Abstract
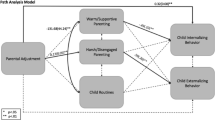
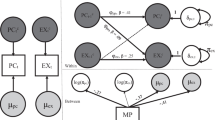
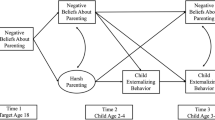
This study investigates the bidirectional perspective of parent–child effects by examining the extent to which parenting quality predicted child externalizing behavior and vice versa. Data was collected over four time points from primary caregivers and early school age children in low-income, primarily single parent homes (N = 249, mean age of children at Time 1 = 6.41 years). Parenting quality was operationalized as primary caregiver perceptions of positive parenting, effectiveness of parenting discipline, parenting efficacy and satisfaction. Child externalizing behavior data was captured via an assessment of the frequency of externalizing behavior as reported by caregivers. We hypothesized that parenting quality and child externalizing behavior would remain stable over time and that a bidirectional relationship would be present. Data was analyzed using structural equation modeling and results indicated that child externalizing behavior predicted subsequent parenting quality, and parenting quality predicted subsequent child externalizing. Specifically, our research team found that the influence of child externalizing behavior on parenting quality decreased with time, while the influence of parenting quality on child externalizing behavior increased with time. Overall results reveal the complex transactional influences of child externalizing behavior and parenting quality in our sample. Findings support the notion that parenting quality and child externalizing behavior are interactive processes which might best be handled by continual assessment and which may be potentially strong targets for interventions.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Achenbach, T. M. (1991). Manual for the child behavior checklist/4–18 and 1991 profile. Burlington, VT: University of Vermont.
Begle, A. M., & Dumas, J. E. (2011). Child and parental outcomes following involvement in a preventive intervention: Efficacy of the PACE program. The Journal of Primary Prevention, 32(2), 67–81.
Bell, R. Q. (1968). A reinterpretation of the direction of effects in studies of socialization. American Psychologist, 75(2), 81–95.
Bell, R. Q. (1977). Socialization findings reexamined. In R. Q. Bell & L. V. Harper (Eds.), Child effects (pp. 53–84). Lincoln, NB: Lawrence Erlbaum Associates Inc.
Bell, R. Q., & Harper, L. V. (Eds.). (1977). Child effects. Cambridge, MA: Harvard University Press.
Belsky, J. (1984). The determinants of parenting: A process model. Child Development, 55, 83–96.
Bentler, P. M. (1990). Comparative fit indexes in structural models. Psychological Bulletin, 107, 238–246.
Bronson, M. B. (2000). Self-regulation in early childhood: Nature and nurture. New York: The Guilford Press.
Browne, M. W., & Cudeck, R. (1993). Alternative ways of assessing model fit. In K. A. Bollen & J. S. Long (Eds.), Testing structural equation models (pp. 136–162). Newbury Park, CA: Sage.
Bugental, D. B., & Goodnow, J. J. (1998). Socialization processes. In W. Damon & N. Eisenberg (Eds.), Social, emotional, and personality development (pp. 389–462). New York, NY: Wiley.
Burke, J. D., Pardini, D. A., & Loeber, R. (2008). Reciprocal relationships between parenting behavior and disruptive psychopathology from childhood through adolescence. Journal of Abnormal Child Psychology, 36, 679–692.
Calkins, S. D. (1994). Origins and outcomes of individual differences in emotional regulation. In N.A. Fox (Ed.). Emotion regulation: Behavioral and biological considerations. Monographs of the Society for Research in Child Development.
Calkins, S. D., & Dedmon, S. A. (2000). Physiological and behavioral regulation in two-year-old children with aggressive/destructive behavior problems. Journal of Abnormal Child Psychology, 28, 103–118.
Calkins, S. D., Dedmon, S., & Hungerford, A. (2004). Mothers’ interactions with temperamentally frustrated infants. Infant Mental Health Journal, 25, 219–239.
Campbell, S. B. (2002). Behavior problems in preschool children: Clinical and developmental issues (2nd ed.). New York: Guilford Press.
Cummings, E. M., Iannotti, R. J., & Zahn-Waxler, C. (1989). Aggression between peers in early childhood: Individual continuity and developmental change. Child Development, 60, 887–895.
Curran, P. J., West, S. G., & Finch, J. F. (1996). The robustness of test statistics to nonnormality and specification error in confirmatory factor analysis. Psychological Methods, 1(1), 16–29.
Deater-Deckard, K., & Dodge, K. A. (1997). Externalizing behavior problems and discipline revisited: Nonlinear effects and variation by culture, context, and gender. Psychological Inquiry, 8, 161–175.
