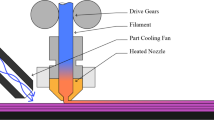
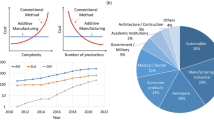
Abstract
As the 3D printing polymer material extrusion process is moving beyond niche markets and into large-scale manufacturing, still commercial systems employed by this process work in an open-loop environment where no feedback or control solution is provided from batch-to-batch production. This issue causes significant differences in part quality and generates lower production efficiency. However, there are substantial innovations in terms of smart manufacturing (SM) technologies, where the use of integrated smart sensors, the internet-of-things (IoT), big data, and artificial intelligence (AI) tools, that applied can let the systems evolve into a closed-loop higher rentability mass production process. This study investigates the available smart manufacturing technologies applied to evaluate the current state-of-the-art. This paper used scientometric analysis to analyze the most important contributions in this area. A systematic review aims to verify the results and understand the publications related to the polymer material extrusion process in detail. The analysis concludes that the most investigated aspect is the relation between the mechanical properties of materials and the high anisotropy presented in the process. The conclusions show that different sensors have been integrated, such as digital cameras, thermal cameras, thermocouples, and accelerometers, among others. They all obtain metrics and use data models to make supported decisions. Furthermore, AI algorithms have been applied to the process, and significant progress has been made to detect quality failures or part defects. Finally, as a substantial conclusion, it has been found that there is still no system in the market that can provide integral feedback control and process adjustment in real-time. This brings a positive opportunity to improve and achieve a fully smart manufacturing system in the 3D printing polymer material extrusion process.












Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- SM:
-
Smart manufacturing
- IoT:
-
Internet of Things
- AI:
-
Artificial intelligence
- ML:
-
Machine learning
- AM:
-
Additive manufacturing
- FDM:
-
Fused deposition modelling
- FFF:
-
Fused filament fabrication
- SMEs:
-
Small and medium enterprises
- EPC:
-
Engineering process control
- SPC:
-
Statistical process control
- CPPS:
-
Cyber physical production system
- PLA:
-
Polylactic acid
- ABS:
-
Acrylonitrile butadiene styrene
- SVM:
-
Supported vector machine
- HUE:
-
Hue saturation lightness
- ANN:
-
Artificial neural network
- GBC:
-
Gradient boosting classifier
- CNN:
-
Convolutional neural network
- DML:
-
Distributed machine learning
- ESN:
-
Echo state network
- IMU:
-
Inertial mapping unit
- GAN:
-
Generative adversarial network
References
Aggour, K. S., Gupta, V. K., Ruscitto, D., Ajdelsztajn, L., Bian, X., Brosnan, K. H., Kumar, N.C., Dheeradhada, V., Hanlon, T., Iyer, N., & Karandikar, J. (2019). Artificial intelligence/machine learning in manufacturing and inspection: A GE perspective. MRS Bulletin, 44(7), 545–558. https://doi.org/10.1557/mrs.2019.157
Ahn, S. H., Montero, M., Odell, D., Roundy, S., & Wright, P. K. (2002). Anisotropic material properties of fused deposition modeling ABS. Rapid Prototyping Journal, 8(4), 248–257. https://doi.org/10.1108/13552540210441166
Ahuett-Garza, H., & Kurfess, T. (2018). A brief discussion on the trends of habilitating technologies for Industry 4.0 and Smart manufacturing. Manufacturing Letters, 15, 60–63. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mfglet.2018.02.011
Alsayyed, B., Siadat, A., Alghamdy, M., Ahmad, R., & Alsayyed, B. (2019). Material selection methodology for additive manufacturing applications. Procedia CIRP, 84, 486–490. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.procir.2019.04.265
Anderegg, D. A., Bryant, H. A., Ruffin, D. C., Skrip, S. M., Fallon, J. J., Gilmer, E. L., & Bortner, M. J. (2019). In-situ monitoring of polymer flow temperature and pressure in extrusion based additive manufacturing. Additive Manufacturing, 26, 76–83. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.addma.2019.01.002
Arinez, J. F., Chang, Q., Gao, R. X., Xu, C., & Zhang, J. (2020). Artificial intelligence in advanced manufacturing: Current status and future outlook. Journal of Manufacturing Science and Engineering. https://doi.org/10.1115/1.4047855
Ashima, R., Haleem, A., Bahl, S., Javaid, M., Mahla, S. K., & Singh, S. (2021). Automation and manufacturing of smart materials in additive manufacturing technologies using Internet of Things towards the adoption of industry 4.0. Materials Today: Proceedings, 45, 5081–5088. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matpr.2021.01.583
