Abstract
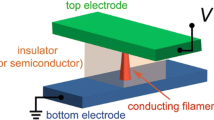
To block sneak current in a crossbar array, we propose asymmetric resistive switching device based on zinc oxide (ZnO) and magnetic iron oxide (Fe2O3) heterojunction, which has highly bendable performance with low power consumption. The ZnO/Fe2O3 heterojunction based active layer is fabricated on indium tin oxide (ITO). Polyethylene terephthalate (PET) substrate through spin coater and silver (Ag) is used as top electrode. Particularly, the active layer is protected by the magnetic force of Fe2O3 covered on ZnO, and hence, it can be bent under 1 mm diameter. The proposed memory is operated at low voltage of ± 1 V with reading voltage of ± 0.10204 V. In forward current, the fabricated device has high resistance state (HRS) of ~ 16.17 MΩ and low resistance state (LRS) of ~ 179.41 kΩ, respectively, at read voltage of + 0.10204 V, and Roff/Ron ratio is recorded as ~ 90.1. In reverse current, the HRS of ~ 15.69 MΩ and LRS of ~ 9.23 MΩ are recorded at read voltage of − 0.10204 V, and Roff/Ron ratio is ~ 1.6976, which insure that the proposed asymmetric memory device helps to reduce sneak current problem.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
J.D. Meindl, Q. Chen, J.A. Davis, Limits on silicon nanoelectronics for terascale integration. Science 293(5537), 2044 (2001)
C. Xu, D. Niu, N. Muralimanohar, R. Balasubramonian, T. Zhang, S. Yu, Y. Xie, Overcoming the challenges of crossbar resistive memory architectures, in 2015 IEEE 21st international symposium on high performance computer architecture (HPCA), 2015 7–11 Feb 2015, pp. 476–488
L. Chua, Memristor—the missing circuit element. IEEE Trans. Circuit Theor. 18(5), 507–519 (1971)
J.J. Yang, M.D. Pickett, X. Li, D.A.A. Ohlberg, D.R. Stewart, R.S. Williams, Memristive switching mechanism for metal/oxide/metal nanodevices. Nat. Nanotechnol. 3, 429 (2008)
M.U. Khan, G. Hassan, M.A. Raza, J. Bae, Bipolar resistive switching device based on N, N′-bis(3-methylphenyl)-N, N′-diphenylbenzidine and poly(3,4-ethylenedioxythiophene):poly(styrene sulfonate)/poly(vinyl alcohol) bilayer stacked structure. Appl. Phys. A 124(10), 726 (2018)
Yu-R Jeon, Y. Abbas, A.S. Sokolov, S. Kim, B. Ku, C. Choi, Study of in situ silver migration in amorphous boron nitride CBRAM device. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 11(26), 23329–23336 (2019)
Y. Abbas, S.R. Dugasani, M.T. Raza, Yu-R Jeon, S. Ha-Park, C. Choi, The observation of resistive switching characteristics using transparent and biocompatible Cu2+ -doped salmon DNA composite thin film. Nanotechnology 30(33), 335203 (2019)
S. Ali, J. Bae, K.H. Choi, C.H. Lee, Y.H. Doh, S. Shin, N.P. Kobayashi, Organic non-volatile memory cell based on resistive elements through electro-hydrodynamic technique. Org. Electron. 17, 121–128 (2015)
H.-J. Koo, J.-H. So, M.D. Dickey, O.D. Velev, Towards all-soft matter circuits: prototypes of quasi-liquid devices with memristor characteristics. Adv. Mater. 23(31), 3559–3564 (2011)
M. Cassinerio, N. Ciocchini, D. Ielmini, Logic computation in phase change materials by threshold and memory switching. Adv. Mater. 25(41), 5975–5980 (2013)
G. Hassan, M.U. Khan, J. Bae, Solution-processed flexible non-volatile resistive switching device based on poly[(9,9-di-n-octylfluorenyl-2,7-diyl)-alt-(benzo[2,1,3]thiadiazol-4, 8-diyl)]: polyvinylpyrrolidone composite and its conduction mechanism. Appl. Phys. A 125(1), 18 (2018)
G. Hassan, S. Ali, J. Bae, C.H. Lee, Flexible resistive switching device based on poly(3,4-ethylenedioxythiophene):poly(styrene sulfonate) (PEDOT:PSS)/poly(4-vinylphenol) (PVP) composite and methyl red heterojunction. Appl. Phys. A 123(4), 256 (2017)
L. Zhu, J. Zhou, Z. Guo, Z. Sun, An overview of materials issues in resistive random access memory. J. Materiomics 1(4), 285–295 (2015)
A.S. Sokolov, M. Ali, R. Riaz, Y. Abbas, M.J. Ko, C. Choi, Silver-adapted diffusive memristor based on organic nitrogen-doped graphene oxide quantum dots (N-GOQDs) for artificial biosynapse applications. Adv. Funct. Mater. 29, 1807504 (2019)
S. Shin, K. Kim, S. Kang, Memristor applications for programmable analog ICs. IEEE Trans. Nanotechnol. 10(2), 266–274 (2011)
M.A. Zidan, H.A.H. Fahmy, M.M. Hussain, K.N. Salama, Memristor-based memory: the sneak paths problem and solutions. Microelectron. J. 44(2), 176–183 (2013)