Deater-Deckard, K., Dodge, K. A., Bates, J. E., & Pettit, G. S. (1996). Physical discipline among African American and European American mothers: Links to children’s externalizing behaviors. Developmental Psychology, 32, 1065–1072.
Dodge, K. A., Pettit, G. S., & Bates, J. E. (1994). Socialization mediators of the relation between socioeconomic status and child conduct problems. Child Development, 65, 649–665.
Dornbusch, S. M., Ritter, P. L., Leiderman, H., Roberts, D. F., & Fraleigh, M. J. (1987). The relation of parenting style to adolescent performance. Child Development, 58, 1244–1257.
Florsheim, P., Tolan, P. H., & Gorman-Smith, D. (1996). Family processes and risk for externalizing behavior problems among African American and Hispanic boys. Journal of Consulting and Clinical Psychology, 64(6), 1222–1230.
Fox, L., Dunlap, G., & Cushing, L. (2002). Early intervention, positive behavior support, and transition to school. Journal of Emotional and Behavioral Disorders, 10, 149–157.
French, B. F., & Mantzicopoulos, P. Y. (2007). An examination of the first/second-grade form of the pictorial scale of perceived competence and social acceptance: Factor structure and stability by grade and gender across groups of economically disadvantaged children. Journal of School Psychology, 45, 311–331.
Frick, P. J., Kimonis, E. R., Dandreaux, D. M., & Farell, J. M. (2003). The 4 year stability of psychopathic traits in non-referred youth. Behavioral Sciences & the Law, 21(6), 713–736.
Galambos, N. L., Barker, E. T., & Almeida, D. M. (2003). Parents do matter: Trajectories of change in externalizing and internalizing problems in early adolescence. Child Development, 74(2), 578–594.
Greenbaum, P. E., & Dedrick, R. F. (1998). Hierarchical confirmatory factor analysis of the child behavior checklist/4-18. Psychological Assessment, 10(2), 149–155.
Gunnoe, M. L., & Mariner, C. L. (1997). Toward a developmental-contextual model of the effects of parental spanking on children’s aggression. Archives of Pediatric and Adolescent Medicine, 151, 768–775.
Hamre, B. K., & Pianta, R. C. (2001). Early teacher-child relationships and the trajectory of children’s school outcomes through eighth grade. Child Development, 72, 625–638.
Hancock, G. R. (1997). Structural equation modeling methods of hypothesis testing of latent variable means. Measurement and Evaluation in Counseling and Development, 30, 91–105.
Harkness, S., & Super, C. (1995). Parental ethnotheories in action. In I. E. Sigel, A. V. McGillicuddy-DeLisi, & J. J. Goodnow (Eds.), Parental belief systems: The psychological consequence of children (2nd ed., pp. 373–392). Hillsale, NJ: Earlum.
Hayduk, L., Cummings, G. G., Boadu, K., Pazderka-Robinson, H., & Boulianne, S. (2007). Testing! Testing! One, two, three—testing the theory in structural equation models! Personality and Individual Differences, 42, 841–850.
Hollingshead, A. B., & Redlich, F. C. (1958). Social class and mental illness: A community study. New York, NY: Wiley.
Hoyle, R. H. (1995). Structural equation modeling: Concepts, issues, and applications. Thousand Oaks, CA: Sage.
Jastrowski Mano, K. E., Hobart Davies, W., Klein-Tasman, B. P., & Adesso, V. J. (2009). Measurement equivalence of the child behavior checklist among parents of African American adolescents. Journal of Child and Family Studies, 18(5), 606–620.
Johnston, C., & Mash, E. J. (1989). A measure of parenting satisfaction and efficacy. Journal of Clinical Child Psychology, 18(2), 167–175.
Joreskog, K. G., & Sorbom, D. (2005). LISREL 8.72 for windows [Computer software]. Lincolnwood, IL: Scientific Software International.
Keenan, K. (2000). Emotion dysregulation as a risk factor for child psychopathology. Clinical Psychology: Science and Practice, 7(4), 418–434.
Keiley, M. K., Bates, J. E., Dodge, K. A., & Pettit, G. S. (2000). A cross-domain growth analysis: Externalizing and internalizing behaviors during 8 years of childhood. Journal of Abnormal Child Psychology, 28(2), 161–179.
Ladd, G. W., & Burgess, K. B. (2001). Do relational risks and protective factors moderate the linkages between childhood aggression and early psychological and school adjustment? Child Development, 72, 1579–1601.
