Abstract
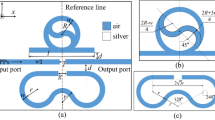
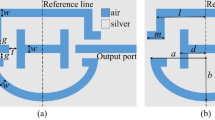
In this paper, a metal–insulator–metal waveguide coupled with double Fibonacci spiral structure is designed and studied. The Fano resonance characteristics of the structure are analyzed in detail by means of transmission spectra and magnetic field distribution using finite element method. By changing the geometric parameters and refractive index, the sensing characteristics of the structure are quantitatively analyzed. This structure can be used in sensors, not only the sensitivity can reach an extremely high value of 3350 nm/RIU, but also the refractive index and peak wavelength show an excellent linear relationship. This structure provides a new scheme for the design of high sensitivity sensors. In addition, by measuring the refractive index of sodium chloride solution, it is proved that the structure has practical application prospect.










Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
The data that support the findings of this study are available on request from the corresponding author upon reasonable request.
Abbreviations
- SPPs:
-
Surface plasmon polaritons
- MIM:
-
Metal–insulator–metal
- DFSS:
-
Double Fibonacci spirals structure
- TM0 :
-
The fundamental transverse magnetic mode
References
Kazanskiy, N.L., Khonina, S.N., Butt, M.A.: Plasmonic sensors based on Metal-insulator-metal waveguides for refractive index sensing applications: a brief review. Phys. E-Low-Dimens. Syst. Nanostruct. 117, 113798 (2020)
Barnes, W.L., Dereux, A., Ebbesen, T.W.: Surface plasmon subwavelength optics. Nature 424(6950), 824–830 (2003)
Qiao, L.T., et al.: Study on the Fano resonance of coupling M-type cavity based on surface plasmon polaritons. Opt. Commun. 433, 144–149 (2019)
Tian, J.P., et al.: Fano resonance and its application using a defective disk resonator coupled to an MDM plasmon waveguide with a nano-wall. Optik 208, 164136 (2020)
Chen, J.F., et al.: Refractive index sensing based on multiple fano resonances in a split-ring cavity-coupled MIM waveguide. Photonics 8(11), 472 (2021)
Xiao, G.L., et al.: High sensitivity plasmonic sensor based on fano resonance with inverted U-Shaped resonator. Sensors 21(4), 1164 (2021)
Wang, Y.L., Hou, Z.L., Yu, L.: Plasmonic nanosensor based on sharp Fano resonances induced by aperture-coupled slot system. Opt. Commun. 480, 126438 (2021)
Salehnezhad, Z., Soroosh, M., Farmani, A.: Design and numerical simulation of a sensitive plasmonic-based nanosensor utilizing MoS2 monolayer and graphene. Diam. Related Mater. 131, 109594 (2023)
Farmani, A.: Three-dimensional FDTD analysis of a nanostructured plasmonic sensor in the near-infrared range. J. Opt. Soc. Am. B-Opt. Phys. 36(2), 401–407 (2019)
Huang, Y., et al.: Actively tunable fano resonance based on a bowtie-shaped black phosphorus terahertz sensor. Nanomaterials 11(6), 1442 (2021)
Chauhan, D., et al.: Subwavelength plasmonic liquid sensor using Fano resonance in a ring resonator structure. Optik 223, 165545 (2020)
Krishnamoorthy, R., Soubache, I.D., Farmani, A.: Exploring surface plasmon resonance ring resonator structure for high sensitivity and ultra-high-Q optical filter with FDTD method. Opt. Quantum Electron. 54(2), 1–13 (2022)
Chen, X.H.: Synthesis of multi-band filters based on multi-prototype transformation. IET Microwaves Antennas Propag. 15(2), 103–114 (2021)
Khani, S., A. Farmani, and P. Rezaei.: Optical resistance switch for optical sensing. Artificial Intelligence in Mechatronics and Civil Engineering, p. 1–38, (2023)
Stern, L., Grajower, M., Levy, U.: Fano resonances and all-optical switching in a resonantly coupled plasmonic-atomic system. Nature Commun. 5(1), 4865 (2014)