Ayrilmis, N., Kariz, M., Kwon, J. H., & Kitek Kuzman, M. (2019). Effect of printing layer thickness on water absorption and mechanical properties of 3D-printed wood/PLA composite materials. International Journal of Advanced Manufacturing Technology, 102(5–8), 2195–2200. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-019-03299-9
Baca, D., & Ahmad, R. (2020). The impact on the mechanical properties of multi-material polymers fabricated with a single mixing nozzle and multi-nozzle systems via fused deposition modeling. International Journal of Advanced Manufacturing Technology, 106(9–10), 4509–4520. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-020-04937-3
Balletti, C., Ballarin, M., & Guerra, F. (2017). 3D printing: State of the art and future perspectives. Journal of Cultural Heritage, 26, 172–182. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.culher.2017.02.010
Banadaki, Y. M. (2019). On the use of machine learning for additive manufacturing technology in industry 4.0. Journal of Computer Science and Information Technology. https://doi.org/10.15640/jcsit.v7n2a7
Banjanin, B., Vladić, G., Pál, M., Baloš, S., Dramićanin, M., Rackov, M., & Kneţević, I. (2018). Consistency analysis of mechanical properties of elements produced by FDM additive manufacturing technology. Revista Materia. https://doi.org/10.1590/s1517-707620180004.0584
Basgul, C., MacDonald, D. W., Siskey, R., & Kurtz, S. M. (2020). Thermal localization improves the interlayer adhesion and structural integrity of 3D printed PEEK lumbar spinal cages. Materialia. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mtla.2020.100650
Baumann, F., & Roller, D. (2016). Vision based error detection for 3D printing processes. MATEC Web of Conferences. https://doi.org/10.1051/conf/2016
Baumann, F., Schön, M., Eichhoff, J., & Roller, D. (2016). Concept development of a sensor array for 3D printer. Procedia CIRP, 51, 24–31. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.procir.2016.05.041
Bisheh, M. N., Chang, S. I., & Lei, S. (2021). A layer-by-layer quality monitoring framework for 3D printing. Computers and Industrial Engineering. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cie.2021.107314
Cai, Y., Wu, J., & Zaheer, M. (2022). Analysis the research hotspots and key technical of intelligent manufacturing. ACM International Conference Proceeding Series. https://doi.org/10.1145/3535782.3535827
Cantrell, J. T., Rohde, S., Damiani, D., Gurnani, R., DiSandro, L., Anton, J., Young, A., Jerez, A., Steinbach, D., Kroese, C. & Ifju, P. (2017). Experimental characterization of the mechanical properties of 3D-printed ABS and polycarbonate parts. Rapid Prototyping Journal, 23(4), 811–824. https://doi.org/10.1108/RPJ-03-2016-0042
Chen, C. (2004). Searching for intellectual turning points: Progressive knowledge domain visualization. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 101(SUPPL. 1), 5303–5310. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.0307513100
Chen, M. Y., Skewes, J., Woodruff, M. A., Dasgupta, P., & Rukin, N. J. (2020). Multi-colour extrusion fused deposition modelling: A low-cost 3D printing method for anatomical prostate cancer models. Scientific Reports, 10(1), 3–7. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-020-67082-7
Christiyan, K. G. J., Chandrasekhar, U., & Venkateswarlu, K. (2016). A study on the influence of process parameters on the Mechanical Properties of 3D printed ABS composite. IOP Conference Series: Materials Science and Engineering. https://doi.org/10.1088/1757-899X/114/1/012109
Coogan, T. J., & Kazmer, D. O. (2017). Healing simulation for bond strength prediction of FDM. Rapid Prototyping Journal, 23(3), 551–561. https://doi.org/10.1108/RPJ-03-2016-0051
Coogan, T. J., & Kazmer, D. O. (2019). In-line rheological monitoring of fused deposition modeling. Journal of Rheology, 63(1), 141–155. https://doi.org/10.1122/1.5054648
Costa, S. F., Duarte, F. M., & Covas, J. A. (2015). Thermal conditions affecting heat transfer in FDM/FFE: A contribution towards the numerical modelling of the process: This paper investigates convection, conduction and radiation phenomena in the filament deposition process. Virtual and Physical Prototyping, 10(1), 35–46. https://doi.org/10.1080/17452759.2014.984042
Craveiro, F., Duarte, J. P., Bartolo, H., & Bartolo, P. J. (2019). Additive manufacturing as an enabling technology for digital construction: A perspective on Construction 4.0. Automation in Construction, 103(March), 251–267. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.autcon.2019.03.011
Cruz, S., Paulino, A., Duraes, J., & Mendes, M. (2021). Real-time quality control of heat sealed bottles using thermal images and artificial neural network. Journal of Imaging. https://doi.org/10.3390/jimaging7020024