Y.W. Choi, D. Kang, P.V. Pikhitsa, T. Lee, S.M. Kim, G. Lee, D. Tahk, M. Choi, Ultra-sensitive pressure sensor based on guided straight mechanical cracks. Sci. Rep. 7, 40116 (2017)
N. Matsuhisa, M. Kaltenbrunner, T. Yokota, H. Jinno, K. Kuribara, T. Sekitani, T. Someya, Printable elastic conductors with a high conductivity for electronic textile applications. Nat. Commun. 6, 7461 (2015)
M.U. Khan, G. Hassan, M.A. Raza, J. Bae, N.P. Kobayashi, Schottky diode based resistive switching device based on ZnO/PEDOT:PSS heterojunction to reduce sneak current problem. J. Mater. Sci.: Mater. Electron. 30(5), 4607–4617 (2019)
I. Vourkas, G.C. Sirakoulis, Nano-crossbar memories comprising parallel/serial complementary memristive switches. BioNanoScience 4(2), 166–179 (2014)
Z.-J. Liu, J.-Y. Gan, T.-R. Yew, ZnO-based one diode-one resistor device structure for crossbar memory applications. Appl. Phys. Lett. 100(15), 153503 (2012)
S. Ali, J. Bae, C.H. Lee, N.P. Kobayashi, S. Shin, A. Ali, Resistive switching device with highly asymmetric current–voltage characteristics: a solution to backward sneak current in passive crossbar arrays. Nanotechnology 29(45), 455201 (2018)
J. Bae, N.P. Kobayashi, Resistive switching device with highly-asymmetric current-voltage characteristics: its error analysis and new design parameter. Semicond. Sci. Technol. 34(2), 025007 (2019)
K. Sekizawa, K. Oh-ishi, K. Kataoka, T. Arai, T.M. Suzuki, T. Morikawa, Stoichiometric water splitting using a p-type Fe2O3 based photocathode with the aid of a multi-heterojunction. J. Mater. Chem. A 5(14), 6483–6493 (2017)
K. Woo, J. Hong, S. Choi, H.-W. Lee, J.-P. Ahn, C.S. Kim, S.W. Lee, Easy synthesis and magnetic properties of iron oxide nanoparticles. Chem. Mater. 16(14), 2814–2818 (2004)
K. Dukenbayev, I. Korolkov, D. Tishkevich, A. Kozlovskiy, S. Trukhanov, Y. Gorin, E. Shumskaya, E. Kaniukov, D. Vinnik, M. Zdorovets, M. Anisovich, A. Trukhanov, D. Tosi, C. Molardi, Fe3O4 nanoparticles for complex targeted delivery and boron neutron capture therapy. Nanomaterials. 9, 494 (2019)
D.Z. Tulebayeva, A.L. Kozlovskiy, I.V. Korolkov, Y.G. Gorin, A.V. Kazantsev, L. Abylgazina, E.E. Shumskaya, E.Y. Kaniukov, M.V. Zdorovets, Modification of Fe3O4 nanoparticles with carboranes. Mater. Res. Exp. 5, 105011 (2018)
T. Seadira, G. Sadanandam, T.A. Ntho, X. Lu, C.M. Masuku, M. Scurrell, Hydrogen production from glycerol reforming: conventional and green production. Rev. Chem. Eng. 34(5), 695–726 (2018)
S.A. Jadhav, S.V. Patil, Facile synthesis of magnetic iron oxide nanoparticles and their characterization. Front. Mater. Sci. 8(2), 193–198 (2014)
J. Sun, S. Zhou, P. Hou, Y. Yang, J. Weng, X. Li, M. Li, Synthesis and characterization of biocompatible Fe3O4 nanoparticles. J. Biomed. Mater. Res., Part A 80A(2), 333–341 (2007)
M.A. Hoque, M.R. Ahmed, G.T. Rahman, M.T. Rahman, M.A. Islam, M.A. Khan, M.K. Hossain, Fabrication and comparative study of magnetic Fe and α-Fe2O3 nanoparticles dispersed hybrid polymer (PVA + Chitosan) novel nanocomposite film. Results Phys. 10, 434–443 (2018)
S.M.A. Naqvi, H. Soleimani, N. Yahya, K. Irshad, Structural and optical properties of chromium doped zinc oxide nanoparticles synthesized by sol–gel method. AIP Conf. Proc. 1621, 530–537 (2014)
M.U. Khan, G. Hassan, J. Bae, Resistive switching device based on water and zinc oxide heterojunction for soft memory applications. J. Mater. Sci. 30, 18744–18752 (2019)
G. Hassan, J. Bae, M.U. Khan, S. Ali, Resistive switching device based on water and zinc oxide heterojunction for soft memory applications. Mater. Sci. Eng. B 246, 1–6 (2019)
M.U. Khan, G. Hassan, J. Bae, Non-volatile resistive switching based on zirconium dioxide: poly (4-vinylphenol) nano-composite. Appl. Phys. A 125, 378 (2019)
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF) grant funded by the Korea government (MSIP) (NRF-2016R1A2B4015627).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Khan, M.U., Hassan, G. & Bae, J. Highly bendable asymmetric resistive switching memory based on zinc oxide and magnetic iron oxide heterojunction. J Mater Sci: Mater Electron 31, 1105–1115 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-019-02622-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-019-02622-0