Degheidy, A.R., Elkenany, E.B., Alfrnwani, O.A.: Influence of composition, temperature and pressure on the optoelectronic and mechanical properties of InPxSb1-x alloys. Comput. Condens. Matter. 16, 1–7 (2018)
Zangeneh, A.M.R., et al.: Enhanced sensing of terahertz surface plasmon polaritons in graphene/J-aggregate coupler using FDTD method. Diam. Related Mater. 125, 109005 (2022)
Yu, Y., et al.: Research on fano resonance sensing characteristics based on racetrack resonant cavity. Micromachines 12(11), 1359 (2021)
Shi, H.R., et al.: Nanosensor based on Fano resonance in a metal-insulator-metal waveguide structure coupled with a half-ring. Results Phys. 21, 103842 (2021)
Chao, C.T.C., et al.: Highly sensitive and tunable plasmonic sensor based on a nanoring resonator with silver nanorods. Nanomaterials 10(7), 1399 (2020)
Zafar, R., Salim, M.: Enhanced figure of merit in fano resonance-based plasmonic refractive index sensor. IEEE Sens. J. 15(11), 6313–6317 (2015)
Hu, J.G., et al.: Strong longitudinal coupling of Tamm plasmon polaritons in graphene/DBR/Ag hybrid structure. Opt. Express 27(13), 18642–18652 (2019)
Gai, H.F., Wang, J., Tian, Q.: Modified Debye model parameters of metals applicable for broadband calculations. Appl. Opt. 46(12), 2229–2233 (2007)
Kekatpure, R.D., et al.: Solving dielectric and plasmonic waveguide dispersion relations on a pocket calculator. Opt. Express 17(26), 24112–24129 (2009)
Rakhshani, M.R., Mansouri-Birjandi, M.A.: High sensitivity plasmonic refractive index sensing and its application for human blood group identification. Sens. Actuat. B-Chem. 249, 168–176 (2017)
Khodadadi, M., Moshiri, S.M.M., Nozhat, N.: Theoretical analysis of a simultaneous graphene-based circular plasmonic refractive index and thickness bio-sensor. IEEE Sens. J. 20(16), 9114–9123 (2020)
Rahmatiyar, M., Afsahi, M., Danaie, M.: Design of a refractive index plasmonic sensor based on a ring resonator coupled to a MIM waveguide containing tapered defects. Plasmonics 15(6), 2169–2176 (2020)
Butt, M.A., Kazanskiy, N.L., Khonina, S.N.: Highly sensitive refractive index sensor based on plasmonic bow tie configuration. Photonic Sens. 10(3), 223–232 (2020)
Dong, L., et al.: Effects of different concentrations of intraluminal sodium chloride solution on intracavitary ECG used for arm infusion port implantation. Sci. Rep. 12(1), 13813 (2022)
Lin, C.C., et al.: A sodium chloride modification of SnO2 electron transport layers to enhance the performance of perovskite solar cells. ACS Omega 6(28), 17880–17889 (2021)
Xu, L.P., et al.: Ultrasensitive optical refractive index detection of NaCl and alcohol solutions based on weak value amplification. Plasmonics 15(3), 671–678 (2020)
Funding
Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities of China (2572021DJ05).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
DQ and CL wrote the paper. QW and YS provide research ideas and revision discussion for this paper.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors promise that there is no conflict of interest in this article.
Consent for publication
The authors agree to publish this article.
Ethical approval and Consent to participate
There are no ethical problems in this article.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Qu, D., Wu, Q., Sun, Y. et al. Research on high sensitivity fano resonance sensing based on MIM waveguide coupled with double Fibonacci spirals. J Comput Electron 22, 1500–1506 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10825-023-02069-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10825-023-02069-x