Abstract
In this paper, all-optical plasmonic switches are proposed and analyzed. These structures consist of a rectangular resonator filled with a Kerr-type material (AuSiO2) which is coupled to isolated metal–insulator–metal plasmonic waveguides. The resonators contain periodic arrays of nano-rods with rectangular and triangular patterns. The horizontal and vertical waveguides are used for data and control signals, respectively. Using two separate paths for the data and control signals results in suitable isolation between the signals. The finite difference time domain (FDTD) method is used for numerical investigation of the designed structures. To provide more insight, the FDTD results of the building blocks of the switches are compared with transmission line method results. The most important benefits of the proposed topologies are requiring lower pump intensities, needing smaller footprints and having isolated data and control ports. The proposed switch needs a pump intensity equal to 193.2 mW/μm2 and requires a 0.593 μm2 footprint area. A 11.3 dB contrast ratio exists between the On and Off states of the switch. Based on the mentioned advantages, these switches have the potential to be used in complex integrated optical circuits.



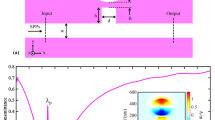
source for a Switch I and b Switch II














Similar content being viewed by others
References
Danaie, M., Kaatuzian, H.: Bandwidth improvement for a photonic crystal optical Y-splitter. J. Opt. Soc. Korea 15(3), 283–288 (2011)
Danaie, M., Attari, A.R., Mirsalehi, M.M., Naseh, S.: Optimization of two-dimensional photonic crystal waveguides for TE and TM polarizations. Optica. Applicata. 38(4), 643–655 (2008)
Foghani, S., Kaatuzian, H., Danaie, M.: Simulation and design of a wideband T-shaped photonic crystal splitter. Optica. Applicata. 40(4), 863–872 (2010)
Swarnakar, S., Kumar, S., Sharma, S.: Performance analysis of all-optical full-adder based on two-dimensional photonic crystals. J. Comput. Electron. 17(3), 1124–1134 (2018)
Danaee, E., Geravand, A., Danaie, M.: Wide-band low cross-talk photonic crystal waveguide intersections using self-collimation phenomenon. Opt. Commun. 431, 216–228 (2019)
Farmani, A., Mir, A., Irannejad, M.: 2D-FDTD simulation of ultra-compact multifunctional logic gates with nonlinear photonic crystal. JOSA B 36(4), 811–818 (2019)
Danaie, M., Nasirifar, R., Dideban, A.: Design of adjustable T-shaped and Y-shaped photonic crystal power splitters for TM and TE polarizations. Turkish J. Electrical Eng. Comput. Sci. 25(5), 4398–4408 (2017)
Saghaei, H., Zahedi, A., Karimzadeh, R., Parandin, F.: Line defects on As2Se3-Chalcogenide photonic crystals for the design of all-optical power splitters and digital logic gates. Superlattices. Microstruct. 110, 133–138 (2017)
Moradi, M., Danaie, M., Orouji, A.A.: Design and analysis of an optical full-adder based on nonlinear photonic crystal ring resonators. Optik 172, 127–136 (2018)
Barnes, W.L., Dereux, A., Ebbesen, T.W.: Surface plasmon subwavelength optics. Nature 424(6950), 824–830 (2003)
Sellai, A., Elzain, M.: Characteristics of a dielectric–metal–dielectric plasmonic waveguide. Physica. E. 41(1), 106–109 (2008)
Khani, S., Danaie, M., Rezaei, P.: Miniaturized microstrip dual-band bandpass filter with wide upper stop-band bandwidth. Analog. Integr. Circ. Sig. Process 98(2), 367–376 (2019)
Khani, S., Mousavi, S.M.H., Danaie, M., Rezaei, P.: Tunable compact microstrip dual-band bandpass filter with tapered resonators. Microwave Opt Tech Letters 60(5), 1256–1261 (2018)
Khani, S., Hayati, M.: Compact microstrip lowpass filter with wide stopband and sharp roll-off. Microw. J. 60(11), 86–92 (2017)
