Abstract
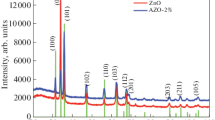
Aluminum doped zinc oxide (AZO) thin films have become technologically important materials due to their application potential for thermoelectric devices. In this paper, AZO thin films are deposited on the glass substrates using the solution derived by sol–gel route for dip-coating cycles and the radio-frequency sputtering process. The crystalline structure of two types of AZO films is characterized by X-ray diffraction exhibiting the typical hexagonal wurzite structure of ZnO. The rough surface of the heat treated films are observed by the SEM image. The average grain size of obtained films is evaluated based on these investigations showing they are consistent with each other. The sheet resistivity and Seebeck coefficient are measured between room temperature and 400 °C and used to determine the electrical conductivity and power factor of all films. The obtained results provide the advantages and disadvantages of the prepared films by each method for aiming at thermoelectrical applications.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
D.M. Rowe, Handbook of Thermoelectrics—Macro to Nano (CRC/Taylor & Francis, Boca Raton, 2006)
H. Julian Goldsmid, Introduction to Thermoelectricity, e-ISBN 978-3-642-00716-3, (Springer, Heidelberg Dordrecht London New York, 2010)
L. Li, L. Fang, X.J. Zhou, Z.Y. Liu, L. Zhao, S. Jiang, X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy study and thermoelectric properties of Al-doped ZnO thin films. J. Electron Spectrosc. Relat. Phenom. 173, 7–11 (2009)
M. Ruoho, V. Pale, M. Erdmanis, I. Tittonen, Influence of aluminium doping on thermoelectric performance of atomic layer deposited ZnO thin films. Appl. Phys. Lett. 103, 203903 (2013). doi:10.1063/1.4831980
M.H. Hong, C.S. Park, W.S. Seo, Y.S. Lim, J.K. Lee, H.H. Park, Thermoelectric properties of Al-doped mesoporous ZnO thin films. J. Nanomater. 2013, 1 (2013). doi:10.1155/2013/131537
A.I. Abutaha, S.R. Sarath Kumar, H.N. Alshareef, Crystal orientation dependent thermoelectric properties of highly oriented aluminum-doped zinc oxide thin films. Appl. Phys. Lett. 102(5), 053507 (2013)
Z. H. Zheng, P. Fan, G. X. Liang, P. J. Liu, P. J. Cao, D. P. Zhang, Z. K. Cai1, X. Ou, C. Y. Lai, Thermoelectric Properties of Al Doped ZnO Thin Films, in Materials Science Forum, vol. 743–744 (Trans Tech Publications, Switzerland, 2013), pp. 138–143
P. Fan, Y.-Z. Li, Z.-H. Zhenga, Q.-Y. Lin, J.-T. Luo, G.-X. Liang, M.-Q. Zhang, M.-C. Chen, Thermoelectric properties optimization of Al-doped ZnO thin films prepared by reactive sputtering Zn–Al alloy target. Appl. Surf. Sci. 284, 145–149 (2013)
J. Loureiro, N. Neves, R. Barros, T. Mateus, R. Santos, S. Filonovich, S. Reparaz, C.M. Sotomayor-Torres, F. Wyczisk, L. Divay, R. Martins, I. Ferreira, Transparent aluminium zinc oxide thin films with enhanced thermoelectric properties. J. Mater. Chem. A 2, 6649–6655 (2014)
S. Saini, P. Mele, H. Honda, K. Matsumoto, K. Miyazaki, A. Ichinose, Thermoelectric properties of Al-doped ZnO thin films. J. Electron. Mater. 43(6), 2145–2150 (2014)
P. Mele, S. Saini, H. Honda, K. Matsumoto, K. Miyazaki et al., Effect of substrate on thermoelectric properties of Al-doped ZnO thin films. Appl. Phys. Lett. 102, 253903 (2013). doi:10.1063/1.4812401
G.G. Valle, P. Hammer, S.H. Pulcinelli, C.V. Santilli, Transparent and conductive ZnO: Al thin films prepared by sol-gel dip-coating. J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 24, 1009–1013 (2004)
H.-M. Zhou, D.-Q. Yi, Z.-M. Yu, L.-R. Xiao, J. Li, Preparation of aluminum doped zinc oxide films and the study of their microstructure, electrical and optical properties. Thin Solid Films 515, 6909–6914 (2007)
T. Kemmitt, B. Ingham, R. Linklater, Optimization of SolGel-formed ZnO: Al processing parameters by observation of dopant Ion location using solid-state Al NMR spectrometry. J. Phys. Chem. C 115, 15031–15039 (2011)
M.-C. Jun, S.-U. Park, J.-H. Koh, Comparative studies of Al-doped ZnO and Ga-doped ZnO transparent conducting oxide thin films. Nanoscale res. lett. 7, 639 (2012)
M.F. Malek, M.H. Mamat, Z. Khusaimi, M.Z. Sahdan, M.Z. Musa, A.R. Zainun, A.B. Suriani, N.D. Md Sin, S.B. Abd Hamid, M. Rusop, Sonicated sol–gel preparation of nanoparticulate ZnO thin films with various deposition speeds: the highly preferred c-axis (002) orientation enhances the final properties. J. Alloy. Compd. 582, 12–21 (2014)
E. Mokaripoor, M.-M. Bagheri-Mohagheghi, Effect of very low to high Sb-doping on the structural, electrical, photo-conductive and thermoelectric properties of fluorine-doped SnO2 (FTO) thin films prepared by spray pyrolysis technique. J. Mater. Sci.: Mater. Electron. (2015). doi:10.1007/s10854-015-4026-8
M. Adelifard, R. Torkamani, Influence of growth temperature and silver to sulfur molar ratios on optical, electrical and thermoelectrical properties of nanostructured Ag2S thin films. J. Mater. Sci.: Mater. Electron. (2015). doi:10.1007/s10854-015-3392-6
P. Fan, Y. Zhang, Z.-H. Zheng, W.-F. Fan, J.-T. Luo, G.-X. Liang, D.-P. Zhang, Thermoelectric properties of cobalt antimony thin films deposited on flexible substrates by radio frequency magnetron sputtering. J. Electron. Mater. 44(2), 630–635 (2015). doi:10.1007/s11664-014-3546-y
Acknowledgments
This work has been supported by the Vietnam’s National Foundation for Science and Technology Development (NAFOSTED) grant funded by Ministry of Science and Technology (MOST) under Grant Number 103.02-2013.52.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Trinh, T.Q., Nguyen, T.T., Vu, D.V. et al. Structural and thermoelectric properties of Al-doped ZnO thin films grown by chemical and physical methods. J Mater Sci: Mater Electron 28, 236–240 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-016-5516-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-016-5516-z