Abstract
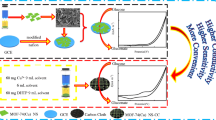
Surface engineering of human hair via electroless copper-plating process was successfully carried out as a self-supported electrochemical sensor for successful detection of glucose in human serum. Polydopamine (PDA) coating was first grafted on the surface of a single hair through oxidative self-polymerization of dopamine, and subsequently, the ultrathin metal layer composed of copper nanoparticles (CuNPs) on the hair surface was achieved using by the convenient electroless deposition process. The single hair@CuNPs composite with a uniformly dispersed conductive layer (8 μm in thickness) exhibited prominent electrocatalytic activity to glucose oxidation. The amperometric response of the self-supported nonenzymatic glucose sensor comprised two linear ranges (i.e., 0.002–5 mM and 5–35 mM), respectively, with a better detection limit of 1.62 μM and the best sensitivity of 110.98 μA−1 mM cm−2. As revealed by the finding, the surface engineering technique on single hair was confirmed as a simple and low-cost method for detecting glucose in human serum samples. The hair@CuNPs composite can be utilized as a promising potential in the next generation wearable and implantable bioelectronics application.
Graphical abstract








Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
Data will be made available on request.
References
Salek-Maghsoudi A, Vakhshiteh F, Torabi R, Hassani S, Ganjali MR, Norouzi P, Hosseini M, Abdollahi M (2018) Recent advances in biosensor technology in assessment of early diabetes biomarkers. Biosens Bioelectron 99:122–135. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bios.2017.07.047
Rumpler M, Mader JK, Fischer JP, Thar R, Granger JM, Deliane F, Klimant I, Aberer F, Sinner F, Pieber TR, Hajnsek M (2017) First application of a transcutaneous optical single-port glucose monitoring device in patients with type 1 diabetes mellitus. Biosens Bioelectron 88:240–248. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bios.2016.08.039
Shabnam L, Faisal SN, Roy AK, Haque E, Minett AI, Gomes VG (2017) Doped graphene/Cu nanocomposite: a high sensitivity non-enzymatic glucose sensor for food. Food Chem 221:751–759. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2016.11.107
Nam DJ, Kim Y, Yang EH, Lee HC, Ryoo J-H (2020) Relationship between urinary phthalate metabolites and diabetes: Korean National Environmental health Survey. Ann of Occup Environ Med 32:e34. https://doi.org/10.35371/aoem.2020.32.e34
Clark LC, Lyons C (1962) Electrode systems for continuous monitoring in cardiovascular surgery. Ann NY Acad Sci 102:29–45. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1749-6632.1962.tb13623.x
Thome-Duret V, Aussedat B, Reach G, Gangnerau MN, Lemonnier F, Klein JC, Zhang Y, Hu Y, Wilson GS (1998) Continuous glucose monitoring in the free-moving rat. Metabolism 47:799–803. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0026-0495(98)90115-9
Ward WK, Jansen LB, Anderson E, Reach G, Klein JC, Wilson GS (2002) A new amperometric glucose microsensor: in vitro and short-term in vivo evaluation. Biosens Bioelectron 17:181–189. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0956-5663(01)00268-8
Hu J (2009) The evolution of commercialized glucose sensors in China. Biosens Bioelectron 24:1083–1089. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bios.2008.08.051
Newman JD, Turner APF (2005) Home blood glucose biosensors: a commercial perspective. Biosens Bioelectron 20:2435–2453. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bios.2004.11.012
Hwang D-W, Lee S, Seo M, Chung TD (2018) Recent advances in electrochemical non-enzymatic glucose sensors-A review. Anal Chim Acta 1033:1–34. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aca.2018.05.051
