Abstract
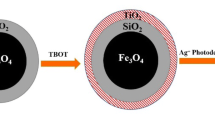
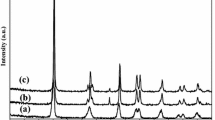
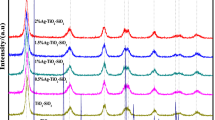
In this research, Fe3O4/SiO2/TiO2–Ag (FST–Ag) cubes were synthesized via a facile method. FST–Ag cubes have been characterized by some techniques contain field emission scanning electron microscopy (FESEM) with an energy-dispersive X-ray (EDX) spectroscopy analysis, Transmission electron microscope (TEM), X-ray diffraction (XRD), vibrating sample magnetometer (VSM). The photocatalytic degradation of phenol was examined and reaction parameters were determined for best catalyst performance. Results revealed FST–Ag cubes have been successfully synthesized with Core/Shell/shell Nano-structure. The higher surface to volume ratio of the cube shape increased photo-catalytic properties. The influence of various parameters on photo-catalytic performance, like pH, photo-catalyst dose and initial concentration of phenol were examined. Catalyst dose of 0.2 g/L was obtained as the optimum amount. The degradation efficiency of phenol was increased in acidic solution pH. The removal efficiency was decreased with increasing initial phenol concentration. So, the highest degradation efficiency of phenol with photo-catalytic UV/Fe3O4/SiO2/TiO2–Ag process was caused 98.1% degradation at initial phenol concentration of 50 mg/L, solution pH of 3 during 150 min contact time, while 90.6% degradation of phenol was achieved under UV/Fe3O4/SiO2/TiO2 without Ag particles. The FST–Ag cubes are recovered and could be re-used again.












Similar content being viewed by others
References
D. Zhang, G. Li, C.Y. Jimmy, Inorganic materials for photocatalytic water disinfection. J. Mater. Chem. 20, 4529–4536 (2010)
R.-S. Juang, W.-C. Huang, Y.-H. Hsu, Treatment of phenol in synthetic saline wastewater by solvent extraction and two-phase membrane biodegradation. J. Hazard. Mater. 164, 46–52 (2009)
Y. Li, S. Sun, M. Ma, Y. Ouyang, W. Yan, Kinetic study and model of the photocatalytic degradation of rhodamine B (RhB) by a TiO2-coated activated carbon catalyst: effects of initial RhB content, light intensity and TiO2 content in the catalyst. Chem. Eng. J. 142, 147–155 (2008)
S. Eydivand, M. Nikazar, Degradation of 1, 2-dichloroethane in simulated wastewater solution: a comprehensive study by photocatalysis using TiO2 and ZnO nanoparticles. Chem. Eng. Commun. 202, 102–111 (2015)
J. Wang, R. Li, Z. Zhang, W. Sun, Y. Xie, R. Xu, Z. Xing, X. Zhang, Solar photocatalytic degradation of dye wastewater in the presence of heat-treated anatase TiO2 powder. Environ. Prog. 27, 242–249 (2008)
Z. Zhang, X. Wang, J. Long, Z. Ding, X. Fu, X. Fu, H2–O2 promoting effect on photocatalytic degradation of organic pollutants in an aqueous solution without an external H2 supply. Appl. Catal. A 380, 178–184 (2010)
Y. Sakatani, D. Grosso, L. Nicole, C. Boissiere, G.J.A.A. de Soler-Illia, C. Sanchez, Optimised photocatalytic activity of grid-like mesoporous TiO2 films: effect of crystallinity, pore size distribution, and pore accessibility. J. Mater. Chem. 16, 77–82 (2006)
H. Liu, Z. Jia, S. Ji, Y. Zheng, M. Li, H. Yang, Synthesis of TiO2/SiO2@Fe3O4 magnetic microspheres and their properties of photocatalytic degradation dyestuff. Catal. Today 175, 293–298 (2011)
V. Polshettiwar, R. Luque, A. Fihri, H. Zhu, M. Bouhrara, J.-M. Basset, Magnetically recoverable nanocatalysts. Chem. Rev. 111, 3036–3075 (2011)
Y. Gao, B. Chen, H. Li, Y. Ma, Preparation and characterization of a magnetically separated photocatalyst and its catalytic properties. Mater. Chem. Phys. 80, 348–355 (2003)
