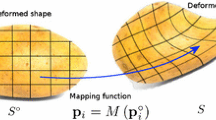
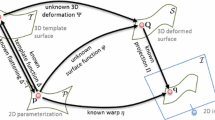
Abstract
Automatic estimation of skinning transformations is a popular way to deform a single reference shape into a new pose by providing a small number of control parameters. We generalize this approach by efficiently enabling the use of multiple exemplar shapes. Using a small set of representative natural poses, we propose to express an unseen appearance by a low-dimensional linear subspace, specified by a redundant dictionary of weighted vertex positions. Minimizing a nonlinear functional that regulates the example manifold, the suggested approach supports local-rigid deformations of articulated objects, as well as nearly isometric embeddings of smooth shapes. A real-time nonrigid deformation system is demonstrated, and a shape completion and partial registration framework is introduced. These applications can recover a target pose and implicit inverse kinematics from a small number of examples and just a few vertex positions. The resulting reconstruction is more accurate compared to alternative reduced deformable models.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alexa, M.: Differential coordinates for local mesh morphing and deformation. Vis. Comput. 19(2), 105–114 (2003)
Alexa, M., Cohen-Or, D., Levin, D.: As-rigid-as-possible shape interpolation. In: Proceedings of the 27th Annual Conference on Computer Graphics and Interactive Techniques, SIGGRAPH’00, pp. 157–164. ACM Press/Addison-Wesley Publishing Co., New York, NY, USA (2000). https://doi.org/10.1145/344779.344859
Allen, B., Curless, B., Popović, Z.: The space of human body shapes: reconstruction and parameterization from range scans. ACM Trans. Graph. 22(3), 587–594 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1145/882262.882311
Amberg, B., Romdhani, S., Vetter, T.: Optimal step nonrigid icp algorithms for surface registration. In: IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, 2007. CVPR ’07, pp. 1–8 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1109/CVPR.2007.383165
Anguelov, D., Srinivasan, P., cheung Pang, H., Koller, D., Thrun, S., Davis, J.: The correlated correspondence algorithm for unsupervised registration of nonrigid surfaces. In: Saul, L.K., Weiss, Y., Bottou, L. (eds.) Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems vol. 17, pp. 33–40. MIT Press, Cambridge (2005). http://papers.nips.cc/paper/2601-the-correlated-correspondence-algorithm-for-unsupervised-registration-of-nonrigid-surfaces.pdf
Bogo, F., Romero, J., Loper, M., Black, M.J.: Faust: dataset and evaluation for 3d mesh registration. In: The IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR) (2014)
Bouaziz, S., Martin, S., Liu, T., Kavan, L., Pauly, M.: Projective dynamics: fusing constraint projections for fast simulation. ACM Trans. Graph. 33(4), 154:1–154:11 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1145/2601097.2601116
Bouaziz, S., Wang, Y., Pauly, M.: Online modeling for realtime facial animation. ACM Trans. Graph. (TOG) 32(4), 40 (2013)
Bronstein, A.M., Bronstein, M.M., Kimmel, R.: Numerical Geometry of Non-rigid Shapes. Springer, Berlin (2008)
Brunton, A., Wand, M., Wuhrer, S., Seidel, H.P., Weinkauf, T.: A low-dimensional representation for robust partial isometric correspondences computation. Graph. Models 76(2), 70–85 (2014)
Chao, I., Pinkall, U., Sanan, P., Schröder, P.: A simple geometric model for elastic deformations. In: ACM SIGGRAPH 2010 Papers, SIGGRAPH’10, pp. 38:1–38:6. ACM, New York, NY, USA (2010). https://doi.org/10.1145/1833349.1778775
Der, K.G., Sumner, R.W., Popović, J.: Inverse kinematics for reduced deformable models. ACM Trans. Graph. 25(3), 1174–1179 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1145/1141911.1142011
Dey, T.K., Ranjan, P., Wang, Y.: Eigen deformation of 3d models. Vis. Comput. 28(6–8), 585–595 (2012)
Elad, M.: Sparse and Redundant Representations: From Theory to Applications in Signal and Image Processing. Springer, Berlin (2010)