Tsai T-W, Heckert G, Neves LF, Tan Y, Kao D-Y, Harrison RG, Resasco DE, Schmidtke DW (2009) Adsorption of glucose oxidase onto single-walled carbon nanotubes and its application in layer-by-layer biosensors. Anal Chem 81:7917–7925. https://doi.org/10.1021/ac900650r
Soomro RA, Akyuz OP, Ozturk R, Ibupoto ZH (2016) Highly sensitive non-enzymatic glucose sensing using gold nanocagesas as efficient electrode material. Sens Actuators B 233:230–236. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.snb.2016.04.065
Wei C, Li X, Xiang W, Yu Z, Liu Q (2020) MOF derived seaweed-like CoCu oxides nanorod arrays for electrochemical non-enzymatic glucose sensing with ultrahigh sensitivity. Sens Actuators B 324:128773. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.snb.2020.128773
Ahmed J, Faisal M, Alsareii SA, Harraz FA (2022) Highly sensitive and selective non-enzymatic uric acid electrochemical sensor based on novel polypyrrole-carbon black-Co3O4 nanocomposite. Adv Compos Hybrid Mater 5:920–933. https://doi.org/10.1007/s42114-021-00391-1
Lee S, Lee J, Park S, Boo H, Kim HC, Chung TD (2018) Disposable non-enzymatic blood glucose sensing strip based on nanoporous platinum particles. Appl Mater Today 10:24–29. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apmt.2017.11.009
Zhong G-X, Zhang W-X, Sun Y-M, Wei Y-Q, Lei Y, Peng H-P, Liu A-L, Chen Y-Z, Lin X-H (2015) A nonenzymatic amperometric glucose sensor based on three dimensional nanostructure gold electrode. Sens Actuators B 212:72–77. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.snb.2015.02.003
Shu H, Cao L, Chang G, He H, Zhang Y, He Y (2014) Direct electrodeposition of gold nanostructures onto glassy carbon electrodes for non-enzymatic detection of glucose. Electrochim Acta 132:524–532. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.electacta.2014.04.031
Wang B, Luo Y, Gao L, Liu B, Duan G (2021) High-performance field-effect transistor glucose biosensors based on bimetallic Ni/Cu metal-organic frameworks. Biosens Bioelectron 171:112736. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bios.2020.112736
Chen M, Cao X, Chang K, Xiang H, Wang R (2021) A novel electrochemical non-enzymatic glucose sensor based on Au nanoparticle-modified indium tin oxide electrode and boronate affinity. Electrochim Acta 368:137603. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.electacta.2020.137603
Alle M, Park SC, Bandi R, Lee S-H, Kim J-C (2021) Rapid in-situ growth of gold nanoparticles on cationic cellulose nanofibrils: Recyclable nanozyme for the colorimetric glucose detection. Carbohydr Polym 253:117239. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2020.117239
Vinoth V, Pugazhenthiran N, Viswanathan Mangalaraja R, Syed A, Marraiki N, Valdes H, Anandan S (2020) Development of an electrochemical enzyme-free glucose sensor based on self-assembled Pt-Pd bimetallic nanosuperlattices. Analyst 145:7898–7906. https://doi.org/10.1039/d0an01526a
Guo M-m, Xia Y, Huang W, Li Z (2015) Electrochemical fabrication of stalactite-like copper micropillar arrays via surface rebuilding for ultrasensitive nonenzymatic sensing of glucose. Electrochim Acta 151:340–346. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.electacta.2014.11.041
Hou L, Zhao H, Bi S, Xu Y, Lu Y (2017) Ultrasensitive and highly selective sandpaper-supported copper framework for non-enzymatic glucose sensor. Electrochim Acta 248:281–291. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.electacta.2017.07.142
Anupriya J, Velmurugan S, Chen S-M, Hahn Y-B (2022) Enhanced electrochemical performance of in-situ synthesized Cu nanoparticle/C spheres composite for highly sensitive sensing of azathioprine immunosuppressive drug. Compos B 242:110079. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compositesb.2022.110079
