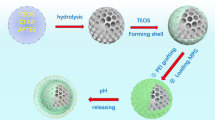
Abstract
The stimulus-responsive drug delivery system has attracted increasing attention due to its ability to enhance therapeutic efficacy and reduce side effects. Herein, a pH and glutathione (GSH) dually responsive drug carrier, hollow silica–-polyelectrolyte composite nanoparticle, was successfully prepared by using a template of spherical polyelectrolyte brush (SPB) which consists of a polystyrene (PS) core and a densely grafted linear poly(acrylic acid) (PAA) shell. The existence of PAA chains and introduction of disulfide bonds in silica framework endow the composite nanoparticles with pH and GSH dually responsive properties which were confirmed by dynamic light scattering (DLS) and small-angle X-ray scattering (SAXS). With doxorubicin hydrochloride (DOX) as the model drug, the loading content and encapsulation efficiency could reach up to 43% and 96%, respectively. The drug release behavior was investigated under various environments, showing that the drug release rate increased with the decrease in pH value and the increase in GSH concentration. The prepared hollow SiO2–PAA composite nanoparticles possess a great potential as carriers for controlled drug delivery.












Similar content being viewed by others
References
Liu CQ, Zhang Y, Liu M, Chen ZW, Lin YH, Li W, Cao FF, Liu Z, Ren JS, Qu XG (2017) A NIR-controlled cage mimicking system for hydrophobic drug mediated cancer therapy. Biomaterials 139:151–162
Tian H, Luo ZY, Liu LL, Zheng MB, Chen Z, Ma AQ, Liang RJ, Han ZQ, Lu CY, Cai LT (2017) Cancer cell membrane-biomimetic oxygen nanocarrier for breaking hypoxia-induced chemoresistance. Adv Func Mater 27(38):7. https://doi.org/10.1002/adfm.201703197
Yang GB, Zhang R, Liang C, Zhao H, Yi X, Shen SD, Yang K, Cheng L, Liu Z (2018) Manganese dioxide coated WS2@Fe3O4/sSiO(2) nanocomposites for pH-responsive MR imaging and oxygen-elevated synergetic therapy. Small 14(2):9. https://doi.org/10.1002/smll.201702664
Joo KI, Xiao L, Liu SL, Liu YR, Lee CL, Conti PS, Wong MK, Li ZB, Wang P (2013) Crosslinked multilamellar liposomes for controlled delivery of anticancer drugs. Biomaterials 34(12):3098–3109
Chen W, Zhong P, Meng FH, Cheng R, Deng C, Feijen J, Zhong ZY (2013) Redox and pH-responsive degradable micelles for dually activated intracellular anticancer drug release. J Control Release 169(3):171–179
Wang Y, Wang J, Yuan Z, Han H, Li T, Li L, Guo X (2017) Chitosan cross-linked poly(acrylic acid) hydrogels: drug release control and mechanism. Colloids Surf B 152:252
Zhao Y, Lin LN, Lu Y, Chen SF, Dong L, Yu SH (2010) Templating synthesis of preloaded Doxorubicin in hollow mesoporous silica nanospheres for biomedical applications. Adv Mater 22(46):5255–5259
Vallet-Regi M, Ramila A, del Real RP, Perez-Pariente J (2001) A new property of MCM-41: drug delivery system. Chem Mater 13(2):308–311
Slowing II, Trewyn BG, Giri S, Lin VSY (2007) Mesoporous silica nanoparticles for drug delivery and biosensing applications. Adv Func Mater 17(8):1225–1236
Fan W, Lu N, Huang P, Liu Y, Yang Z, Wang S, Yu G, Liu Y, Hu J, He Q (2017) Glucose-responsive sequential generation of hydrogen peroxide and nitric oxide for synergistic cancer Starving-like/gas therapy. Angew Chem Int Edit 129(5):1229–1233
Zhu YF, Shi JL, Li YS, Chen HR, Shen WH, Dong XP (2005) Storage and release of ibuprofen drug molecules in hollow mesoporous silica spheres with modified pore surface. Microporous Mesoporous Mat 85(1–2):75–81
Zhu Y, Prof JS, Shen W, Dong X, Feng J, Ruan M, Li Y (2005) Stimuli-responsive controlled drug release from a hollow mesoporous silica sphere/polyelectrolyte multilayer core–shell structure. Angew Chem Int Edit 44(32):5083–5087
Li YH, Li N, Pan W, Yu ZZ, Yang LM, Tang B (2017) Hollow mesoporous silica nanoparticles with tunable structures for controlled drug delivery. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 9(3):2123–2129
Han L, Tang C, Yin CH (2016) pH-responsive core-shell structured nanoparticles for triple-stage targeted delivery of doxorubicin to tumors. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 8(36):23498–23508