Dadhwal, R., Kumar, R., Singh Chohan, J., Singh, S., & Maurya, S. (2023). Research trends and applications of artificial intelligence in 3D printing-A scientometric analysis. Springer. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-19-2538-2_39
Dave, H. K., Patadiya, N. H., Prajapati, A. R., & Rajpurohit, S. R. (2021). Effect of infill pattern and infill density at varying part orientation on tensile properties of fused deposition modeling-printed poly-lactic acid part. Proceedings of the Institution of Mechanical Engineers, Part C: Journal of Mechanical Engineering Science, 235(10), 1811–1827. https://doi.org/10.1177/0954406219856383
Delli, U., & Chang, S. (2018). Automated process monitoring in 3D printing using supervised machine learning. Procedia Manufacturing, 26, 865–870. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.promfg.2018.07.111
Deng, X., Zeng, Z., Peng, B., Yan, S., & Ke, W. (2018). Mechanical properties optimization of poly-ether-ether-ketone via fused deposition modeling. Materials. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma11020216
Dezaki, M. L., Mohd Ariffin, M. K. A., & Ariffin, M. K. A. M. (2020). The effects of combined infill patterns on mechanical properties in fdm process. Polymers, 12(12), 1–20. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym12122792
Dilberoglu, U. M., Gharehpapagh, B., Yaman, U., & Dolen, M. (2017). The role of additive manufacturing in the era of Industry 4.0. Procedia Manufacturing, 11(June), 545–554. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.promfg.2017.07.148
Dinwiddie, R. B., Love, L. J., & Rowe, J. C. (2013). Real-time process monitoring and temperature mapping of a 3D polymer printing process. Thermosense: Thermal Infrared Applications XXXV, 8705, 87050L. https://doi.org/10.1117/12.1518454
Dudescu, C., & Racz, L. (2017). Effects of raster orientation, infill rate and infill pattern on the mechanical properties of 3D printed materials. ACTA Universitatis Cibiniensis, 69(1), 23–30. https://doi.org/10.1515/aucts-2017-0004
Durgun, I., & Ertan, R. (2014). Experimental investigation of FDM process for improvement of mechanical properties and production cost. Rapid Prototyping Journal, 20(3), 228–235. https://doi.org/10.1108/RPJ-10-2012-0091
Duty, C., Failla, J., Kim, S., Lindahl, J., Post, B., Love, L., & Kunc, V. (2020). Reducing mechanical anisotropy in extrusion-based printed parts. In: Solid Freeform Fabrication 2017: Proceedings of the 28th annual international solid freeform fabrication symposium—An additive manufacturing conference, SFF 2017 (pp. 1602–1611).
Duty, C., Failla, J., Kim, S., Smith, T., Lindahl, J., & Kunc, V. (2019). Z-Pinning approach for 3D printing mechanically isotropic materials. Additive Manufacturing, 27(March), 175–184. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.addma.2019.03.007
Elkaseer, A., Schneider, S., & Scholz, G. (2020). Experiment-based process modeling and optimization for high-quality and resource-efficient. Applied Science, 10, 2899.
Fatimatuzahraa, A. W., Farahaina, B., & Yusoff, W. A. Y. Y. (2011). The effect of employing different raster orientations on the mechanical properties and microstructure of Fused Deposition Modeling parts. In ISBEIA 2011 - 2011 IEEE symposium on business, engineering and industrial applications (pp. 22–27). https://doi.org/10.1109/ISBEIA.2011.6088811
Ferraris, E., Zhang, J., Hooreweder, B. V., & Van Hooreweder, B. (2019). Thermography based in-process monitoring of Fused Filament Fabrication of polymeric parts. CIRP Annals, 68(1), 213–216. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cirp.2019.04.123
Frazier, W. E. (2014). Metal additive manufacturing: A review. Journal of Materials Engineering and Performance, 23(6), 1917–1928. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11665-014-0958-z
Galeta, T., Raos, P., Stojšić, J., & Pakši, I. (2016). Influence of structure on mechanical properties of 3D printed objects. Procedia Engineering, 149(June), 100–104. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.proeng.2016.06.644
Gardan, J. (2016). Additive manufacturing technologies: State of the art and trends. International Journal of Production Research, 54(10), 3118–3132. https://doi.org/10.1080/00207543.2015.1115909
Goh, G. D., Sing, S. L., & Yeong, W. Y. (2021). A review on machine learning in 3D printing: Applications, potential, and challenges. Artificial Intelligence Review. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10462-020-09876-9
Gonabadi, H., Yadav, & A., & Bull, S. J. (n.d.). The effect of processing parameters on the mechanical characteristics of PLA produced by a 3D FFF printer. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-020-06138-4/Published
Granovsky, Y. V. (2001). Is it possible to measure science? V. V. Nalimov’s research in scientometrics. Scientometrics, 52, 127–150.
