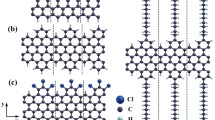
Abstract
In the last decade, graphene photodetectors have been introduced and investigated in many works. In any photodetector, the separation of the photo-excited electrons and holes is one of the most basic mechanisms. However, a few distinct methods have already been introduced for the separation and all of them are based on the usage of a longitudinal electric field. In this paper, a new method is proposed. Our method is based on applying a vertical electric field which induces an asymmetric potential barrier in front of one or both of the photo-excited carriers. First, a simple one-dimensional toy model consisting of a one-dimensional atomic chain is used to focus on the concept. Many aspects, including the effects of the potential barrier location, its height, and its width, are investigated by this model. Then, in order to extend to real applications, a new structure is introduced in this paper; it is based on graphene nanoribbons and an asymmetric metal gate. Our results show that this structure results in appropriate carrier separation. The nonequilibrium Green function method with a tight-binding model is employed for the simulation of the proposed devices, and the results are shown in the paper.















Similar content being viewed by others
References
Neto, A.C., Guinea, F., Peres, N., Novoselov, K.S., Geim, A.K.: The electronic properties of graphene. Rev. Mod. Phys. 81(1), 109 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1103/RevModPhys.81.109
Novoselov, K.S., Fal, V., Colombo, L., Gellert, P., Schwab, M., Kim, K.: A roadmap for graphene. Nature 490(7419), 192–200 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1038/nature11458
Yoon, Y., Fiori, G., Hong, S., Iannaccone, G., Guo, J.: Performance comparison of graphene nanoribbon FETs with Schottky contacts and doped reservoirs. IEEE Trans. Electron Devices 55(9), 2314–2323 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1109/TED.2008.928021
Sanaeepur, M., Goharrizi, A.Y., Sharifi, M.J.: Performance analysis of graphene nanoribbon field effect transistors in the presence of surface roughness. IEEE Trans. Electron Devices 61(4), 1193–1198 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1109/TED.2013.2290049
Bonaccorso, F., Sun, Z., Hasan, T., Ferrari, A.: Graphene photonics and optoelectronics. Nat. Photonics 4(9), 611–622 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1038/nphoton.2010.186
Xia, F., Mueller, T., Lin, Y.-M., Valdes-Garcia, A., Avouris, P.: Ultrafast graphene photodetector. Nat. Nanotechnol. 4(12), 839–843 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1038/nnano.2009.292
Mueller, T., Xia, F., Avouris, P.: Graphene photodetectors for high-speed optical communications. Nat. Photonics 4(5), 297–301 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1038/nphoton.2010.40
Shiue, R.-J., Gan, X., Gao, Y., Li, L., Yao, X., Szep, A., Walker Jr., D., Hone, J., Englund, D.: Enhanced photodetection in graphene-integrated photonic crystal cavity. Appl. Phys. Lett. 103(24), 241109 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1063/1.4839235
Furchi, M., Urich, A., Pospischil, A., Lilley, G., Unterrainer, K., Detz, H., Klang, P., Andrews, A.M., Schrenk, W., Strasser, G.: Microcavity-integrated graphene photodetector. Nano Lett. 12(6), 2773–2777 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1021/nl204512x
Konstantatos, G., Badioli, M., Gaudreau, L., Osmond, J., Bernechea, M., de Arquer, F.P.G., Gatti, F., Koppens, F.H.: Hybrid graphene-quantum dot phototransistors with ultrahigh gain. Nat. Nanotechnol. 7(6), 363–368 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1038/nnano.2012.60
Sze, S.M., Ng, K.K.: Physics of Semiconductor Devices. Wiley, New York (2006)
Ryzhii, V., Ryabova, N., Ryzhii, M., Baryshnikov, N., Karasik, V., Mitin, V., Otsuji, T.: Terahertz and infrared photodetectors based on multiple graphene layer and nanoribbon structures. Opto-Electron. Rev. 20(1), 15–25 (2012). https://doi.org/10.2478/s11772-012-0009-y
Gao, Q., Guo, J.: Quantum mechanical simulation of graphene photodetectors. J. Appl. Phys. 112(8), 084316 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1063/1.4759369
Zarei, M., Sharifi, M.: Defect-based graphene nanoribbon photodetectors: a numerical study. J. Appl. Phys. 119(21), 213104 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1063/1.4953003
Datta, S.: Quantum Transport: Atom to Transistor. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge (2005)
Henrickson, L.E.: Nonequilibrium photocurrent modeling in resonant tunneling photodetectors. J. Appl. Phys. 91(10), 6273–6281 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1063/1.1473677
Ouyang, Y., Yoon, Y., Guo, J.: Scaling behaviors of graphene nanoribbon FETs: a three-dimensional quantum simulation study. IEEE Trans. Electron Devices 54(9), 2223–2231 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1109/TED.2007.902692
Ostovari, F., Moravvej-Farshi, M.K.: Photodetectors with zigzag and armchair graphene nanoribbon channels and asymmetric source and drain contacts: detectors for visible and solar blind applications. J. Appl. Phys. (2016). https://doi.org/10.1063/1.4964436
Anantram, M., Lundstrom, M.S., Nikonov, D.E.: Modeling of nanoscale devices. Proc. IEEE 96(9), 1511–1550 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1109/JPROC.2008.927355
Pereira, V.M., Neto, A.C., Peres, N.: Tight-binding approach to uniaxial strain in graphene. Phys. Rev. B 80(4), 045401 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevB.80.045401
Sancho, M.L., Sancho, J.L., Sancho, J.L., Rubio, J.: Highly convergent schemes for the calculation of bulk and surface Green functions. J. Phys. F Met. Phys. 15(4), 851 (1985)
Yariv, A.: An Introduction to Theory and Applications of Quantum Mechanics. Courier Corporation, North Chelmsford (2013)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zarei, M.H., Sharifi, M.J. Graphene nanoribbon photodetectors based on an asymmetric potential barrier: a new concept and a new structure. J Comput Electron 17, 531–539 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10825-018-1132-x
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10825-018-1132-x