Khani, S., Danaie, M., Rezaei, P., Shahzadi, A.: Compact ultra-wide upper stopband microstrip dual-band BPF using tapered and octagonal loop resonators. Frequenz 74(1–2), 1–11 (2019)
Zeng, D., Zhang, L., Xiong, Q., Ma, J.: Directional coupler based on an elliptic cylindrical nanowire hybrid plasmonic waveguide. Appl. Opt. 57(16), 4701–4706 (2018)
Petráček, J.: Nonlinear directional coupling between plasmonic slot waveguides. Appl. Phys. B 112(4), 593–598 (2013)
Huang, B., Meng, H., Wang, Q., Wang, H., Zhang, X., Yu, W., Wang, F.: Plasmonic-induced transparency and slow-light effect based on stub waveguide with nanodisk resonator. Plasmonics 11(2), 543–550 (2016)
Wang, G., Zhang, W., Gong, Y., Liang, J.: Tunable slow light based on plasmon-induced transparency in dual-stub-coupled waveguide. IEEE Photonics Technol. Lett. 27(1), 89–92 (2014)
Tian, M., Lu, P., Chen, L., Liu, D., Peyghambarian, N.: Plasmonic Bragg reflectors based on metal-embedded MIM structure. Opt. Commun. 285(24), 5122–5127 (2012)
Shafagh, S.G., Kaatuzian, H., Danaie, M.: Analysis, design and simulation of MIM plasmonic filters with different geometries for technical parameters improvement. Commun. Theor. Phys. 72(8), 085502 (2020)
Jiang, C., Liang, S., Wan, L., Du, K., Zhang, W., Li, Z., Mei, T.: Plasmonic color filter based on a hetero-metal-insulator-metal grating. Appl. Opt. 59(14), 4432–4436 (2020)
Janfaza, M., Mansouri-Birjandi, M.A., Tavousi, A.: Tunable plasmonic band-pass filter based on Fabry-Perot graphene nanoribbons. Appl. Phys. B 123(10), 262 (2017)
Nasirifar, R., Danaie, M., Dideban, A.: Hollow-core graded index optical fiber refractive index sensor based on surface plasmon resonance. Opt. Quant. Electron. 52(7), 1–23 (2020)
Kaur, V., Singh, S.: A dual-channel surface plasmon resonance biosensor based on a photonic crystal fiber for multianalyte sensing. J. Comput. Electron. 18(1), 319–328 (2019)
Nasirifar, R., Danaie, M., Dideban, A.: Dual channel optical fiber refractive index sensor based on surface plasmon resonance. Optik 186, 194–204 (2019)
Khani, S., Danaie, M., Rezaei, P.: Double and triple-wavelength plasmonic demultiplexers based on improved circular nanodisk resonators. Opt. Eng. 57(10), 107102 (2018)
Wu, C.T., Huang, C.C., Lee, Y.C.: Plasmonic wavelength demultiplexer with a ring resonator using high-order resonant modes. Appl. Opt. 56(14), 4039–4044 (2017)
Hajshahvaladi, L., Kaatuzian, H., Danaie, M.: Design and analysis of a plasmonic demultiplexer based on band-stop filters using double-nanodisk-shaped resonators. Opt. Quant. Electron. 51(12), 391 (2019)
Gogoi, N., Sahu, P.P.: All-optical tunable power splitter based on a surface plasmonic two-mode interference waveguide. Appl. Opt. 57(10), 2715–2719 (2018)
Wen, K., Hu, Y., Chen, L., Zhou, J., Lei, L., Meng, Z.: Plasmonic bidirectional/unidirectional wavelength splitter based on metal-dielectric-metal waveguides. Plasmonics 11(1), 71–77 (2016)
Danaie, M., Geravand, A.: Design of low-cross-talk metal–insulator–metal plasmonic waveguide intersections based on proposed cross-shaped resonators. J. Nanophotonics 12(4), 046009 (2018)
Wen, K., Yan, L., Hu, Y., Chen, L., Lei, L.: A plasmonic wavelength-selected intersection structure. Plasmonics 9(3), 685–690 (2014)
Kaboli, M., Akhlaghi, M.: Investigating the optical AND gate using plasmonic nano-spheres. J. Comput. Electron. 15(1), 295–300 (2016)
Moradi, M., Danaie, M., Orouji, A.A.: Design of all-optical XOR and XNOR logic gates based on Fano resonance in plasmonic ring resonators. Opt. Quant. Electron. 51(5), 154 (2019)
Kumar, S., Singh, L., Raghuwanshi, S.K.: Design of plasmonic half-adder and half-subtractor circuits employing nonlinear effect in Mach-Zehnder interferometer. J. Comput. Electron. 16(1), 139–147 (2017)
