Abstract
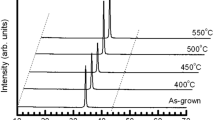
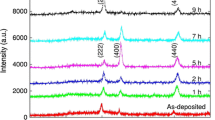
In this study, structural, morphological, optical, electrical properties and their correlations of the Yttrium Oxide (Y2O3) thin films were studied in details. The variations in these parameters by annealing of the samples at 500, 700, 900 °C were examined and optimum annealing conditions for the Y2O3 thin films were also determined. The structural parameters were studied by X-ray diffractometer analysis while scanning electron microscopy (SEM) was used for investigating the morphological properties of the devices. The reflection measurements were performed and band gap (Eg) calculations have been done by using the spectroscopic reflectometer measurements. The electrical parameters were examined by specifying surface state density and alternating-current (a.c.) conductivity. The results have revealed that the crystallizations, grain sizes of the thin films were improved with annealing due to agglomeration of the small particles around the bigger cluster thanks to high thermal energy which can also be seen in SEM measurements. On the other hand, both the reflection and the Eg were enhanced with annealing. The films having disorder structure, and higher defects density localised in the energy gap of dielectrics layer caused additionally allowed states. These additionally allowed states may affect the optical characteristics. Hence, it may deflect the optical performance of the films. The surface state densities almost decrease and the a.c. the conductivity of the thin films increases with increasing in annealing temperature due to rise in the grain sizes of the films. The number of the defect centres localised in the intra-crystallites boundary of the grains cause lattice and impurity scattering hence increase the bulk resistivity of layers. Therefore, the films having higher grain sizes decrease the number of the grain boundary; hence, increase the a.c. the conductivity of devices. Considering these results, strong relations were observed among structural, morphological, optical and electrical characteristics of the thin films and the devices which were annealed at 900 °C exhibited demanding characteristics for microelectronic applications.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
I.S. Park, T. Lee, H. Ko, J. Ahn, J. Korean Phys. Soc. 49, 760–763 (2006)
A.M. Mahajan, A.G. Khairnar, B.J. Thibeault, Semiconductors 48 497–500 (2014)
S. Kaya, E. Yilmaz, A. Kahraman, H. Karacali, Nucl. Instrum. Methods B 358 188–193 (2015)
J. Zhu, Z.G. Liu, Appl. Phys. A 78, 741–744 (2004)
R. Paily, A. DasGupta, N. DasGupta, P. Bhattacharya, P. Misra, T. Ganguli, L.M. Kukreja, A.K. Balamurugan, S. Rajagopalan, A.K. Tyagi, Appl. Surf. Sci. 187, 297–304 (2002)
A. Boukerika, L. Guerbous, J. Lumin. 145, 148–153 (2014)
V.H. Mudavakkat, V.V. Atuchin, V.N. Kruchinin, A. Kayani, C.V. Ramana, Opt. Mater. 34, 893–900 (2012)
A. Dimoulas, G. Vellianitis, A. Travlos, V. Ioannou-Sougleridis, A.G. Nassiopoulou, J. Appl. Phys. 92, 426–431 (2002)
S.J. Pearce, G.J. Parker, M.D.B. Charlton, J.S. Wilkinson, J. Vac. Sci. Technol. A 28 1388 (2010)
S.K. Sharma, S. Mohan, Appl. Surf. Sci. 282, 492–498 (2013)
T.M. Pan, C.C. Huang, Appl. Surf. Sci. 256, 7186–7193 (2010)
S. Kaya, E. Yilmaz, A. Aktag, J. Seidel, J. Mater. Sci. 26 5987–5993 (2015)