Sahoo B, Devi KS, Banerjee R, Maiti TK, Pramanik P, Dhara D (2013) Thermal and pH responsive polymer-tethered multifunctional magnetic nanoparticles for targeted delivery of anticancer drug. Appl Mater Interfaces 5(9):3884–3893
Yang GB, Sun XQ, Liu JJ, Feng LZ, Liu Z (2016) Light-responsive, singlet-oxygen-triggered on-demand drug release from photosensitizer-doped mesoporous silica nanorods for cancer combination therapy. Adv Func Mater 26(26):4722–4732
Hayashi K, Maruhashi T, Nakamura M, Sakamoto W, Yogo T (2016) One-pot synthesis of dual stimulus-responsive degradable hollow hybrid nanoparticles for image-guided trimodal therapy. Adv Func Mater 26(47):8613–8622
Kang T, Li FY, Baik S, Shao W, Ling DS, Hyeon T (2017) Surface design of magnetic nanoparticles for stimuli-responsive cancer imaging and therapy. Biomaterials 136:98–114
Mura S, Nicolas J, Couvreur P (2013) Stimuli-responsive nanocarriers for drug delivery. Nat Mater 12(11):991–1003
Feng W, Zhou XJ, He CL, Qiu KX, Nie W, Chen L, Wang HS, Mo XM, Zhang YZ (2013) Polyelectrolyte multilayer functionalized mesoporous silica nanoparticles for pH-responsive drug delivery: layer thickness-dependent release profiles and biocompatibility. J Mater Chem B 1(43):5886–5898
Yuan L, Tang QQ, Yang D, Zhang JZ, Zhang FY, Hu JH (2011) preparation of pH-responsive mesoporous silica nanoparticles and their application in controlled drug delivery. J Phys Chem C 115(20):9926–9932
Liu X, Yu D, Jin CS, Song XW, Cheng JZ, Zhao X, Qi XM, Zhang GX (2014) A dual responsive targeted drug delivery system based on smart polymer coated mesoporous silica for laryngeal carcinoma treatment. New J Chem 38(10):4830–4836
Huang L, Liu MY, Mao LC, Huang Q, Huang HY, Zeng GJ, Tian JW, Wen YQ, Zhang XY, Wei Y (2018) A facile FeBr 3 based photoATRP for surface modification of mesoporous silica nanoparticles for controlled delivery cisplatin. Appl Surf Sci 434:204–210
Hong CY, Li X, Pan CY (2009) Fabrication of smart nanocontainers with a mesoporous core and a pH-responsive shell for controlled uptake and release. J Mater Chem 19(29):5155–5160
Chen W, Shi Y, Feng H, Du M, Zhang JZ, Hu J, Yang D (2012) Preparation of copolymer paclitaxel covalently linked via a disulfide bond and its application on controlled drug delivery. J Phys Chem B 116(30):9231–9237
Kim H, Kim S, Park C, Lee H, Park HJ, Kim C (2010) Glutathione-induced intracellular release of guests from mesoporous silica nanocontainers with cyclodextrin gatekeepers. Adv Mater 22(38):4280–4283
Zhang Q, Shen C, Zhao N, Xu FJ (2017) Redox-responsive and drug-embedded silica nanoparticles with unique self-destruction features for efficient gene/drug codelivery. Adv Func Mater 27(10):12. https://doi.org/10.1002/adfm.201606229
Wu X, Wang ZY, Zhu D, Zong SF, Yang LP, Zhong Y, Cui YP (2013) pH and thermo dual-stimuli-responsive drug carrier based on mesoporous silica nanoparticles encapsulated in a copolymer-lipid bilayer. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 5(21):10895–10903
Gosecka M, Gosecki M (2015) Characterization methods of polymer core-shell particles. Colloid Polym Sci 293(10):2719–2740
Ruckdeschel P, Dulle M, Honold T, Forster S, Karg M, Retsch M (2016) Monodisperse hollow silica spheres: an in-depth scattering analysis. Nano Res 9(5):1366–1376
Li T, Senesi AJ, Lee B (2016) Small angle X-ray scattering for nanoparticle research. Chem Rev 116(18):11128–11180
Guo X, Weiss A, Ballauff M (1999) Synthesis of spherical polyelectrolyte brushes by photoemulsion polymerization. Macromolecules 32(19):6043–6046
Rosenfeldt S, Wittemann A, Ballauff M, Breininger E, Bolze J, Dingenouts N (2004) Interaction of proteins with spherical polyelectrolyte brushes in solution as studied by small-angle x-ray scattering. Phys Rev E 70(6):10. https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevE.70.061403
Henzler K, Wittemann A, Breininger E, Matthias Ballauff A, Rosenfeldt S (2007) Adsorption of bovine hemoglobin onto spherical polyelectrolyte brushes monitored by small-angle X-ray scattering and fourier transform infrared spectroscopy. Biomacromol 8(11):3674–3681