Vahed, H., Ahmadi, S.S.: Graphene-based plasmonic electro-optic modulator with sub-wavelength thickness and improved modulation depth. Appl. Phys. B 123(11), 265 (2017)
Emami, F., Akhlaghi, M., Nozhat, N.: Binary optimization of gold nano-rods for designing an optical modulator. J. Comput. Electron. 14(2), 574–581 (2015)
Khani, S., Danaie, M., Rezaei, P.: Hybrid All-Optical Infrared Metal Insulator Metal Plasmonic Switch Incorporating Photonic Crystal Bandgap Structures. Photonics Nanostruct Fundam Appl. 40, 100802 (2020)
Khani, S., Danaie, M., Rezaei, P.: All-optical plasmonic switches based on asymmetric directional couplers incorporating Bragg gratings. Plasmonics 15(3), 869–879 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11468-019-01106-5
Babaei, M., Zarifkar, A., Miri, M.: Compact and broadband 2×2 optical switch based on hybrid plasmonic waveguides and curved directional couplers. Appl. Opt. 59(4), 975–984 (2020)
Khani, S., Danaie, M., Rezaei, P.: Tunable single-mode bandpass filter based on metal–insulator–metal plasmonic coupled U-shaped cavities. IET Optoelectron. 13(4), 161–171 (2019)
Xu, H., Xiao, G., Xiao, W., Chen, Q.: Tunable multimode plasmonic filter based on asymmetric dual side-coupled U-shape cavities resonators. Optik 182, 324–330 (2019)
Wu, T., Cao, W.: A multifunction filter based on plasmonic waveguide with double-nanodisk-shaped resonators. Optik 127(20), 8976–8982 (2016)
Danaie, M., Kaatuzian, H.: Improvement of power coupling in a nonlinear photonic crystal directional coupler switch. Photonics Nanostruct. Fundam. Appl. 9(1), 70–81 (2011)
Beggs, D.M., White, T.P., Cairns, L., O’Faolain, L., Krauss, T.F.: Demonstration of an integrated optical switch in a silicon photonic crystal directional coupler. Physica. E 41(6), 1111–1114 (2009)
Danaie, M., Kaatuzian, H.: Design of a photonic crystal differential phase comparator for a Mach-Zehnder switch. J. Opt. 13(1), 015504 (2010)
Janjan, B., Fathi, D., Miri, M., Ghaffari-Miab, M.: Ultra-wideband high-speed Mach-Zehnder switch based on hybrid plasmonic waveguides. Appl. Opt. 56(6), 1717–1723 (2017)
Khani, S., Danaie, M., Rezaei, P.: Realization of a plasmonic optical switch using improved nano-disk resonators with Kerr-type nonlinearity: A theoretical and numerical study on challenges and solutions. Opt. Commun. 477, 126359 (2020)
Taheri, A.N., Kaatuzian, H.: Simulation and design of a submicron ultrafast plasmonic switch based on nonlinear doped silicon MIM waveguide. J. Comput. Commun. 1(07), 23 (2013)
Armaghani, S., Khani, S., Danaie, M.: Design of all-optical graphene switches based on a Mach-Zehnder interferometer employing optical Kerr effect. Superlattices Microstruct. 135, 106244 (2019)
Zhang, H., Chen, X., Wang, Q., Zhang, X., Chang, J., Gao, L., Li, J.: Graphene-based passively Q-switched Nd: KLu (WO 4) 2 eye-safe laser operating at 1,425 nm. Appl. Phys. B 114(3), 313–317 (2014)
Liu, X., Liu, H., Sun, Q., Huang, N.: Metamaterial terahertz switch based on split-ring resonator embedded with photoconductive silicon. Appl. Opt. 54(11), 3478–3483 (2015)
Hajizadegan, M., Fathi, D., Sakhdari, M.S.: All-optical metamaterial switch based on Kerr effect with MWCNT composite. Physica E 48, 1–6 (2013)
Ma, Y., Peng, Z., Ding, S., Peng, F., Zhang, Q., Yu, X.: Diode-pumped acousto-optically Q-switched laser with Nd3+ doped GdYNbO4 mixed crystal. Infrared Phys. Technol. 92, 295–298 (2018)
Tao, J., Wang, Q.J., Huang, X.G.: All-optical plasmonic switches based on coupled nano-disk cavity structures containing nonlinear material. Plasmonics 6(4), 753 (2011)
Tian, M., Lu, P., Chen, L., Liu, D., Lv, C.(2012).All-optical switching in MIM waveguide resonator with an outer portion smooth bend structure containing nonlinear optical materials. Opt. Commun.285:(21–22),4562–4566