C. Wang, L. Yin, L. Zhang, L. Kang, X. Wang, R. Gao, Magnetic (γ-Fe2O3@SiO2)n@TiO2 functional hybrid nanoparticles with actived photocatalytic ability. J. Phys. Chem. C 113, 4008–4011 (2009)
X. Huang, G. Wang, M. Yang, W. Guo, H. Gao, Synthesis of polyaniline-modified Fe3O4/SiO2/TiO2 composite microspheres and their photocatalytic application. Mater. Lett. 65, 2887–2890 (2011)
C. Adán, A. Bahamonde, M. Fernández-García, A. Martínez-Arias, Structure and activity of nanosized iron-doped anatase TiO2 catalysts for phenol photocatalytic degradation. Appl. Catal. B 72, 11–17 (2007)
M. Zhou, J. Yu, B. Cheng, Effects of Fe-doping on the photocatalytic activity of mesoporous TiO2 powders prepared by an ultrasonic method. J. Hazard. Mater. 137, 1838–1847 (2006)
T. Hirakawa, P.V. Kamat, Charge separation and catalytic activity of Ag@TiO2 core–shell composite clusters under UV–irradiation. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 127, 3928–3934 (2005)
X. He, Y. Cai, H. Zhang, C. Liang, Photocatalytic degradation of organic pollutants with Ag decorated free-standing TiO2 nanotube arrays and interface electrochemical response. J. Mater. Chem. 21, 475–480 (2011)
I. Arabatzis, T. Stergiopoulos, M. Bernard, D. Labou, S. Neophytides, P. Falaras, Silver-modified titanium dioxide thin films for efficient photodegradation of methyl orange. Appl. Catal. B 42, 187–201 (2003)
B. MirzaHedayat, M. Noorisepehr, E. Dehghanifard, A. Esrafili, R. Norozi, Evaluation of photocatalytic degradation of 2, 4-dinitrophenol from synthetic wastewater using Fe3O4@SiO2@TiO2/rGO magnetic nanoparticles. J. Mol. Liq. 264, 571–578 (2018)
Z. Dai, D. Li, L. Chi, Y. Li, B. Gao, N. Qiu, Q. Duan, Y. Li, Preparation of porphyrin sensitized three layers magnetic nanocomposite Fe3O4@SiO2@TiO2 as an efficient photocatalyst. Mater. Lett. 241, 239–242 (2019)
J. Yang, J. Wang, X. Li, D. Wang, H. Song, Synthesis of urchin-like Fe3O4@SiO2@ZnO/CdS core–shell microspheres for the repeated photocatalytic degradation of rhodamine B under visible light. Catal. Sci. Technol. 6, 4525–4534 (2016)
Y. Chi, Q. Yuan, Y. Li, L. Zhao, N. Li, X. Li, W. Yan, Magnetically separable Fe3O4@ SiO2@ TiO2–Ag microspheres with well-designed nanostructure and enhanced photocatalytic activity. J. Hazard. Mater. 262, 404–411 (2013)
F. Bavarsiha, M. Rajabi, M. Montazeri-Pour, Synthesis of SrFe12O19/SiO2/TiO2 composites with core/shell/shell nano-structure and evaluation of their photo-catalytic efficiency for degradation of methylene blue. J. Mater. Sci. 29, 1877–1887 (2018)
M. Abbas, B.P. Rao, V. Reddy, C. Kim, Fe3O4/TiO2 core/shell nanocubes: single-batch surfactantless synthesis, characterization and efficient catalysts for methylene blue degradation. Ceram. Int. 40, 11177–11186 (2014)
M. Abbas, M. Takahashi, C. Kim, Facile sonochemical synthesis of high-moment magnetite (Fe3O4) nanocube. J. Nanopart. Res. 15, 1354 (2013)
J. Su, Y. Zhang, S. Xu, S. Wang, H. Ding, S. Pan, G. Wang, G. Li, H. Zhao, Highly efficient and recyclable triple-shelled Ag@Fe3O4@SiO2@TiO2 photocatalysts for degradation of organic pollutants and reduction of hexavalent chromium ions. Nanoscale 6, 5181–5192 (2014)
B. Cui, H. Peng, H. Xia, X. Guo, H. Guo, Magnetically recoverable core–shell nanocomposites γ-Fe2O3@SiO2@TiO2–Ag with enhanced photocatalytic activity and antibacterial activity. Sep. Purif. Technol. 103, 251–257 (2013)
S. Qin, W. Cai, X. Tang, L. Yang, Sensitively monitoring photodegradation process of organic dye molecules by surface-enhanced Raman spectroscopy based on Fe3O4@SiO2@TiO2@Ag particle. Analyst 139, 5509–5515 (2014)
R. Thiruvenkatachari, S. Vigneswaran, I.S. Moon, A review on UV/TiO2 photocatalytic oxidation process (journal review). Korean J. Chem. Eng. 25, 64–72 (2008)
