Abstract
Purpose
The purpose of this study is to identify the electrophysiological factors affecting symptoms in paroxysmal atrial fibrillation (PAF) using patients with paroxysmal atrial fibrillation and pacemakers with advanced atrial fibrillation (AF) diagnostics.
Methods
Seventy-nine patients (age 71.0 ± 8.2, 54.4% male) with symptomatic PAF and AF burden of 1% to 50% with DDDRP pacemakers implanted were assessed for 6 months. Patients recorded symptom onset and duration and these were correlated with device-derived electrophysiological data.
Results
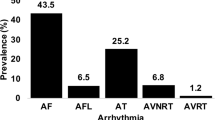
Of 2,638 AF episodes, 333 were symptomatic and 2,305 asymptomatic, with 194 non-atrial tachyarrhythmia symptomatic episodes giving a sensitivity of 12.6% and a positive predictive value of 63.2% for specific AF symptoms. Symptomatic AF episodes were 3.8 times more common diurnally than nocturnally (p < 0.001). Diurnally, symptomatic AF was significantly associated with a shorter AF cycle length (CL; p = 0.04), faster ventricular rate (p = 0.004), shorter PR interval (p < 0.001), faster preceding heart rate (p = 0.001) and increased early recurrence of AF (p < 0.04). Nocturnally, a significantly longer AF CL (p = 0.04) and PR interval (p < 0.001) prior to AF onset predicted symptomatic AF.
Conclusions
Symptoms in PAF are predicted by changes in AF episode duration, ventricular rate during AF, preceding sinus heart rate, AV nodal conduction and AF cycle length but not ventricular irregularity. Excess diurnal sympathetic tone and excess nocturnal vagal tone predispose to symptomatic PAF. These findings may have relevance for therapies for symptom control of PAF.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Strickberger, S. A., IP, J., Saksena, S., Curry, K., Bahnson, T. D., & Ziegler, P. D. (2005). Relationship between atrial tachyarrhythmias and symptoms. Heart Rhythm, 2(2), 125–131.
Israel, C. W., Gronefeld, G., Ehrlich, J. R., Li, Y. G., & Hohnloser, S. H. (2004). Long-term risk of recurrent atrial fibrillation as documented by an implantable monitoring device: implications for optimal patient care. Journal of the American College of Cardiology, 43(1), 47–52.
Hoffmann, E., Sulke, N., Edvardsson, N., Ruiter, J., Lewalter, T., Capucci, A., et al. (2006). New insights into the initiation of atrial fibrillation: a detailed intraindividual and interindividual analysis of the spontaneous onset of atrial fibrillation using new diagnostic pacemaker features. Circulation, 113(16), 1933–1941.
Sulke, N., Silberbauer, J., Boodhoo, L., Freemantle, N., Kamalvand, K., O'Nunain, S., et al. (2007). The use of atrial overdrive and ventricular rate stabilization pacing algorithms for the prevention and treatment of paroxysmal atrial fibrillation: the Pacemaker Atrial Fibrillation Suppression (PAFS) study. Europace, 9(9), 790–797.
Carlioz, R., Perrier, E., Thomas, O., Fossati, F., Jarwe, M., Klug, D., et al. (2000). Accuracy of atrial tachyarrhythmia monitoring in a Selection device: correlation with an external Holter recording. Europace, 1(Suppl D), 9–10. Ref Type: Abstract.
Silberbauer, J., Arya, A., Freemantle, N., Paul, V., Lloyd, G. W., Patel, N. R., et al. (2006). How accurate are beat to beat Holters in implantable devices? Heart Rhythm, 3(1S), 126.
de Voogt, W. G., Van Hemel, N. M., van de Bos, A. A., Koistinen, J., & Fast, J. H. (2006). Verification of pacemaker automatic mode switching for the detection of atrial fibrillation and atrial tachycardia with Holter recording. Europace, 8(11), 950–961.
Yamasaki, Y., Kodama, M., Matsuhisa, M., Kishimoto, M., Ozaki, H., Tani, A., et al. (1996). Diurnal heart rate variability in healthy subjects: effects of aging and sex difference. American Journal of Physiology, 271(1 Pt 2), H303–H310.