Lansford, J. E., Criss, M. M., Laird, R. D., Shaw, D. S., Pettit, G. S., Bates, J. E., et al. (2011). Reciprocal relations between parents’ physical discipline and children’s externalizing behavior during middle childhood and adolescence. Development and Psychopathology, 23, 225–238.
Lansford, J. E., Deater-Deckard, K., Dodge, K. A., Bates, J. E., & Pettit, G. S. (2004). Ethnic differences in the link between physical discipline and later adolescent externalizing behaviors. Journal of Child Psychology and Psychiatry, 45, 801–812.
Larsson, H., Viding, E., & Rijsdijk, F. V. (2008). Relationships between parental negativity and childhood antisocial behavior over time: A bidirectional effects model in a longitudinal genetically informative design. Journal of Abnormal Child Psychology, 36, 633–645.
Larzelere, R. E., Cox, R., Danelia, K., & Mandara, J. (2008). Do child outcomes of all disciplinary enforcements vary by ethnicity? Paper presented at the annual conference of the National Council of Family Relations, November 5, 2008.
Lengua, L. J., & Kovacs, E. A. (2005). Bidirectional associations between temperament and parenting and the prediction of adjustment problems in middle childhood. Journal of Applied Developmental Psychology, 26(1), 21–38.
Loeber, R., Stouthamer-Loeber, M., van Kammen, W., & Farrington, D. P. (1991). Initiation, escalation and desistance in juvenile offending and their correlates. Journal of Criminal Law and Criminology, 82, 36–82.
Lopez, C. M., Begle, A. M., Dumas, J. E., & de Arellano, M. A. (2012). Parental child abuse potential and subsequent coping competence in disadvantaged preschool children: Moderating effects of sex and ethnicity. Child Abuse and Neglect, 36, 226–235.
Lundahl, B., Risser, H. J., & Lovejoy, M. C. (2006). A meta-analysis of parent training: moderators and follow-up effects. Clinical Psychology Review, 26, 86–104.
Luthar, S. S. (1999). Poverty and children’s adjustment. Thousand Oaks, CA: Sage.
Lynam, D. R., Loeber, R., & Stouthamer-Loever, M. (2008). The stability of psychopathy from adolescence into adulthood: The search for moderators. Criminal Justice and Behavior, 35(2), 228–243.
McAdoo, H. P. (2002). African American parenting. In M.H. Bornstein (Ed.), Handbook of parenting: Vol. 4 Social conditions and applied parenting (pp. 47–58). Mahwah, NJ: Erlbaum.
McLeod, J. D., Kruttschnitt, C., & Dornfield, M. (1994). Does parenting explain the effects of structural conditions on children’s antisocial behavior? A comparison of Blacks and Whites. Social Forces, 73, 575–604.
McLoyd, V. C. (1990). The impact of economic hardship on black families and children: Psychological distress, parenting, and socioeconomic development. Child Development, 61(2), 311–346.
McLoyd, V. C. (1998). Socioeconomic disadvantage and child development. American Psychologist, 55, 185–204.
Mitchell, S. J., Lewin, A., Rasmussen, A., Horn, I. B., & Joseph, J. G. (2010). Maternal distress explains the relationship of young African American mothers’ violence exposure with their preschoolers’ behavior. Journal of Interpersonal Violence, 26(3), 580–603.
Pardini, D. A., Fite, P. J., & Burke, J. D. (2008). Bidirectional associations between parenting practices and conduct problems in boys from childhood to adolescent: The moderating effect of age and African-American ethnicity. Journal of Abnormal Child Psychology, 36, 647–662.
Pardini, D. A., & Loeber, R. (2008). Interpersonal callousness trajectories across adolescence: Early social influences and adult outcomes. Criminal Justice and Behavior, 35(2), 173–196.
Parke, R. D., & Buriel, R. (1998). Socialization in the family: Ecological and ethnic perspectives. In W. Damon (Series Ed.), & N. Eisenberg (Vol. Ed.), Handbook of child psychology: Vol. 3. Social, emotional, and personality development, 5th ed. (pp. 463–552). New York, NY: Wiley.
Patterson, G. R. (1982). Coercive family processes. Eugene, OR: Castilla.
Pearl, A., French, B. F., & Dumas, J. E. (2009). Parenting quality and child adjustment: An example of longitudinal panel data analysis. In T. Teo & M. S. Khine (Eds.), Structural equation modeling in educational research: Concepts and applications. Rotterdam: Sense Publishers.