Q. Zhang, J. Li, X. Chou, L. Gao, Z. Hai, C. Xue, Synthesis of superparamagnetic iron oxide nanoparticles in carbon reduction method. Micro Nano Lett. 8, 598–601 (2013)
M. Ye, Q. Zhang, Y. Hu, J. Ge, Z. Lu, L. He, Z. Chen, Y. Yin, Magnetically recoverable core–shell nanocomposites with enhanced photocatalytic activity. Chem. A 16, 6243–6250 (2010)
N. Kashif, F. Ouyang, Parameters effect on heterogeneous photocatalysed degradation of phenol in aqueous dispersion of TiO2. J. Environ. Sci. 21, 527–533 (2009)
Z. Wang, L. Shen, S. Zhu, Synthesis of core-shell@@ microspheres and their application as recyclable photocatalysts. Int. J. Photoenergy (2012). https://doi.org/10.1155/2012/202519
X. Sun, F. Liu, L. Sun, Q. Wang, Y. Ding, Well-dispersed Fe3O4/SiO2 nanoparticles synthesized by a mechanical stirring and ultrasonication assisted st÷ ber method. J. Inorg. Organomet. Polym Mater. 22, 311–315 (2012)
J. Lee, M. Othman, Y. Eom, T. Lee, W. Kim, J. Kim, The effects of sonification and TiO2 deposition on the micro-characteristics of the thermally treated SiO2/TiO2 spherical core–shell particles for photo-catalysis of methyl orange. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 116, 561–568 (2008)
J.-W. Lee, K. Hong, W.-S. Kim, J. Kim, Effect of HPC concentration and ultrasonic dispersion on the morphology of titania-coated silica particles. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 11, 609–614 (2005)
H. Qi, J. Ye, N. Tao, M. Wen, Q. Chen, Synthesis of octahedral magnetite microcrystals with high crystallinity and low coercive field. J. Cryst. Growth 311, 394–398 (2009)
X. Wang, L. Wang, X. He, Y. Zhang, L. Chen, A molecularly imprinted polymer-coated nanocomposite of magnetic nanoparticles for estrone recognition. Talanta 78, 327–332 (2009)
W. Bahnemann, M. Muneer, M.M. Haque, Titanium dioxide-mediated photocatalysed degradation of few selected organic pollutants in aqueous suspensions. Catal. Today 124, 133–148 (2007)
S. Ahmed, M. Rasul, R. Brown, M. Hashib, Influence of parameters on the heterogeneous photocatalytic degradation of pesticides and phenolic contaminants in wastewater: a short review. J. Environ. Manag. 92, 311–330 (2011)
S. Hamzezadeh-Nakhjavani, O. Tavakoli, S.P. Akhlaghi, Z. Salehi, P. Esmailnejad-Ahranjani, A. Arpanaei, Efficient photocatalytic degradation of organic pollutants by magnetically recoverable nitrogen-doped TiO2 nanocomposite photocatalysts under visible light irradiation. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 22, 18859–18873 (2015)
J. Rashid, M. Barakat, Y. Ruzmanova, A. Chianese, Fe3O4/SiO2/TiO2 nanoparticles for photocatalytic degradation of 2-chlorophenol in simulated wastewater. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 22, 3149–3157 (2015)
M.M. Haque, M. Muneer, D.W. Bahnemann, Semiconductor-mediated photocatalyzed degradation of a herbicide derivative, chlorotoluron, in aqueous suspensions. Environ. Sci. Technol. 40, 4765–4770 (2006)
F. Caturla, J. Martin-Martinez, M. Molina-Sabio, F. Rodriguez-Reinoso, R. Torregrosa, Adsorption of substituted phenols on activated carbon. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 124, 528–534 (1988)
G. Busca, S. Berardinelli, C. Resini, L. Arrighi, Technologies for the removal of phenol from fluid streams: a short review of recent developments. J. Hazard. Mater. 160, 265–288 (2008)
S.-S. Hong, C.-S. Ju, C.-G. Lim, B.-H. Ahn, K.-T. Lim, G.-D. Lee, A photocatalytic degradation of phenol over TiO2 prepared by sol-gel method. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 7, 99–104 (2001)