Feng, W.W., Kim, B.U., Yu, Y.: Real-time data driven deformation using kernel canonical correlation analysis. In: ACM SIGGRAPH 2008 Papers, SIGGRAPH’08, pp. 91:1–91:9. ACM, New York, NY, USA (2008). https://doi.org/10.1145/1399504.1360690
Fröhlich, S., Botsch, M.: Example-driven deformations based on discrete shells. Comput. Graph. Forum 30(8), 2246–2257 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1467-8659.2011.01974.x
Gao, L., Lai, Y.K., Liang, D., Chen, S.Y., Xia, S.: Efficient and flexible deformation representation for data-driven surface modeling. ACM Trans. Graph. (TOG) 35(5), 158 (2016)
Grinspun, E., Hirani, A.N., Desbrun, M., Schröder, P.: Discrete shells. In: Proceedings of the 2003 ACM SIGGRAPH/Eurographics Symposium on Computer Animation, SCA’03, pp. 62–67. Eurographics Association, Aire-la-Ville, Switzerland, Switzerland (2003)
Jacobson, A., Baran, I., Kavan, L., Popović, J., Sorkine, O.: Fast automatic skinning transformations. ACM Trans. Graph. 31(4), 77:1–77:10 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1145/2185520.2185573
Jacobson, A., Baran, I., Popović, J., Sorkine-Hornung, O.: Bounded biharmonic weights for real-time deformation. Commun. ACM 57(4), 99–106 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1145/2578850
James, D.L., Twigg, C.D.: Skinning mesh animations. In: ACM SIGGRAPH 2005 Papers, SIGGRAPH’05, pp. 399–407. ACM, New York, NY, USA (2005). https://doi.org/10.1145/1186822.1073206
Kaufman, L., Rousseeuw, P.: Clustering by Means of Medoids. North-Holland, Amsterdam (1987)
Kavan, L., Sloan, P.P., O’Sullivan, C.: Fast and efficient skinning of animated meshes. Comput. Graph. Forum 29(2), 327–336 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1467-8659.2009.01602.x
Kim, V.G., Lipman, Y., Funkhouser, T.: Blended intrinsic maps. In: ACM SIGGRAPH 2011 Papers, SIGGRAPH’11, pp. 79:1–79:12. ACM, New York, NY, USA (2011). https://doi.org/10.1145/1964921.1964974
Koyama, Y., Takayama, K., Umetani, N., Igarashi, T.: Real-time example-based elastic deformation. In: Proceedings of the 11th ACM SIGGRAPH/Eurographics Conference on Computer Animation, EUROSCA’12, pp. 19–24. Eurographics Association, Aire-la-Ville, Switzerland, Switzerland (2012). https://doi.org/10.2312/SCA/SCA12/019-024
Kry, P.G., James, D.L., Pai, D.K.: Eigenskin: real time large deformation character skinning in hardware. In: Proceedings of the 2002 ACM SIGGRAPH/Eurographics Symposium on Computer Animation, SCA’02, pp. 153–159. ACM, New York, NY, USA (2002). https://doi.org/10.1145/545261.545286
Le, B.H., Deng, Z.: Robust and accurate skeletal rigging from mesh sequences. ACM Trans. Graph. 33(4), 84:1–84:10 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1145/2601097.2601161
Levi, Z., Gotsman, C.: Smooth rotation enhanced as-rigid-as-possible mesh animation. IEEE Trans. Vis. Comput. Graph. 21(2), 264–277 (2015)
Lewis, J.P., Cordner, M., Fong, N.: Pose space deformation: a unified approach to shape interpolation and skeleton-driven deformation. In: Proceedings of the 27th Annual Conference on Computer Graphics and Interactive Techniques, SIGGRAPH’00, pp. 165–172. ACM Press/Addison-Wesley Publishing Co., New York, NY, USA (2000). https://doi.org/10.1145/344779.344862
Li, H., Sumner, R.W., Pauly, M.: Global correspondence optimization for non-rigid registration of depth scans. Comput. Graph. Forum 27(5), 1421–1430 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1467-8659.2008.01282.x
Lipman, Y., Sorkine, O., Cohen-Or, D., Levin, D., Rossi, C., Seidel, H.P.: Differential coordinates for interactive mesh editing. In: Shape Modeling Applications, 2004. Proceedings, pp. 181–190 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1109/SMI.2004.1314505
Liu, L., Zhang, L., Xu, Y., Gotsman, C., Gortler, S.J.: A local/global approach to mesh parameterization. Comput. Graph. Forum 27(5), 1495–1504 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1467-8659.2008.01290.x