V. Ioannou-Sougleridis, V. Constantoudis, M. Alexe, R. Scholz, G. Vellianitis, A. Dimoulas, Thin Solid Films 468, 303–309 (2004)
S.J. Park, D.P. Norton, Thin Solid Films 510, 143–147 (2006)
A. Pandey, V. Kumar, R.E. Kroon, H.C. Swart, J. Alloys Compd. 672, 190–196 (2016)
S.Q. Zhang, R.F. Xiao, J. Appl. Phys. 83, 3842–3848 (1998)
P. Lei, W. Leroy, B. Dai, J.Q. Zhu, X.T. Chen, J.C. Han, D. Depla, Surf. Coat. Technol. 276 39–46 (2015)
S. Barve, M. Deo, R. Kar, N. Sreenivasan, R. Kishore, A. Biswas, B. Bhanage, M. Rao, L.M. Gantayet, D. Patil, Plasma Process. Polym. 8 740–749 (2011)
H.J. Quah, K.Y. Cheong, J. Exp. Nanosci. 10, 19–28 (2013)
X.J. Wang, L.D. Zhang, J.P. Zhang, G. He, M. Liu, L.Q. Zhu, Mater. Lett 62, 4235–4237 (2008)
M.H. Cho, D.H. Ko, K. Jeong, S.W. Whangbo, C.N. Whang, S.C. Choi, S.J. Cho, Thin Solid Films 349, 266–269 (1999)
D.G. Lim, J.H. Lee, J. Yi, J. Korean Phys. Soc. 40, 167–171 (2002)
A. Monshi, M.R. Foroughi, M.R. Monshi, World J. Nano Sci. Eng. 02, 154–160 (2012)
G. Bilir, G. Ozen, J. Collins, B. Di Bartolo, Appl. Phys. A 115 263–273 (2014)
H. Malkas, S. Kaya, E. Yilmaz, J. Electron. Mater. 43 4011–4017 (2014)
H.J. Quah, K.Y. Cheong, Mater. Chem. Phys. 130, 1007–1015 (2011)
E.J. Rubio, V.V. Atuchin, V.N. Kruchinin, L.D. Pokrovsky, I.P. Prosvirin, C.V. Ramana, J. Phys. Chem. C 118, 13644–13651 (2014)
I.Z. Mitrovic, M. Althobaiti, A.D. Weerakkody, V.R. Dhanak, W.M. Linhart, T.D. Veal, N. Sedghi, S. Hall, P.R. Chalker, D. Tsoutsou, A. Dimoulas, J. Appl. Phys. 115, 114102 (2014)
R. Lopez, R. Gomez, J. Sol-Gel Sci. Technol. 61 1–7 (2012)
A.B. Murphy, Sol. Energy Mater. Sol. C 91 1326–1337 (2007)
J. Zhu, Z.G. Liu, Appl. Phys. A 78, 741–744 (2004)
G. Shankar, P.S. Joseph, M.Y. Suvakin, A. Sebastiyan, Opt. Commun. 295, 134–139 (2013)
S.M. Sze, Physics of Semiconductor Devices (New York, Wiley, 1981)
S.V. Gaponenko, Optical Properties of Semiconductor Nanocrystals (Cambridge University, Cambridge, 1998
I. Yucedag, A. Kaya, S. Altindal, I. Uslu, Chin. Phys. B 23 (2014)
S.K. S. Abubakar, H. Karacali, E. Yilmaz, Sens. Actuators A 258 44–48 (2017)
R. Lok, S. Kaya, H. Kacali, E. Yilmaz, J. Mater. Sci. 27 13154–13160 (2016)
P. Laha, S.S. Dahiwale, I. Banerjee, S.K. Pabi, D. Kimd, P.K. Barhai, V.N. Bhoraskar, S.K. Mahapatra, Nucl. Instrum. Methods B 269 2740–2744 (2011)
A. Srivastava, R.K. Nahar, C.K. Sarkar, W.P. Singh, Y. Malhotra, Microelectron. Reliab. 51, 751–755 (2011)
M. Nath, A. Roy, J. Mater. Sci. 26 9107–9116 (2015)
A. Bansal, P. Srivastava, B.R. Singh, J. Mater. Sci. 26 639–645 (2015)
A.C. Rastogi, R.N. Sharma, Semicond. Sci. Technol. 16 641–650 (2001)
Acknowledgements
This work is supported by Abant Izzet Baysal University under Contract Number: AIBU, BAP. 2015.03.02.870, and BAP. 2014.03.02.722 and the Ministry of Development of Turkey under Contract Numbers: 2016K121110.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Abubakar, S., Kaya, S., Aktag, A. et al. Yttrium oxide nanostructured thin films deposited by radio frequency sputtering: the annealing optimizations and correlations between structural, morphological, optical and electrical properties. J Mater Sci: Mater Electron 28, 13920–13927 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-017-7241-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-017-7241-7