Guo, N., & Leu, M. C. (2013). Additive manufacturing: Technology, applications and research needs. Frontiers of Mechanical Engineering. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11465-013-0248-8
Han, Y., & Jia, G. (2017). Optimizing product manufacturability in 3D printing. Frontiers of Computer Science, 11(2), 347–357. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11704-016-6154-6
Hermann, M., Pentek, T., & Otto, B. (2016). Design principles for industrie 4.0 scenarios. In Proceedings of the Annual Hawaii International Conference on System Sciences (Vol. 2016-March, pp. 3928–3937). IEEE Computer Society. https://doi.org/10.1109/HICSS.2016.488
Herron, C., Ivus, M., Kotak, A. (2021). Just Press "Print": Canada’s additive manufacturing ecosystem. In Information and Communications Technology Council (ICTC), Ottawa, Canada.
Holzmond, O., & Li, X. (2017). In situ real time defect detection of 3D printed parts. Additive Manufacturing, 17, 135–142. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.addma.2017.08.003
Hossain, M. S., Ramos, J., Espalin, D., Perez, M., Wicker, R., & Keck, W. M. Improving tensile mechanical properties of FDM-manufactured specimens via modifying build parameters (2013)
Hu, J. (2020). Study on STL-based slicing process for 3D printing. In Solid freeform fabrication 2017: Proceedings of the 28th annual international solid freeform fabrication symposium—An additive manufacturing conference, SFF 2017 (pp. 885–895).
Huang, T., Wang, S., & He, K. (2015). Quality control for fused deposition modeling based additive manufacturing: Current research and future trends. In Proceedings of 2015 the 1st international conference on reliability systems engineering, ICRSE 2015. Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers Inc. https://doi.org/10.1109/ICRSE.2015.7366500
Jain, P., & Kuthe, A. M. (2013). Feasibility study of manufacturing using rapid prototyping: FDM approach. Procedia Engineering, 63, 4–11. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.proeng.2013.08.275
Jan van Eck, N., & Waltman, L. (2022). VOSviewer Manual. Manual for VOSviewer version 1.6.18.
Jawad Qureshi, A. (2015). Design for scalability and strength Optimisation for components created through FDM process. https://www.researchgate.net/publication/281068948
Kang, H. S., Lee, J. Y., Choi, S., Kim, H., Park, J. H., Son, J. Y., Kim, B. H., & Noh, S. D. (2016). Smart manufacturing: Past research, present findings, and future directions. International Journal of Precision Engineering and Manufacturing - Green Technology, 3(1), 111–128. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40684-016-0015-5
Karakurt, I., & Lin, L. (2020). 3D printing technologies: Techniques, materials, and post-processing. Current Opinion in Chemical Engineering, 28, 134–143. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.coche.2020.04.001
Kariz, M., Sernek, M., & Kuzman, M. K. (2018). Effect of humidity on 3D-printed specimens from wood-pla filaments. Wood Research, 63(5), 917–922.
Kazemian, A., & Khoshnevis, B. (2021). Real-time extrusion quality monitoring techniques for construction 3D printing. Construction and Building Materials, 303(January), 124520. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2021.124520
Khan, M. F., Alam, A., Siddiqui, M. A., Alam, M. S., Rafat, Y., Salik, N., & Al-Saidan, I. (2020). Real-time defect detection in 3D printing using machine learning. Materials Today: Proceedings, 42, 521–528. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matpr.2020.10.482
Khandpur, M. S., Galati, M., Minetola, P., Marchiandi, G., Fontana, L., & Stiuso, V. (2021). Development of a low-cost monitoring system for open 3 d printing. IOP Conference Series: Materials Science and Engineering. https://doi.org/10.1088/1757-899x/1136/1/012044
Khoo, Z. X., Teoh, J. E. M., Liu, Y., Chua, C. K., Yang, S., An, J., Leong, K. F., & Yeong, W. Y. (2015). 3D printing of smart materials: A review on recent progresses in 4D printing. Virtual and Physical Prototyping, 10(3), 103–122. https://doi.org/10.1080/17452759.2015.1097054
Kim, D.-S., & Tran-Dang, H. (2019). Industrial sensors and controls in communication networks. Cham: Springer. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-04927-0
Kopsacheilis, C., Charalampous, P., Kostavelis, I., & Tzovaras, D. (2020) In situ visual quality control in 3D printing. In 11th international conference on information visualization theory and applications. https://orcid.org/0000-0002-9399-4387
Korner, M. E. H., Lambán, M. P., Albajez, J. A., Santolaria, J., Corrales, L. D. C. N., & Royo, J. (2020). Systematic literature review: Integration of additive manufacturing and industry 4.0. Metals, 10(8), 1–24. https://doi.org/10.3390/met10081061
