Abstract
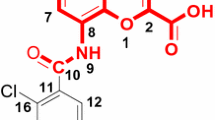
The three-dimensional quantitative structure–activity relationship (3D-QSAR) has been studied on 90 hallucinogenic phenylalkylamines by the comparative molecular field analysis (CoMFA). Two conformations were compared during the modeling. Conformation I referred to the amino group close to ring position 6 and conformation II related to the amino group trans to the phenyl ring. Satisfactory results were obtained by using both conformations. There were still differences between the two models. The model based on conformation I got better statistical results than the one about conformation II. And this may suggest that conformation I be preponderant when the hallucinogenic phenylalkylamines interact with the receptor. To further confirm the predictive capability of the CoMFA model, 18 compounds with conformation I were randomly selected as a test set and the remaining ones as training set. The best CoMFA model based on the training set had a cross-validation coefficient q 2 of 0.549 at five components and non cross-validation coefficient R 2 of 0.835, the standard error of estimation was 0.219. The model showed good predictive ability in the external test with a coefficient R 2pre of 0.611. The CoMFA coefficient contour maps suggested that both steric and electrostatic interactions play an important role. The contributions from the steric and electrostatic fields were 0.450 and 0.550, respectively.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Nichols DE (2004) Pharmacol Ther 101:131
Krebs-Thomson K, Paulus MP, Geyer MA (1998) Neuropsychopharmacology 18:339
Nichols DE (1981) J Pharm Sci 70:839
Gupta SP, Singh P, Bindal MC (1983) Chem Rev 83:633
Clare BW (1990) J Med Chem 33:687
Clare BW (2002) Computer-Aided Mol Des 16:611
Schulze-Alexandru M, Kovar K-A (1999) Quant Struct-Act Relat 18:548
Cramer RD, Patterson DE, Bunce JD (1988) J Am Chem Soc 110:5959
Klebe G, Abraham U, Mietzner T (1994) J Med Chem 37:4130
Song MH, Breneman CM, Sukumar N (2004) Bioorg Med Chem 12:489
Kennard O, Giacovazzo C, Horn AS, Mongiorgi R, Riva di Sanseverino L (1974) J Chem Soc Perkin Trans II 10:1160
Hu WX, Yun LH (1992) Chin Chem Lett 3:271
Pauling P, Data N (1980) J Pro Natl Acad Sci USA 77:708
Tripos Inc. (2005) Sybyl 7.1. Manual, St. Louis, MO
Chambers JJ, Nichols DE (2002) J Comput-Aided Mol Des 16:511
McLean TH, Chambers JJ, Parrish JC, Braden MR, Marona-Lewicka D, Kurrasch-Orbaugh D, Nichols DE (2006) J Med Chem 49:4269
Glennon RA, Young R, Benington F, Morint RD (1982) J Med Chem 25:1163
Domelsmith LN, Eaton TA, Houk KN, Anderson GM, Glennon RA, Shulgin AT, Castagnoli N, Kollman PA (1981) J Med Chem 24:1414
Braun U, Braun G, Jacob P III, Nichols DE, Shulgin AT (1978) NIDA Res Monogr 22:35
Parker MA, Lewicka DM, Lucaites VL, Nelson DL, Nichols DE (1998) J Med Chem 41:5148
Acknowledgements
This work is supported by the Science and Technology Program of Beijing Municipal Government and the Scientific Research Common Program of Commission of Education.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, Z., An, L., Hu, W. et al. 3D-QSAR study of hallucinogenic phenylalkylamines by using CoMFA approach. J Comput Aided Mol Des 21, 145–153 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10822-006-9090-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10822-006-9090-y