Henzler K, Haupt B, Rosenfeldt S, Harnau L, Narayanan T, Ballauff M (2011) Interaction strength between proteins and polyelectrolyte brushes: a small angle X-ray scattering study. Phys Chem Chem Phys 13(39):17599–17605
Wang W, Li L, Yu X, Han H, Guo X (2015) Distribution of magnetic nanoparticles in spherical polyelectrolyte brushes as observed by small-angle X-ray scattering. J Polym Sci Part B Polym Phys 52(24):1681–1688
Wang WH, Li L, Henzler K, Lu Y, Wang Jy, Han Hy, Tian YC, Wang YW, Zhou ZM, Lotze G, Narayanan T, Ballauff M, Guo XH (2017) Protein immobilization onto cationic spherical polyelectrolyte brushes studied by small angle X-ray scattering. Biomacromol 18(5):1574–1581
Han HY, Li L, Wang WH, Tian YC, Wang YW, Wang JY, von Klitzing R, Guo XH (2017) Core-shell-corona silica hybrid nanoparticles templated by spherical polyelectrolyte brushes: a study by small angle X-ray scattering. Langmuir 33(38):9857–9865
Han HY, Li L, Yang QS, Tian YC, Wang YW, Ye ZS, Klitzing R, Guo XH (2018) Characterization of hollow silica-polyelectrolyte composite nanoparticles by small-angle X-ray scattering. J Mater Sci 53(5):3210–3224. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10853-017-1747-5
Dingenouts N, Norhausen C, Ballauff M (1998) Observation of the volume transition in thermosensitive core-shell latex particles by small-angle X-ray scattering. Macromolecules 31(25):8912–8917
Robillard Q, Guo X, Ballauff M, Narayanan T (2000) Spatial correlation of spherical polyelectrolyte brushes in salt-free solution as observed by small-angle X-ray scattering. Macromolecules 33(24):9109–9114
Huang S, Yu X, Dong Y, Li L, Guo X (2012) Spherical polyelectrolyte brushes: ideal templates for preparing pH-sensitive core-shell and hollow silica nanoparticles. Colloids Surf A 415(415):22–30
Li YJ, Guo WW, Su XD, Ou-Yang L, Dang M, Tao J, Lu GM, Teng ZG (2018) Small size mesoporous organosilica nanorods with different aspect ratios: synthesis and cellular uptake. J Colloid Interface Sci 512:134–140
Niu YT, Yu MH, Zhang J, Yang YN, Xu C, Yeh M, Taran E, Hou JJC, Gray PP, Yu CZ (2015) Synthesis of silica nanoparticles with controllable surface roughness for therapeutic protein delivery. J Mater Chem B 3(43):8477–8485
Zhang HJ, Xu HJ, Wu MH, Zhong YF, Wang DH, Jiao Z (2015) A soft-hard template approach towards hollow mesoporous silica nanoparticles with rough surfaces for controlled drug delivery and protein adsorption. J Mater Chem B 3(31):6480–6489
Murugan B, Ramana LN, Gandhi S, Sethuraman S, Krishnan UM (2013) Engineered chemoswitchable mesoporous silica for tumor-specific cytotoxicity. J Mater Chem B 1(28):3494–3505
Li DL, Huang X, Wu YD, Li JW, Cheng WL, He JM, Tian HY, Huang YD (2016) Preparation of pH-responsive mesoporous hydroxyapatite nanoparticles for intracellular controlled release of an anticancer drug. Biomater Sci 4(2):272–280
Zhang Y, Chang YQ, Han L, Zhang Y, Chen ML, Shu Y, Wang JH (2017) Aptamer-anchored di-polymer shell-capped mesoporous carbon as a drug carrier for bi-trigger targeted drug delivery. J Mater Chem B 5(33):6882–6889
Zhang M, Liu J, Kuang Y, Li QL, Zheng DW, Song QF, Chen H, Chen XQ, Xu YL, Li C, Jiang BB (2017) Ingenious pH-sensitive dextran/mesoporous silica nanoparticles based drug delivery systems for controlled intracellular drug release. Int J Biol Macromol 98:691–700. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2017.01.136
Acknowledgements
We gratefully thank the financial support by the NSFC Grants (5171101370, 51773061 and 21476143) and 111 Project Grant (B08021). We also thank Shanghai Synchrotron Radiation Facility for its experimental support.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflicts of interest
The authors declare no competing financial interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yang, Q., Li, L., Zhao, F. et al. Hollow silica–polyelectrolyte composite nanoparticles for controlled drug delivery. J Mater Sci 54, 2552–2565 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10853-018-2996-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10853-018-2996-7