Kuclourya, T., Monroy, R., Cuan-Urquizo, E., Roman-Flores, A., & Ahmad, R. (2022). Scientometric analysis and critical review of fused deposition modeling in the plastic recycling context. Cleaner Waste Systems, 2(April), 100008. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.clwas.2022.100008
Kumar, R., Rogall, C., Thiede, S., Herrmann, C., & Sangwan, K. S. (2021). Development of a decision support system for 3D printing processes based on cyber physical production systems. Procedia CIRP, 98, 348–353. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.procir.2021.01.115
Kusiak, A. (2018). Smart manufacturing. International Journal of Production Research, 56(1–2), 508–517. https://doi.org/10.1080/00207543.2017.1351644
Lambos, N., Vosniakos, G. C., & Papazetis, G. (2020). Low-cost automatic identification of nozzle clogging in material extrusion 3D printers. Procedia Manufacturing, 51, 274–279. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.promfg.2020.10.039
Lee, J. Y., An, J., & Chua, C. K. (2017). Fundamentals and applications of 3D printing for novel materials. Applied Materials Today, 7, 120–133. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apmt.2017.02.004
Lee, W. C., Wei, C. C., & Chung, S. C. (2014). Development of a hybrid rapid prototyping system using low-cost fused deposition modeling and five-axis machining. Journal of Materials Processing Technology, 214(11), 2366–2374. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmatprotec.2014.05.004
Li, C., Cabrera, D., Sancho, F., Cerrada, M., Sánchez, R. V., & Estupinan, E. (2021a). From fault detection to one-class severity discrimination of 3D printers with one-class support vector machine. ISA Transactions, 110, 357–367. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.isatra.2020.10.036
Li, C., Cabrera, D., Sancho, F., Sanchez, R. V., Cerrada, M., De Oliveira, J. V., & De Oliveira, J. V. (2021b). One-shot fault diagnosis of three-dimensional printers through improved feature space learning. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Electronics, 68(9), 8768–8776. https://doi.org/10.1109/TIE.2020.3013546
Li, L., & Liu, J. (2018). Multi-view feature modeling for design-for-additive manufacturing Multi-view feature modeling for design-for-additive manufacturing. Advanced Engineering Informatics. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aei.2018.12.004
Li, S., Freije, E., & Yearling, P. (2017). Monitoring 3D printer performance using internet of things (IoT) application. In ASEE annual conference and exposition, conference proceedings (Vol. 2017-June). American Society for Engineering Education.
Lidong, W., & Guanghui, W. (2016). Big data in cyber-physical systems, digital manufacturing and industry 4.0. International Journal of Engineering and Manufacturing, 6(4), 1–8. https://doi.org/10.5815/ijem.2016.04.01
Liu, J., Chen, Q., Ahmad, R., & Zheng, Y. (2019a). Level set-based heterogeneous object modeling and optimization. Computer-Aided Design. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cad.2019.01.002
Liu, Z., Wang, Y., Wu, B., Cui, C., Guo, Y., & Yan, C. (2019b). A critical review of fused deposition modeling 3D printing technology in manufacturing polylactic acid parts. International Journal of Advanced Manufacturing Technology, 102(9–12), 2877–2889. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-019-03332-x
Lu, Y., & Ju, F. (2017). Smart manufacturing systems based on cyber-physical manufacturing services (CPMS). IFAC-PapersOnLine, 50(1), 15883–15889. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ifacol.2017.08.2349
Luo, X., Zhang, L., Ren, L., & Lali, Y. (2020). A dynamic and static data based matching method for cloud 3D printing. Robotics and Computer-Integrated Manufacturing, 61(September 2019), 101858. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rcim.2019.101858
Lyons, K. (2016). DETC2016-59721 Enabling smart manufacturing technologies for decision- making. In Proc ASME des eng tech conf (pp. 1–10) https://doi.org/10.1115/DETC2016-59721
Ma, G., Li, Z., Wang, L., Wang, F., & Sanjayan, J. (2019). Mechanical anisotropy of aligned fiber reinforced composite for extrusion-based 3D printing. Construction and Building Materials, 202, 770–783. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2019.01.008
Malekipour, E., Attoye, S., & El-Mounayri, H. (2018). Investigation of layer based thermal behavior in fused deposition modeling process by infrared thermography. Procedia Manufacturing, 26, 1014–1022. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.promfg.2018.07.133
Maschio, F., Pandya, M., & Olszewski, R. (2016). Experimental validation of plastic mandible models produced by a “low-cost” 3-dimensional fused deposition modeling printer. Medical Science Monitor, 22, 943–957. https://doi.org/10.12659/MSM.895656
Mehrpouya, M., Dehghanghadikolaei, A., Fotovvati, B., Vosooghnia, A., Emamian, S. S., & Gisario, A. (2019). The potential of additive manufacturing in the smart factory industrial 4.0: A review. Applied Science. https://doi.org/10.3390/app9183865
