Abstract
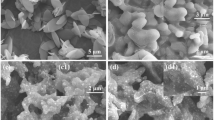
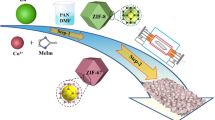
The impedance matching is a very important part to influence materials’ microwave absorption performance. However, a way to further discuss the impedance matching is still weak. We build a novel dielectric–magnetic impedance matching (DMIM) model to analyze the real part and imaginary part of materials’ impedance matching. To verify the practicality of the DMIM model, using MIL-100(Fe) as precursor, a series of FexNi1−x@C are synthesized via one-step pyrolysis by controlling the samples’ Fe–Ni ratio, changing their dielectric loss tangent and magnetic loss tangent and successfully regulating their impedance matching to optimize microwave absorption properties. In addition, the minimum reflection loss for MOF-derived Fe0.8Ni0.2@C can arrive at -71.3 dB at 10.3 GHz with a thickness of 3.1 mm, and the effective absorption bandwidth is 5.3 GHz. And combining with the RLGC equivalent circuit model to further indicate the FexNi1−x@C’s energy loss mechanism. The method of using DMIM model and RLGC model to discuss materials’ impedance matching and energy loss mechanism paves a new way to fabricate high-performance microwave materials with balanced electromagnetic distribution and further reveal the materials' microwave absorbing mechanism.
Graphic abstract












Similar content being viewed by others
References
Chen Y, Seow J, Zhao Q, Xu Z, Ji G (2020) A flexible and lightweight biomass-reinforced microwave absorber. Nano-Micro Lett 12:125
Zhang L, Yu S, Lu X, Fan W, Chi B, Ye Y, Shi X, Zeng J, Li X, Liao X (2020) Two-dimensional bimetallic Zn/Fe-metal-organic framework (MOF)-derived porous carbon nanosheets with a high density of single/paired Fe atoms as high-performance oxygen reduction catalysts. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 12:13878–13887
Wang S, Xu Y, Fu R, Zhu H, Jiao Q, Feng T, Feng C, Shi D, Li H, Zhao Y (2019) Rational construction of hierarchically porous Fe-Co/N-doped carbon/rGO composites for broadband microwave absorption. Nano-Micro Lett 11:331–346
Liang X, Quan B, Man Z, Cao B, Li N, Wang C, Ji G, Yu T (2019) Self-assembly three-dimensional porous carbon networks for efficient dielectric attenuation. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 11:30228–30233
Wang X, Pan F, Xiang Z, Zeng Q, Pei K, Che R, Lu W (2020) Magnetic vortex core-shell Fe3O4@C nanorings with enhanced microwave absorption performance. Carbon 157:130–139
Pan K, Leng T, Song J, Ji C, Zhang J, Li J, Novoselov K, Hu Z (2020) Controlled reduction of graphene oxide laminate and its applications for ultra-wideband microwave absorption. Carbon 160:307–316
Liang X, Zhang X, Liu W, Tang D, Zhang B, Ji G (2016) A simple hydrothermal process to grow MoS2 nanosheets with excellent dielectric loss and microwave absorption performance. J Mater Chem C 4:6816–6821
Luo J, Zhang K, Cheng M, Gu M, Sun X (2020) MoS2 spheres decorated on hollow porous ZnO microspheres with strong wideband microwave absorption. Chem Eng J 380:122625
Lu M, Cao W, Shi H, Fang X, Yang J, Hou Z, Jin H, Wang W, Yuan J, Cao M (2014) Multi-wall carbon nanotubes decorated with ZnO nanocrystals: mild solution-process synthesis and highly efficient microwave absorption properties at elevated temperature. J Mater Chem A 2:10540–10547
Li X, Yu L, Zhao W, Shi Y, Yu L, Dong Y, Zhu Y, Fu Y, Liu X, Fu F (2020) Prism-shaped hollow carbon decorated with polyaniline for microwave absorption. Chem Eng J 379:122393
Zhang Y, Yanga Z, Lia M, Yanga L, Liua J, Hab Y, Wu R (2020) Heterostructured CoFe@C@MnO2 nanocubes for efficient microwave absorption. Chem Eng J 382:123039
Liu P, Gao S, Wang Y, Huang Y, Wang Y, Luo J (2019) Core-shell CoNi@graphitic carbon decorated on B, N-codoped hollow carbon polyhedrons toward lightweight and high-efficiency microwave attenuation. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 11:25624–25635