Pelham, W. E., Gnagy, E. M., Greenslade, K. E., & Milich, R. (1992). Teacher ratings of DSM-III-TR symptoms for the disruptive behavior disorders. Journal of the American Academy of Child Psychology, 31(2), 210–218.
Pettit, G. S., & Arsiwalla, D. D. (2008). Commentary on special section on “bidirectional parent-child relationships”: The continuing evolution of dynamic, transactional models of parenting and youth behavior problems. Journal of Abnormal Child Psychology, 36, 711–718.
Pianta, R. C., Steinberg, M. S., & Rollins, K. B. (1995). The first two years of school: Teacher-child relationships and deflections in children’s classroom adjustment. Development and Psychopathology, 7, 295–312.
Pinderhughes, E. E., Dodge, K. A., Bates, J. E., Pettit, G. S., & Zelli, A. (2000). Discipline responses: Influences of parents’ socioeconomic status, ethnicity, beliefs about parenting, stress, and cognitive-emotional processes. Journal of Family Psychology, 14(3), 380–400.
Rubin, K. H., Burgess, K. B., Dwyer, K. M., & Hastings, P. D. (2003). Predicting preschoolers’ externalizing behaviors from toddler temperament, conflict, and maternal negativity. Developmental Psychology, 39(1), 164–176.
Sameroff, A. J., & Chandler, M. (1975). Reproductive risk and the continuum or caretaking casualty. In F. D. Horowitz (Ed.), Review of child development research (Vol. 4, pp. 187–244). Chicago, IL: University of Chicago Press.
Silver, R. B., Measelle, J. R., Armstrong, J. M., & Essex, M. J. (2005). Trajectories of classroom externalizing behavior: Contributions of child characteristics, family characteristics, and the teacher-child relationship during the school transition. Journal of School Psychology, 43, 39–60.
Skiba, R. J., Michael, R. S., Nardo, A. C., & Peterson, R. L. (2002). The color of discipline: Sources of racial and gender disproportionality in school punishment. The Urban Review, 34, 317–342.
Smith, C. L., Calkins, S. D., Keane, S. P., Anastopoulos, A. D., & Shelton, T. L. (2004). Predicting stability and change in toddler behavior problems: Contributions of maternal behavior and child gender. Developmental Psychology, 40(1), 29–42.
Snyder, J. J. (1991). Discipline as a mediator of the impact of maternal stress and mood on child conduct problems. Development and Psychopathology, 3, 263–276.
Stoolmiller, M., Patterson, G. R., & Snyder, J. (1997). Parental discipline and child antisocial behavior: A contingency-based theory and some methodological refinements. Psychological Inquiry, 8(3), 223–229.
Thomas, A., & Chess, S. (1977). Temperament and development. New York: Bruner-Mazel.
Thornberry, T. P., Huizinga, D., & Loeber, R. (1995). The prevention of serious delinquency and violence: Implications from the program of research on the causes and correlates of delinquency. In J. C. Howell, B. Krisberg, J. D. Hawkins, & J. J. Wilson (Eds.), A sourcebook: Serious, violent, and chronic juvenile offenders (pp. 213–237). Thousand Oaks, CA: Sage Publications.
Toth, J. F., & Xu, X. (1999). Ethnic and cultural diversity in fathers’ involvement: A racial/ethnic comparison of African Americans, Hispanics and white fathers. Youth and Society, 31, 76–99.
Vaillancourt, T., Brendgen, M., Boivin, M., & Tremblay, R. E. (2003). A longitudinal confirmatory factor analysis of indirect and physical aggression: Evidence of two factors over time? Child Development, 74(1), 1628–1638.
Verhoeven, M., Junger, M., Van Aken, C., Deković, M., & Van Aken, M. A. G. (2010). Parenting and children’s externalizing behavior: Bidirectionality during toddlerhood. Journal of Applied Developmental Psychology, 31, 93–105.
Webster-Stratton, C., Hollingsworth, T., & Kolpacoff, M. (1989). The long-term effectiveness and clinical significance of three cost-effective training programs for families with conduct-problem children. Journal of Consulting and Clinical Psychology, 57, 550–553.
Yasui, M., & Dishion, T. J. (2007). The ethnic context of child and adolescent problem behavior: Implications for child and family interventions. Clinical Child and Family Psychology Review, 10(2), 137–179.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Pearl, A.M., French, B.F., Dumas, J.E. et al. Bidirectional Effects of Parenting Quality and Child Externalizing Behavior in Predominantly Single Parent, Under-Resourced African American Families. J Child Fam Stud 23, 177–188 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10826-012-9692-z
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10826-012-9692-z