized with micro-sized Pd islands. J Hazard Mater. 301, 433–442 (2016)
S.F. Bamsaoud, S.B. Rane, R.N. Karekar, R.C. Aiyer, Mater. Chem. Phys 133, 681–687 (2012)
Y.F. Luo, C. Zhang, B.B. Zheng, X. Geng, M. Debliquy, Hydrogen sensors based on noble metal doped metal-oxide semiconductor: a review. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 42, 20386–20397 (2017)
J.Y. Liu, M.J. Dai, T.S. Wang, P. Sun, X.S. Liang, G.Y. Lu, Kengo Shimanoe, and Noboru Yamazoe, enhanced gas sensing properties of SnO2 hollow spheres decorated with CeO2 nanoparticles hetero-structure composite materials. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces. 8, 6669–6677 (2016)
M. Batzill, K. Katsiev, J.M. Burst, U. Diebold, Gas-phase-dependent properties of SnO2(110), (100), and (101) single-crystal surfaces: structure, composition, and electronic properties. Phys. Rev. B. 72, 165414 (2005)
D.E. Motaung, G.H. Mhlongo, P.R. Makgwane, B.P. Dhonge, F.R. Cummings, H.C. Swart, S.S. Ray, Ultra-high sensitive and selective H2 gas sensor manifested by interface of n–n hetero-structure of CeO2-SnO2 nanoparticles. Sens. Actuators B. 254, 984–999 (2018)
Acknowledgements
This research was supported by National Key Research and Development Program of China (2017YFB0102900).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mou, H., Sun, Y., Zeng, Z. et al. Low-temperature hydrogen detection sensor based on CeO2 -DOPED SnO2. J Mater Sci: Mater Electron 31, 15785–15793 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-020-04141-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-020-04141-9