Khani, S., Danaie, M., Rezaei, P.: Compact and low-power all-optical surface plasmon switches with isolated pump and data waveguides and a rectangular cavity containing nano-silver strips. Superlattices Microstruct. 141, 106481 (2020)
Krasavin, A.V., Zayats, A.V.: Electro-optic switching element for dielectric-loaded surface plasmon polariton waveguides. Appl. Phys. Lett. 97(4), 041107 (2010)
Taheri, A.N., Kaatuzian, H.: Design and simulation of a nanoscale electro-plasmonic 1×2 switch based on asymmetric metal–insulator–metal stub filters. Appl. Opt. 53(28), 6546–6553 (2014)
Mei, X., Huang, X.G., Jin, T.: A sub-wavelength electro-optic switch based on plasmonic T-shaped waveguide. Plasmonics 6(4), 613–618 (2011)
Qi, Z., Hu, G., Yun, B., Zhang, X., Cui, Y.: Fast response and low power consumption 1×2 thermo-optic switch based on dielectric-loaded surface plasmon polariton waveguides. J. Mod. Opt. 63(14), 1354–1363 (2016)
Pitilakis, A., Kriezis, E.E.: Longitudinal 2×2 switching configurations based on thermo-optically addressed dielectric-loaded plasmonic waveguides. J. Lightwave Technol. 29(17), 2636–2646 (2011)
Khani, S., Danaie, M., Rezaei, P.: Size reduction of MIM surface plasmon based optical bandpass filters by the introduction of arrays of silver nano-rods. Physica E 113, 25–34 (2019)
Boyd, R.W.: Nonlinear optics. Elsevier, NY (2003)
Liao, H.B., Xiao, R.F., Fu, J.S., Wang, H., Wong, K.S., Wong, G.K.L.: Origin of third-order optical nonlinearity in Au:SiO 2 composite films on femtosecond and picosecond time scales. Opt. Lett. 23(5), 388–390 (1998)
Park, J., Kim, H., Lee, B.: High order plasmonic Bragg reflection in the metal-insulator-metal waveguide Bragg grating. Opt. Express 16(1), 413–425 (2008)
Pannipitiya, A., Rukhlenko, I.D., Premaratne, M., Hattori, H.T., Agrawal, G.P.: Improved transmission model for metal-dielectric-metal plasmonic waveguides with stub structure. Opt. Express 18(6), 6191–6204 (2010)
Liu, J., Fang, G., Zhao, H., Zhang, Y., Liu, S.: Surface plasmon reflector based on serial stub structure. Opt. Express 17(22), 20134–20139 (2009)
Pozar, D.M.: Microwave Engineering, 2nd edn, p. 566. John Wiley & Sons (1998)
Veronis, G., Fan, S.: Bends and splitters in metal-dielectric-metal subwavelength plasmonic waveguides. Appl. Phys. Lett. 87(13), 131102 (2005)
Collin, R.E.: Foundations for microwave engineering. Wiley, NY (2007)
Parker, M.A.: Physics of optoelectronics. CRC Press, FL (2005)
Lu, H., Liu, X., Mao, D., Wang, L., Gong, Y.: Tunable band-pass plasmonic waveguide filters with nanodisk resonators. Opt. Express 18(17), 17922–17927 (2010)
Kong, Y., Lin, R., Qian, W., Wei, Q., Liu, C., Wang, S.: Active dual-wavelength optical switch-based plasmonic demultiplexer using metal-Kerr nonlinear material-metal waveguide. IEEE Photonics J. 9(4), 1–8 (2017)
Nurmohammadi, T., Abbasian, K., Yadipour, R.: Ultra-fast all-optical plasmonic switching in near infra-red spectrum using a Kerr nonlinear ring resonator. Opt. Commun. 410, 142–147 (2018)
Zhang, Z., Yang, J., He, X., Han, Y., Zhang, J., Huang, J., Xu, S.: All-optical multi-channel switching at telecommunication wavelengths based on tunable plasmon-induced transparency. Opt. Commun. 425, 196–203 (2018)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Khani, S., Danaie, M. & Rezaei, P. Plasmonic all-optical metal–insulator–metal switches based on silver nano-rods, comprehensive theoretical analysis and design guidelines. J Comput Electron 20, 442–457 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10825-020-01638-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10825-020-01638-8