Golchinvafa S, Masoudpanah S, Jazirehpour M (2019) Magnetic and microwave absorption properties of FeCo/CoFe2O4 composite powders. J Alloys Compd 809:151746
Shu R, Zhang J, Guo C, Wu Y, Wan Z, Shi J, Liu Y, Zheng M (2020) Facile synthesis of nitrogen-doped reduced graphene oxide/nickel-zinc ferrite composites as high-performance microwave absorbers in the X-band. Chem Eng J 384:123266
Chen X, Wang W, Shi T, Wu G, Lu Y (2020) One pot green synthesis and EM wave absorption performance of MoS2@ nitrogen doped carbon hybrid decorated with ultrasmall cobalt ferrite nanoparticles. Carbon 163:202–212
Kim Y, Hwang J, Khuyen B, Tung B, Kim K, Rhee J, Chen L, Lee Y (2018) Flexible ultrathin metamaterial absorber for wide frequency band, based on 7 conductive fibers. Sci Technol Adv Mater 19:711–717
Gupta S, Chang C, Anbalagan A, Lee C, Tai N (2020) Reduced graphene oxide/zinc oxide coated wearable electrically conductive cotton textile for high microwave absorption. Compos Sci Technol 188:107994
Zhou C, Wang X, Luo H, Deng L, Wei S, Zheng Y, Jia Q, Liu J (2020) Rapid and direct growth of bipyramid TiO2 from Ti3C2Tx MXene to prepare Ni/TiO2/C heterogeneous composites for high-performance microwave absorption. Chem Eng J 383:123095
He J, Liu S, Deng L, Shan D, Cao C, Luo H, Yan S (2020) Tunable electromagnetic and enhanced microwave absorption properties in CoFe2O4 decorated Ti3C2 MXene composites. Appl Surf Sci 504:144210
Huang M, Wang L, Pei K, You W, Yu X, Wu Z, Che R (2020) Multidimension-controllable synthesis of MOF-derived Co@N-doped carbon composite with magnetic-dielectric synergy toward strong microwave absorption. Small 16:2000158
Zhu T, Sun Y, Wang Y, Xing H, Li X, Hu P, Zong Y, Zheng X (2020) A MOF-driven porous iron with high dielectric loss and excellent microwave absorption properties. J Mater Sci-Mater El 31:6843–6854
Liu Y, Zhu Z, Liu X, Lu Q, Yin X, Guo L, Yang Y (2019) Electromagnetic modeling and analysis of the tapered differential through glass vias. Microelectron J 83:27–31
Hasirci Z, Cavdar I (2018) S-parameters-based causal RLGC(f) model of busbar distribution systems for broadband power line communication. Int J Elec Power 95:561–567
Guesh K, Caiuby C, Mayoral Á, Díaz-García M, Díaz I (2017) Sustainable preparation of MIL-100 (Fe) and its photocatalytic behavior in the degradation of methyl orange in water. Cryst Growth Des 17:1806–1813
Yang Y, Xia L, Zhang T, Shi B, Huang L, Zhong B, Zhang X, Wang H, Zhang J, Wen G (2018) Fe3O4@LAS/RGO composites with a multiple transmission-absorption mechanism and enhanced electromagnetic wave absorption performance. Chem Eng J 352:510–518
Kuang B, Song W, Ning M, Li J, Zhao Z, Guo D, Cao M, Jin H (2018) Chemical reduction dependent dielectric properties and dielectric loss mechanism of reduced graphene oxide. Carbon 127:209–217
Moruzzi V, Marcus P (1986) Ferromagnetic phases of bcc and fcc Fe Co, and Ni. Phys Rev B 34:1784–1791
Zhao H, Cheng Y, Liu W, Yang L, Zhang B, Wang L, Ji G, Xu Z (2019) Biomass-derived porous carbon-based nanostructures for microwave absorption. Nano-Micro Lett 11:24
Jiang Y, Fu X, Tian R, Zhang W, Du H, Fu C, Zhang Z, Xie P, Xin J, Fan R (2020) Nitrogen-doped carbon nanofibers with sulfur heteroatoms for improving microwave absorption. J Mater Sci 55:5832–5842. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10853-020-04430-y
Hou T, Wang B, Ma M et al (2020) Preparation of two-dimensional titanium carbide (Ti3C2Tx) and NiCo2O4 composites to achieve excellent microwave absorption properties. Compos Part B-Eng 180:107577
Liang X, Man Z, Quan B, Zheng J, Gu W, Zhang Z, Ji G (2020) Environment-stable CoxNiy encapsulation in stacked porous carbon nanosheets for enhanced microwave absorption. Nano-Micro Lett 12:102