A. Adesina, Industrial exploitation of photocatalysis: progress, perspectives and prospects. Catal. Surv. Asia 8, 265–273 (2004)
Z. Guo, R. Ma, G. Li, Degradation of phenol by nanomaterial TiO2 in wastewater. Chem. Eng. J. 119, 55–59 (2006)
J.-M. Herrmann, Heterogeneous photocatalysis: fundamentals and applications to the removal of various types of aqueous pollutants. Catal. Today 53, 115–129 (1999)
T. Velegraki, I. Poulios, M. Charalabaki, N. Kalogerakis, P. Samaras, D. Mantzavinos, Photocatalytic and sonolytic oxidation of acid orange 7 in aqueous solution. Appl. Catal. B 62, 159–168 (2006)
M.S. Nahar, K. Hasegawa, S. Kagaya, Photocatalytic degradation of phenol by visible light-responsive iron-doped TiO2 and spontaneous sedimentation of the TiO2 particles. Chemosphere 65, 1976–1982 (2006)
C.-H. Chiou, C.-Y. Wu, R.-S. Juang, Influence of operating parameters on photocatalytic degradation of phenol in UV/TiO2 process. Chem. Eng. J. 139, 322–329 (2008)
S. Lathasree, A.N. Rao, B. SivaSankar, V. Sadasivam, K. Rengaraj, Heterogeneous photocatalytic mineralisation of phenols in aqueous solutions. J. Mol. Catal. A 223, 101–105 (2004)
S.H. Borji, S. Nasseri, A.H. Mahvi, R. Nabizadeh, A.H. Javadi, Investigation of photocatalytic degradation of phenol by Fe(III)-doped TiO2 and TiO2 nanoparticles. J. Environ. Health Sci. Eng. 12, 101 (2014)
A. Sobczyński, Ł. Duczmal, W. Zmudziński, Phenol destruction by photocatalysis on TiO2: an attempt to solve the reaction mechanism. J. Mol. Catal. A 213, 225–230 (2004)
E. Sanchez, T. Lopez, Effect of the preparation method on the band gap of titania and platinum-titania sol-gel materials. Mater. Lett. 25, 271–275 (1995)
D. Dvoranova, V. Brezova, M. Mazúr, M.A. Malati, Investigations of metal-doped titanium dioxide photocatalysts. Appl. Catal. B 37, 91–105 (2002)
S. Kato, Y. Hirano, M. Iwata, T. Sano, K. Takeuchi, S. Matsuzawa, Photocatalytic degradation of gaseous sulfur compounds by silver-deposited titanium dioxide. Appl. Catal. B 57, 109–115 (2005)
Y.-C. Liang, C.-C. Wang, C.-C. Kei, Y.-C. Hsueh, W.-H. Cho, T.-P. Perng, Photocatalysis of Ag-loaded TiO2 nanotube arrays formed by atomic layer deposition. J. Phys. Chem. C 115, 9498–9502 (2011)
A. Pearson, S.K. Bhargava, V. Bansal, UV-switchable polyoxometalate sandwiched between TiO2 and metal nanoparticles for enhanced visible and solar light photococatalysis. Langmuir 27, 9245–9252 (2011)
S. Xing, Z. Zhou, Z. Ma, Y. Wu, Characterization and reactivity of Fe3O4/FeMnOx core/shell nanoparticles for methylene blue discoloration with H2O2. Appl. Catal. B 107, 386–392 (2011)
D. Greene, R. Serrano-Garcia, J. Govan, Y. Gun’ko, Synthesis characterization and photocatalytic studies of cobalt ferrite-silica-titania nanocomposites. Nanomaterials 4, 331–343 (2014)
F. Ghasemy-Piranloo, F. Bavarsiha, S. Dadashian, M. Rajabi, Synthesis of core/shell/shell Fe3O4/SiO2/ZnO nanostructure composite material with cubic magnetic cores and study of the photo-degradation ability of methylene blue. J. Aust. Ceram. Soc. (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s41779-019-00359-x
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the Biosphere Technology Company and all experiments were performed in the Environmental Laboratory of the Company.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ghasemy-Piranloo, F., Dadashian, S. & Bavarsiha, F. Fe3O4/SiO2/TiO2–Ag cubes with core/shell/shell nano-structure: synthesis, characterization and efficient photo-catalytic for phenol degradation. J Mater Sci: Mater Electron 30, 12757–12768 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-019-01641-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-019-01641-1