Mittal, S., Khan, M. A., Romero, D., & Wuest, T. (2018). A critical review of smart manufacturing & Industry 4.0 maturity models: Implications for small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs). Journal of Manufacturing Systems, 49(November), 194–214. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmsy.2018.10.005
Molero, E., Fernández, J. J., Rodríguez-Alabanda, O., Guerrero-Vaca, G., & Romero, P. E. (2020). Use of data mining techniques for the prediction of surface roughness of printed parts in polylactic acid (PLA) by fused deposition modeling (FDM): A practical application in frame glasses manufacturing. Polymers. https://doi.org/10.3390/POLYM12040840
Monostori, L. (2014). Cyber-physical production systems: Roots, expectations and R&D challenges. In Procedia CIRP (Vol. 17, pp. 9–13). Elsevier B.V. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.procir.2014.03.115
Morales, N. G., Fleck, T. J., & Rhoads, J. F. (2018). The effect of interlayer cooling on the mechanical properties of components printed via fused deposition. Additive Manufacturing, 24, 243–248. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.addma.2018.09.001
Najjartabar Bisheh, M., Chang, S. I., & Lei, S. (2021). A layer-by-layer quality monitoring framework for 3D printing. Computers and Industrial Engineering. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cie.2021.107314
Ngo, T. D., Kashani, A., Imbalzano, G., Nguyen, K. T. Q., & Hui, D. (2018). Additive manufacturing (3D printing): A review of materials, methods, applications and challenges. Composites Part B: Engineering, 143(February), 172–196. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compositesb.2018.02.012
Nguyen, N. A., Bowland, C. C., & Naskar, A. K. (2018a). A general method to improve 3D-printability and inter-layer adhesion in lignin-based composites. Applied Materials Today, 12, 138–152. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apmt.2018.03.009
Nguyen, N. A., Bowland, C. C., & Naskar, A. K. (2018b). Mechanical, thermal, morphological, and rheological characteristics of high performance 3D-printing lignin-based composites for additive manufacturing applications. Data in Brief, 19, 936–950. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.dib.2018.05.130
Nuchitprasitchai, S., Roggemann, M., & Pearce, J. M. (2017). Factors effecting real-time optical monitoring of fused filament 3D printing. Progress in Additive Manufacturing, 2(3), 133–149. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40964-017-0027-x
Onu, P., & Mbohwa, C. (2021). Industry 4.0 opportunities in manufacturing SMEs: Sustainability outlook. Materials Today: Proceedings, 44, 1925–1930. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matpr.2020.12.095
Osswald, T., & Menges, G. (2012). Material science of polymers for engineers. Hanser. https://doi.org/10.3139/9781569905241.fm
Paraskevoudis, K., Karayannis, P., & Koumoulos, E. P. (2020). Real-time 3d printing remote defect detection (Stringing) with computer vision and artificial intelligence. Processes, 8(11), 1–15. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr8111464
Peng, F., Vogt, B. D., & Cakmak, M. (2018). Complex flow and temperature history during melt extrusion in material extrusion additive manufacturing. Additive Manufacturing, 22, 197–206. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.addma.2018.05.015
Petsiuk, A., & Pearce, J. M. (2021). Towards smart monitored AM: Open source in-situ layer-wise 3D printing image anomaly detection using histograms of oriented gradients and a physics-based rendering engine. https://doi.org/10.48550/arXiv.2111.02703
Pham, T., & Dimov, S. S. A. (2001). Rapid manufacturing: The technologies and applications of rapid prototyping and rapid tooling. New York: Springer. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4471-0703-3
Piedra-Cascón, W., Krishnamurthy, V. R., Att, W., & Revilla-León, M. (2021). 3D printing parameters, supporting structures, slicing, and post-processing procedures of vat-polymerization additive manufacturing technologies: A narrative review. Journal of Dentistry. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jdent.2021.103630
Rayna, T., & Striukova, L. (2016). From rapid prototyping to home fabrication: How 3D printing is changing business model innovation. Technological Forecasting and Social Change, 102, 214–224. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.techfore.2015.07.023
Sathies, T., Senthil, P., & Anoop, M. S. (2020). A review on advancements in applications of fused deposition modelling process. Rapid Prototyping Journal, 26(4), 669–687. https://doi.org/10.1108/RPJ-08-2018-0199