Zhao H, Chen Y, Zhang Z, Yu J, Zheng J, Zhou M, Zhou L, Zhao B, Ji G (2020) Rational design of core-shell Co@C nanotubes towards lightweight and high-efficiency microwave absorption. Compos Part B 19:108119
Hu C, Liu H, Zhang Y, Zhang M, Yu J, Liu X, Zhang X (2019) Tuning microwave absorption properties of multiwalled carbon nanotubes by surface functional groups. J Mater Sci 54:2417–2426. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10853-018-2895-y
Liu W, Liu L, Ji G, Li D, Zhang Y, Ma J, Du Y (2017) Composition design and structural characterization of MOF-derived composites with controllable electromagnetic properties. ACS Sustainable Chem Eng 5:7961–7971
Xiang Z, Song Y, Xiong J, Pan Z, Wang X, Liu L, Liu R, Yang H, Lu W (2019) Enhanced electromagnetic wave absorption of nanoporous Fe3O4 @ carbon composites derived from metal-organic frameworks. Carbon 142:20–31
Liu Q, Liu X, Feng H, Shui H, Yu R (2017) Metal organic framework-derived Fe/carbon porous composite with low Fe content for lightweight and highly efficient electromagnetic wave absorber. Chem Eng J 314:320–327
Rehman S, Liu J, Fang Z, Wang J, Ahmed R, Wang C, Bi H (2019) Heterostructured TiO2/C/Co from ZIF-67 frameworks for microwave-absorbing nanomaterials. ACS Appl Nano Mater 2:4451–4461
Wang L, Yu X, Li X, Zhang J, Wang M, Che R (2020) MOF-derived yolk-shell Ni@C@ZnO Schottky contact structure for enhanced microwave absorption. Chem Eng J 383:123099
Liang B, Wang S, Kuang D, Hou L, Yu B, Lin L (2018) Facile synthesis and excellent microwave absorption properties of FeCo-C core-shell nanoparticles. Nanotechnology 29:085604
Das A, Negi P, Joshi S, Kumar A (2019) Enhanced microwave absorption properties of Co and Ni co-doped iron (II, III)/reduced graphene oxide composites at X-band frequency. J Mater Sci-Mater El 30:19325–19334
Lia Y, Zhao B, Fan S, Liang L, Zhou Y, Wang R, Guo X, Fan B, Zhang R (2019) ZnO amounts-dependent electromagnetic wave absorption capabilities of Ni/ZnO composite microspheres. J Mater Sci-Mater El 30:19966–19976
Majeed A, Khan M, Yousuf L, Ahmad R, Ahmad I (2020) Structural, microwave permittivity, and complex impedance studies of cation (Cr, Bi, Al, In) substituted SrNi-X hexagonal nano-sized ferrites. Ceram Int 46:1907–1915
Kadira L, Sayouri S, Elmesbahi A, Salhi A (2019) Investigation of complex impedance and modulus properties of La or/and Ca doped BaTiO3. Mater Today: Proc 13:1238–1247
Benyoussef M, Zannen M, Belhadi J, Manoun B, Dellis J, Lahmar A, Marssi M (2020) Complex impedance and Raman spectroscopy of Na0.5(Bi1−xDyx)0.5TiO3 ceramics. Ceram Int 46:10979–10991
Tomzawa M, Cordaro J, Singh M (1979) Low frequency dielectric relaxation from complex impedance and complex electric ‘modulus’. J Mater Sci 14:1945–1951. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00551036
Wang L, Zhang J, Wang M, Che R (2019) Hollow porous Fe2O3 microspheres wrapped by reduced graphene oxides with high-performance microwave absorption. J Mater Chem C 7:11167–11176
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by National Natural Science Foundation of China (51572218), Scientific Research Program Funded by Shaanxi Provincial Education Department (18JK0786), Key Project of Research and Development of Shaanxi Province (2018ZDCXL-GY-08-05) and Scientific Research Program Funded by Shaanxi Provincial Education Department (203010036).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Additional information
Handling Editor: Mark Bissett.
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhu, T., Sun, Y., Wang, Y. et al. Controllable synthesis of MOF-derived FexNi1−x@C composites with dielectric–magnetic synergy toward optimized impedance matching and outstanding microwave absorption. J Mater Sci 56, 592–606 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10853-020-05307-w
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10853-020-05307-w