Meurling, C. J., Waktare, J. E., Holmqvist, F., Hedman, A., Camm, A. J., Olsson, S. B., et al. (2001). Diurnal variations of the dominant cycle length of chronic atrial fibrillation. American Journal of Physiology. Heart and Circulatory Physiology, 280(1), H401–H406.
Page, R. L., Wilkinson, W. E., Clair, W. K., McCarthy, E. A., & Pritchett, E. L. (1994). Asymptomatic arrhythmias in patients with symptomatic paroxysmal atrial fibrillation and paroxysmal supraventricular tachycardia. Circulation, 89(1), 224–227.
Frykman, V., Ayers, G. M., Darpo, B., & Rosenqvist, M. (2003). What characterizes episodes of atrial fibrillation requiring cardioversion? Experience from patients with an implantable atrial cardioverter. American Heart Journal, 145(4), 670–675.
Wolk, R., Kulakowski, P., Karczmarewicz, S., Karpinski, G., Makowska, E., Czepiel, A., et al. (1996). The incidence of asymptomatic paroxysmal atrial fibrillation in patients treated with propranolol or propafenone. International Journal of Cardiology, 54(3), 207–211.
Sopher, S. M., Hnatkova, K., Waktare, J. E., Murgatroyd, F. D., Camm, A. J., & Malik, M. (1998). Circadian variation in atrial fibrillation in patients with frequent paroxysms. Pacing and Clinical Electrophysiology, 21(11 Pt 2), 2445–2449.
Mitchell, A. R., Spurrell, P. A., Ahmet, H., Higson, M., & Sulke, N. (2002). Reversal of tachycardiomyopathy by the atrial defibrillator. European Journal of Heart Failure, 4(4), 485–488.
Quiniou, G., Chevalier, J. M., Barbou, F., Bire, F., & Clementy, J. (2000). Tachycardia-induced cardiomyopathy, unusual and reversible cause of left ventricular dysfunction: report of 9 cases. Annales de Cardiologie et d'angéiologie (Paris), 49(5), 301–308.
Patten, M., Maas, R., Karim, A., Muller, H. W., Simonovsky, R., & Meinertz, T. (2006). Event-recorder monitoring in the diagnosis of atrial fibrillation in symptomatic patients: subanalysis of the SOPAT trial. Journal of Cardiovascular Electrophysiology, 17(11), 1216–1220.
Clark, D. M., Plumb, V. J., Epstein, A. E., & Kay, G. N. (1997). Hemodynamic effects of an irregular sequence of ventricular cycle lengths during atrial fibrillation. Journal of the American College of Cardiology, 30(4), 1039–1045.
Daoud, E. G., Weiss, R., Bahu, M., Knight, B. P., Bogun, F., Goyal, R., et al. (1996). Effect of an irregular ventricular rhythm on cardiac output. American Journal of Cardiology, 78(12), 1433–1436.
Brignole, M., Gianfranchi, L., Menozzi, C., Alboni, P., Musso, G., Bongiorni, M. G., et al. (1997). Assessment of atrioventricular junction ablation and DDDR mode-switching pacemaker versus pharmacological treatment in patients with severely symptomatic paroxysmal atrial fibrillation: a randomized controlled study. Circulation, 96(8), 2617–2624.
Kay, G. N., Ellenbogen, K. A., Giudici, M., Redfield, M. M., Jenkins, L. S., Mianulli, M., et al. (1998). The Ablate and Pace Trial: a prospective study of catheter ablation of the AV conduction system and permanent pacemaker implantation for treatment of atrial fibrillation. APT Investigators. Journal of Interventional Cardiac Electrophysiology : An International Journal of Arrhythmias and Pacing, 2(2), 121–135.
Wood, M. A., Brown-Mahoney, C., Kay, G. N., & Ellenbogen, K. A. (2000). Clinical outcomes after ablation and pacing therapy for atrial fibrillation : a meta-analysis. Circulation, 101(10), 1138–1144.
Duckers, H. J., van Hemel, N. M., Kelder, J. C., Bakema, H., & Yee, R. (1997). Effective use of a novel rate-smoothing algorithm in atrial fibrillation by ventricular pacing. European Heart Journal, 18(12), 1951–1955.
Simpson, C. S., Yee, R., Lee, J. K., Braney, M., Klein, G. J., Krahn, A. D., et al. (2001). Safety and feasibility of a novel rate-smoothed ventricular pacing algorithm for atrial fibrillation. American Heart Journal, 142(2), 294–300.