Schöppner, V., Bagsik, A., & Paderborn, K. (2011). Mechanical properties of fused deposition modeling parts manufactured with ULTEM 9085. In Proceedings of 69th annual technical conference of the society of plastics engineers (Vol. 2, pp. 1–5). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.polymertesting.2018.10.040
Sepasgozar, S. M. E., Shi, A., Yang, L., Shirowzhan, S., & Edwards, D. J. (2020). Additive manufacturing applications for industry 4.0: A systematic critical review. Buildings, 10(12), 1–35. https://doi.org/10.3390/buildings10120231
Shaffer, S., Yang, K., Vargas, J., Di Prima, M. A., & Voit, W. (2014). On reducing anisotropy in 3D printed polymers via ionizing radiation. Polymer, 55(23), 5969–5979. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.polymer.2014.07.054
Shahmirzadi, M. R., Gholampour, A., Kashani, A., & Ngo, T. D. (2021). Shrinkage behavior of cementitious 3D printing materials: Effect of temperature and relative humidity. Cement and Concrete Composites, 124, 104238. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cemconcomp.2021.104238
Shahrubudin, N., Lee, T. C., & Ramlan, R. (2019). An overview on 3D printing technology: Technological, materials, and applications. Procedia Manufacturing, 35, 1286–1296. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.promfg.2019.06.089
Shamseer, L., Moher, D., Clarke, M., Ghersi, D., Liberati, A., Petticrew, M., Shekelle, P., & Stewart, L. A. (2015). Preferred reporting items for systematic review and meta-analysis protocols (prisma-p) 2015: Elaboration and explanation. BMJ. https://doi.org/10.1136/bmj.g7647
Shim, J. S., Kim, J. E., Jeong, S. H., Choi, Y. J., & Ryu, J. J. (2020). Printing accuracy, mechanical properties, surface characteristics, and microbial adhesion of 3D-printed resins with various printing orientations. Journal of Prosthetic Dentistry, 124(4), 468–475. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.prosdent.2019.05.034
Silverman, A. E. (2019). Artificial intelligence and legal reasoning In Mind, machine, and metaphor (pp. 3–33). Routledge. https://doi.org/10.4324/9780429038075-2
Singh, R., & Garg, H. K. (2016). Fused deposition modelling—A state of art review and future applications. Elsevier Ltd. https://doi.org/10.1016/b978-0-12-803581-8.04037-6
Srinivasan, R., Giannikas, V., McFarlane, D., & Thorne, A. (2018). Customising with 3D printing: The role of intelligent control. Computers in Industry, 103, 38–46. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compind.2018.09.003
Straub, J. (2015). Initial work on the characterization of additive manufacturing (3D printing) using software image analysis. Machines, 3(2), 55–71. https://doi.org/10.3390/machines3020055
Su, H. N., & Lee, P. C. (2010). Mapping knowledge structure by keyword co-occurrence: A first look at journal papers in Technology Foresight. Scientometrics, 85(1), 65–79. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11192-010-0259-8
Sunny, B. C., Benedict, S., Rajan, M. P., & Srinivas, M. (2019). Impact of printing parameters on energy consumption of 3D printers using IoT cloud architecture. In 2019 IEEE 16th India council international conference, INDICON 2019—symposium proceedings. Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers Inc. https://doi.org/10.1109/INDICON47234.2019.9029069
Syrlybayev, D., Zharylkassyn, B., Seisekulova, A., Akhmetov, M., Perveen, A., & Talamona, D. (2021). Optimisation of strength properties of FDM printed parts—A critical review. Polymers. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym13101587
Tetsuka, H., & Shin, S. R. (2020). Materials and technical innovations in 3D printing in biomedical applications. Journal of Materials Chemistry B, 8(15), 2930–2950. https://doi.org/10.1039/d0tb00034e
Tlegenov, Y., Hong, G. S., & Lu, W. F. (2018). Nozzle condition monitoring in 3D printing. Robotics and Computer-Integrated Manufacturing, 54, 45–55. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rcim.2018.05.010
Torrado, A. R., & Roberson, D. A. (2016). Failure analysis and anisotropy evaluation of 3D-printed tensile test specimens of different geometries and print raster patterns. Journal of Failure Analysis and Prevention, 16(1), 154–164. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11668-016-0067-4
Torrado, A. R., Shemelya, C. M., English, J. D., Lin, Y., Wicker, R. B., & Roberson, D. A. (2015). Characterizing the effect of additives to ABS on the mechanical property anisotropy of specimens fabricated by material extrusion 3D printing. Additive Manufacturing, 6, 16–29. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.addma.2015.02.001
Tymrak, B. M., Kreiger, M., & Pearce, J. M. (2014). Mechanical properties of components fabricated with open-source 3-D printers under realistic environmental conditions. Materials and Design, 58, 242–246. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matdes.2014.02.038