Zhang Y, Li N, Xiang Y, Wang D, Zhang P, Wang Y, Lu S, Xu R, Zhao J (2020) A flexible non-enzymatic glucose sensor based on copper nanoparticles anchored on laser-induced graphene. Carbon 156:506–513. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbon.2019.10.006
Shi L, Zhu X, Liu T, Zhao H, Lan M (2016) Encapsulating Cu nanoparticles into metal-organic frameworks for nonenzymatic glucose sensing. Sens Actuators B 227:583–590. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.snb.2015.12.092
Farid A, Khan AS, Javid M, Usman M, Khan IA, Ahmad AU, Fan Z, Khan AA, Pan L (2022) Construction of a binder-free non-enzymatic glucose sensor based on Cu@Ni core-shell nanoparticles anchored on 3D chiral carbon nanocoils-nickel foam hierarchical scaffold. J Colloid Interface Sci 624:320–337. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcis.2022.05.137
Ye J, Deng D, Wang Y, Luo L, Qian K, Cao S, Feng X (2020) Well-aligned Cu@C nanocubes for highly efficient nonenzymatic glucose detection in human serum. Sens Actuators B 305:127473. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.snb.2019.127473
Luo Y, Liu W, Huang M, Zhang S, Zhao Y, Yang Q, Yan B, Gu Y, Chen S (2021) Copper nanoparticles decorated halloysite nanotube/polyaniline composites for high performance non-enzymatic glucose sensor. J Electrochem Soc 168:086504. https://doi.org/10.1149/1945-7111/ac1b4d
Pramanick B, Cadenas LB, Kim D-M, Lee W, Shim Y-B, Martinez-Chapa SO, Madou MJ, Hwang H (2016) Human hair-derived hollow carbon microfibers for electrochemical sensing. Carbon 107:872–877. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbon.2016.06.095
Xu Y, Qian K, Deng D, Luo L, Ye J, Wu H, Miao M, Feng X (2020) Electroless deposition of silver nanoparticles on cellulose nanofibrils for electromagnetic interference shielding films. Carbohydr Polym 250:116915. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2020.116915
Tong Y-z, W-j Zhao WWu, Zhang D-l, He G-j, Yang Z-t, Cao X-w (2021) Realizing enhanced dielectric and mechanical performance of polyvinylidene fluoride/SiC nanocomposites through a bio-inspired interface design. Adv Compos Hybrid Mater 5:263–277. https://doi.org/10.1007/s42114-021-00333-x
Yang S, Zang G, Peng Q, Fan J, Liu Y, Zhang G, Zhao Y, Li H, Zhang Y (2020) In-situ growth of 3D rosette-like copper nanoparticles on carbon cloth for enhanced sensing of ammonia based on copper electrodissolution. Anal Chim Acta 1104:60–68. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aca.2020.01.010
Na W, Lee J, Jun J, Kim W, Kim YK, Jang J (2019) Highly sensitive copper nanowire conductive electrode for nonenzymatic glucose detection. J Ind Eng Chem 69:358–363. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jiec.2018.09.050
Liu Q, Chen J, Yu F, Wu J, Liu Z, Peng B (2021) Multifunctional book-like CuCo–MOF for highly sensitive glucose detection and electrocatalytic oxygen evolution. New J Chem 45:16714–16721. https://doi.org/10.1039/d1nj02931b
Cheng D, Li P, Zhu X, Liu M, Zhang Y, Liu Y (2021) Enzyme-free electrochemical detection of hydrogen peroxide based on the three-dimensional flower-like Cu-based metal organic frameworks and mxene nanosheets. Chin J Chem 39:2181–2187. https://doi.org/10.1002/cjoc.202100158
Wang C, Huang S, Luo L, Zhou Y, Lu X, Zhang G, Ye H, Gu J, Cao F (2019) Ultrathin two-dimension metal-organic framework nanosheets/multi-walled carbon nanotube composite films for the electrochemical detection of H2O2. J Electroanal Chem 835:178–185. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jelechem.2019.01.030
Ma P, Ma X, Suo Q, Chen F (2019) Cu NPs@NiF electrode preparation by rapid one-step electrodeposition and its sensing performance for glucose. Sens Actuators B 292:203–209. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.snb.2019.04.132