Tse, H. F., Newman, D., Ellenbogen, K. A., Buhr, T., Markowitz, T., & Lau, C. P. (2004). Effects of ventricular rate regularization pacing on quality of life and symptoms in patients with atrial fibrillation (Atrial fibrillation symptoms mediated by pacing to mean rates [AF SYMPTOMS study]). American Journal of Cardiology, 94(7), 938–941.
Liu, L., & Nattel, S. (1997). Differing sympathetic and vagal effects on atrial fibrillation in dogs: role of refractoriness heterogeneity. American Journal of Physiology, 273(2 Pt 2), H805–H816.
Zipes, D. P., Mihalick, M. J., & Robbins, G. T. (1974). Effects of selective vagal and stellate ganglion stimulation of atrial refractoriness. Cardiovascular Research, 8(5), 647–655.
Holmqvist, F., Stridh, M., Waktare, J. E., Brandt, J., Sornmo, L., Roijer, A., et al. (2005). Rapid fluctuations in atrial fibrillatory electrophysiology detected during controlled respiration. American Journal of Physiology. Heart and Circulatory Physiology, 289(2), H754–H760.
Sasaki, T., Niwano, S., Sasaki, S., Imaki, R., Yuge, M., Hirasawa, S., et al. (2006). Long-term follow-up of changes in fibrillation waves in patients with persistent atrial fibrillation: spectral analysis of surface ECG. Circulation Journal, 70(2), 169–173.
Hayano, J., Sakata, S., Okada, A., Mukai, S., & Fujinami, T. (1998). Circadian rhythms of atrioventricular conduction properties in chronic atrial fibrillation with and without heart failure. Journal of the American College of Cardiology, 31(1), 158–166.
Khand, A. U., Rankin, A. C., Cleland, J. G., Gemmell, I., Clark, E., & Macfarlane, P. W. (2006). The assessment of autonomic function in chronic atrial fibrillation: description of a non-invasive technique based on circadian rhythm of atrioventricular nodal functional refractory periods. Europace, 8(11), 927–934.
Bollmann, A., Sonne, K., Esperer, H. D., Toepffer, I., & Klein, H. U. (2000). Circadian variations in atrial fibrillatory frequency in persistent human atrial fibrillation. Pacing and Clinical Electrophysiology, 23(11 Pt 2), 1867–1871.
Chorro, F. J., Kirchhof, C. J., Brugada, J., & Allessie, M. A. (1990). Ventricular response during irregular atrial pacing and atrial fibrillation. American Journal of Physiology, 259(4 Pt 2), H1015–H1021.
Coumel, P. (1996). Autonomic influences in atrial tachyarrhythmias. Journal of Cardiovascular Electrophysiology, 7(10), 999–1007.
Lombardi, F., Tarricone, D., Tundo, F., Colombo, F., Belletti, S., & Fiorentini, C. (2004). Autonomic nervous system and paroxysmal atrial fibrillation: a study based on the analysis of RR interval changes before, during and after paroxysmal atrial fibrillation. European Heart Journal, 25(14), 1242–1248.
Lok, N. S., & Lau, C. P. (1998). Abnormal vasovagal reaction, autonomic function, and heart rate variability in patients with paroxysmal atrial fibrillation. Pacing and Clinical Electrophysiology, 21(2), 386–395.
Lombardi, F., Colombo, A., Basilico, B., Ravaglia, R., Garbin, M., Vergani, D., et al. (2001). Heart rate variability and early recurrence of atrial fibrillation after electrical cardioversion. Journal of the American College of Cardiology, 37(1), 157–162.
Acknowledgements
We are grateful to Professor Nick Freemantle for his review of the statistical methodologies and software tools used in this analysis.
Funding
This work was supported by a research grant from Vitatron BV, Arnhem, The Netherlands.
Conflicts of interest
There are no conflicts of interest to declare.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Silberbauer, J., Veasey, R.A., Cheek, E. et al. Electrophysiological characteristics associated with symptoms in pacemaker patients with paroxysmal atrial fibrillation. J Interv Card Electrophysiol 26, 31–40 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10840-009-9411-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10840-009-9411-x