Magnenat-thalmann, N., Laperrire, R., Thalmann, D., Montral, U.D.: Joint-dependent local deformations for hand animation and object grasping. In: Proceedings on Graphics interface vol. 88, pp. 26–33 (1988)
Martin, S., Thomaszewski, B., Grinspun, E., Gross, M.: Example-based elastic materials. ACM Trans. Graph. 30(4), 72:1–72:8 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1145/2010324.1964967
McAdams, A., Selle, A., Tamstorf, R., Teran, J., Sifakis, E.: Computing the singular value decomposition of 3\(\times \) 3 matrices with minimal branching and elementary floating point operations. Technical Report, University of Wisconsin-Madison (2011)
Pinkall, U., Polthier, K.: Computing discrete minimal surfaces and their conjugates. Exp. Math. 2(1), 15–36 (1993). https://doi.org/10.1080/10586458.1993.10504266
Rodolà, E., Cosmo, L., Bronstein, M.M., Torsello, A., Cremers, D.: Partial functional correspondence. In: Computer Graphics Forum. Wiley Online Library (2016)
Schumacher, C., Thomaszewski, B., Coros, S., Martin, S., Sumner, R., Gross, M.: Efficient simulation of example-based materials. In: Proceedings of the ACM SIGGRAPH/Eurographics Symposium on Computer Animation, pp. 1–8. Eurographics Association (2012)
Sloan, P.P.J., Rose III, C.F., Cohen, M.F.: Shape by example. In: Proceedings of the 2001 Symposium on Interactive 3D Graphics, I3D’01, pp. 135–143. ACM, New York, NY, USA (2001). https://doi.org/10.1145/364338.364382
Sorkine, O., Alexa, M.: As-rigid-as-possible surface modeling. In: Proceedings of EUROGRAPHICS/ACM SIGGRAPH Symposium on Geometry Processing, pp. 109–116 (2007)
Sumner, R.W., Popović, J.: Deformation transfer for triangle meshes. ACM Trans. Graph. 23(3), 399–405 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1145/1015706.1015736
Sumner, R.W., Zwicker, M., Gotsman, C., Popović, J.: Mesh-based inverse kinematics. In: ACM SIGGRAPH 2005 Papers, SIGGRAPH’05, pp. 488–495. ACM, New York, NY, USA (2005). https://doi.org/10.1145/1186822.1073218
van Kaick, O., Zhang, H., Hamarneh, G.: Bilateral maps for partial matching. In: Computer Graphics Forum, vol. 32, pp. 189–200. Wiley Online Library (2013)
Von-Tycowicz, C., Schulz, C., Seidel, H.P., Hildebrandt, K.: Real-time nonlinear shape interpolation. ACM Trans. Graph. 34(3), 34:1–34:10 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1145/2729972
Wang, R.Y., Pulli, K., Popović, J.: Real-time enveloping with rotational regression. ACM Trans. Graph. (2007). https://doi.org/10.1145/1276377.1276468
Wang, Y., Jacobson, A., Barbič, J., Kavan, L.: Linear subspace design for real-time shape deformation. ACM Trans. Graph. (TOG) 34(4), 57 (2015)
Winkler, T., Drieseberg, J., Alexa, M., Hormann, K.: Multi-scale geometry interpolation. Comput. Graph. Forum 29(2), 309–318 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1467-8659.2009.01600.x
Xu, D., Zhang, H., Wang, Q., Bao, H.: Poisson shape interpolation. Graph. Models 68(3), 268–281 (2006)
Zhang, H., Sheffer, A., Cohen-Or, D., Zhou, Q., Van Kaick, O., Tagliasacchi, A.: Deformation-driven shape correspondence. Comput. Graph. Forum 27(5), 1431–1439 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1467-8659.2008.01283.x
Zhang, W., Zheng, J., Thalmann, N.M.: Real-time subspace integration for example-based elastic material. In: Computer Graphics Forum, vol. 34, pp. 395–404. Wiley Online Library (2015)
Zou, H., Hastie, T.: Regularization and variable selection via the elastic net. J. R. Stat. Soc. Ser. B (Stat. Methodol.) 67(2), 301–320 (2005)
Acknowledgements
Funding was provided by European Research Council (Grant No. 267414).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Alon Shtern and Matan Sela have contributed equally to this work.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Supplementary material 1 (mp4 12921 KB)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Shtern, A., Sela, M. & Kimmel, R. Fast Blended Transformations for Partial Shape Registration. J Math Imaging Vis 60, 913–928 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10851-017-0782-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10851-017-0782-9