Xiao X, Peng S, Wang C, Cheng D, Li N, Dong Y, Li Q, Wei D, Liu P, Xie Z, Qu D, Li X (2019) Metal/metal oxide@carbon composites derived from bimetallic Cu/Ni-based MOF and their electrocatalytic performance for glucose sensing. J Electroanal Chem 841:94–100. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jelechem.2019.04.038
Song Y, Xu M, Gong C, Shen Y, Wang L, Xie Y, Wang L (2018) Ratiometric electrochemical glucose biosensor based on GOD/AuNPs/Cu-BTC MOFs/macroporous carbon integrated electrode. Sens Actuators B 257:792–799. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.snb.2017.11.004
Dang W, Sun Y, Jiao H, Xu L, Lin M (2020) AuNPs-NH2/Cu-MOF modified glassy carbon electrode as enzyme-free electrochemical sensor detecting H2O2. J Electroanal Chem 856:113592. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jelechem.2019.113592
Wang F, Zhang Y, Liang W, Chen L, Li Y, He X (2018) Non-enzymatic glucose sensor with high sensitivity based on Cu-Al layered double hydroxides. Sens Actuators B 273:41–47. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.snb.2018.06.038
Li Z-H, Zhao X-L, Jiang X-C, Wu Y-H, Chen C, Zhu Z-G, Marty J-L, Chen Q-S (2018) An enhanced nonenzymatic electrochemical glucose sensor based on copper-palladium nanoparticles modified glassy carbon electrodes. Electroanalysis 30:1811–1819. https://doi.org/10.1002/elan.201800017
Gao Y, Yang F, Yu Q, Fan R, Yang M, Rao S, Lan Q, Yang Z, Yang Z (2019) Three-dimensional porous Cu@Cu2O aerogels for direct voltammetric sensing of glucose. Mikrochim Acta 186:192. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-019-3263-6
Barbee B, Muchharla B, Adedeji A, Karoui A, Kumar Sadasivuni K, Sha MS, Abdullah AM, Slaughter G, Kumar B (2022) Cu and Ni Co-sputtered heteroatomic thin film for enhanced nonenzymatic glucose detection. Sci Rep 12:7507. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-022-11563-4
Tang L, Huan K, Deng D, Han L, Zeng Z, Luo L (2020) Glucose sensor based on Pd nanosheets deposited on Cu/Cu2O nanocomposites by galvanic replacement. Colloids Surf B 188:110797. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.colsurfb.2020.110797
Xu G-R, Ge C, Liu D, Jin L, Li Y-C, Zhang T-H, Rahman MM, Li X-B, Kim W (2019) In-situ electrochemical deposition of dendritic Cu–Cu2S nanocomposites onto glassy carbon electrode for sensitive and non-enzymatic detection of glucose. J Electroanal Chem 847:113177. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jelechem.2019.05.059
Acknowledgements
This work was financially supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Nos. 61571280 and 61971274) and the Science and Technology Commission of Shanghai Municipality (20230742300 and 18595800700).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
KQ was involved in methodology, investigation, data curation, writing and original draft. YX contributed to conceptualization, methodology, data curation. MM was involved in investigation. DD contributed to writing-review & editing and funding acquisition. LL contributed to writing-review & editing, funding acquisition and supervision. XF contributed to writing-review & editing, supervision, resources and funding acquisition.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Ethical approval
Not applicable.
Additional information
Handling Editor: Maude Jimenez.
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Supplementary file1 (MP4 1281 kb)
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Qian, K., Xu, Y., Miao, M. et al. Engineering metalized surface of single hair via electroless Cu-plating strategy for self-supported nonenzymatic glucose sensor. J Mater Sci 58, 15074–15085 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10853-023-08974-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10853-023-08974-7