Upadhyay, K., Dwivedi, R., & Singh, A. K. (2016). Determination and comparison of the anisotropic strengths of fused deposition modeling P400 ABS. In Advances in 3D printing and additive manufacturing technologies (pp. 9–28). Springer. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-10-0812-2_2
Vanaei, H. R., Raissi, K., Deligant, M., Shirinbayan, M., Fitoussi, J., Khelladi, S., & Tcharkhtchi, A. (2020). Toward the understanding of temperature effect on bonding strength, dimensions and geometry of 3D-printed parts. Journal of Materials Science, 55(29), 14677–14689. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10853-020-05057-9
Walsh, G. S., Przychodzen, J., & Przychodzen, W. (2017). Supporting the SME commercialization process: The case of 3D printing platforms. Small Enterprise Research, 24(3), 257–273. https://doi.org/10.1080/13215906.2017.1396490
Wang, B., Tao, F., Fang, X., Liu, C., Liu, Y., & Freiheit, T. (2021). Smart manufacturing and intelligent manufacturing: A comparative review. Engineering, 7(6), 738–757. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eng.2020.07.017
Wickramasinghe, S., Do, T., & Tran, P. (2020). FDM-Based 3D printing of polymer and associated composite: A review on mechanical properties, defects and treatments. Polymers, 12(7), 1–42. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym12071529
Wu, H. C., & Chen, T. C. T. (2018). Quality control issues in 3D-printing manufacturing: A review. Rapid Prototyping Journal, 24(3), 607–614. https://doi.org/10.1108/RPJ-02-2017-0031
Xu, L. D., He, W., & Li, S. (2014). Internet of things in industries: A survey. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Informatics. https://doi.org/10.1109/TII.2014.2300753
Yang, H., Kumara, S., Bukkapatnam, S. T. S., & Tsung, F. (2019). The internet of things for smart manufacturing: A review. IISE Transactions, 51(11), 1190–1216. https://doi.org/10.1080/24725854.2018.1555383
Yao, X., Zhou, J., Zhang, J., & Boer, C. R. (2017). From intelligent manufacturing to smart manufacturing for Industry 4.0 driven by next generation artificial intelligence and further on. In Proceedings—2017 5th international conference on enterprise systems: industrial digitalization by enterprise systems, ES 2017 (pp. 311–318). https://doi.org/10.1109/ES.2017.58
Yin, J., Lu, C., Fu, J., Huang, Y., & Zheng, Y. (2018). Interfacial bonding during multi-material fused deposition modeling (FDM) process due to inter-molecular diffusion. Materials and Design, 150, 104–112. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matdes.2018.04.029
Yu, H., Hong, H., Cao, S., & Ahmad, R. (2020). Topology optimization for multipatch fused deposition modeling 3D printing. Applied Sciences (switzerland). https://doi.org/10.3390/app10030943
Zhang, S., He, K., Cabrera, D., Li, C., Bai, Y., & Long, J. (2019). Transmission condition monitoring of 3d printers based on the echo state network. Applied Sciences (switzerland). https://doi.org/10.3390/app9153058
Zheng, P., Wang, H., Sang, Z., Zhong, R. Y., Liu, Y., Liu, C., Mubarok, K., Yu, S., & Xu, X. (2018). Smart manufacturing systems for Industry 4.0: Conceptual framework, scenarios, and future perspectives. Frontiers of Mechanical Engineering, 13(2), 137–150. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11465-018-0499-5
Zheng, Y., Zhang, W., Lopez, D. M. B., & Ahmad, R. (2021). Scientometric analysis and systematic review of multi-material additive manufacturing of polymers. Polymers. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym13121957
Zhong, R. Y., Xu, X., Klotz, E., & Newman, S. T. (2017). Intelligent manufacturing in the context of Industry 4.0: A review. Engineering, 3(5), 616–630. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.ENG.2017.05.015
Zhou, X., Hsieh, S. J., & Sun, Y. (2017). Experimental and numerical investigation of the thermal behaviour of polylactic acid during the fused deposition process. Virtual and Physical Prototyping, 12(3), 221–233. https://doi.org/10.1080/17452759.2017.1317214
Acknowledgements
The authors acknowledge the financial support of this work by the Natural Sciences and Engineering Research Council of Canada (Grant No. NSERC ALLRP 561048-20 Ahmad) and Alberta Innovates (Grant No. AB Innovat ADVANCE 202102739A) for funding this project. The authors express their sincere gratitude to all the team members of the Laboratory of Intelligent Manufacturing, Design, and Automation (LIMDA) group for sharing their thoughts and wisdom during the research.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Castillo, M., Monroy, R. & Ahmad, R. Scientometric analysis and systematic review of smart manufacturing technologies applied to the 3D printing polymer material extrusion system. J Intell Manuf 35, 3–33 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10845-022-02049-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10845-022-02049-1