Abstract
Purpose
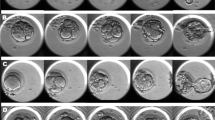
Recently, we established a noninvasive system for selecting human blastocysts with a high pre-transfer implantation potential based on first and second division patterns. The present study was carried out to improve the selection system.
Methods
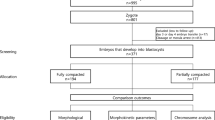
Embryos that completed first and second divisions within 25.90 and 37.88 h after culture, respectively, were selected using a time-lapse incubator. We examined the effects of compaction and blastocyst formation times on pregnancy rates after transferring these embryos at the blastocyst stage.
Results
The completion of compaction and blastocyst formation times (79.93 and 97.47 h after culture, respectively) of embryos resulting in pregnancies after transfer were significantly (P < 0.01) shorter than those (86.46 and 100.34 h after culture, respectively) of embryos that failed to induce pregnancies. Embryo selection based on completion of compaction time improved pregnancy rates (40.9 vs. 74.6%, P < 0.01).
Conclusions
Of the embryos that formed two cells during the first division within 25.90 h after culture and four cells during the second division within 37.88 h after culture, those that completed compaction within 79.93 h after culture before reaching the blastocyst stage had a high implantation potential.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Kirkegaard K, Juhl Hindkjaer J, Ingerslev HJ. Human embryonic development after blastomere removal: a time-lapse analysis. Hum Reprod. 2012;27:97–105.
Kirkegaard K, Agerholm IE, Ingerslev HJ. Time-lapse monitoring as a tool for clinical embryo assessment. Hum Reprod. 2012;27:1277–85.
Cruz M, Gadea B, Garrido N, Pedersen KS, Martínez M, Pérez-Cano I, et al. Embryo quality, blastocyst and ongoing pregnancy rates in oocyte donation patients whose embryos were monitored by time-lapse imaging. J Assist Reprod Genet. 2011;28:569–73.
Rubio I, Galán A, Larreategui Z, Ayerdi F, Bellver J, Herrero J, et al. Clinical validation of embryo culture and selection by morphokinetic analysis: a randomized, controlled trial of the EmbryoScope. Fertil Steril. 2014;102:1287–94.
Pinborg A, Loft A, Schmidt L, Andersen AN. Morbidity in a Danish national cohort of 472 IVF/ICSI twins, 1132 non-IVF/ICSI twins and 634 IVF/ICSI singletons: health-related and social implications for the children and their families. Hum Reprod. 2003;18:1234–43.
Pinborg A, Loft A, Rasmussen S, Schmidt L, Langhoff-Roos J, Greisen G, et al. Neonatal outcome in a Danish national cohort of 3438 IVF/ICSI and 10,362 non-IVF/ICSI twins born between 1995 and 2000. Hum Reprod. 2004;19:435–41.
Milki AA, Hinckley MD, Fisch JD, Dasig D, Behr B. Comparison of blastocyst transfer with day 3 embryo transfer in similar patient populations. Fertil Steril. 2000;73:126–9.
Dennis SJ, Thomas MA, Williams DB, Robins JC. Embryo morphology score on day 3 is predictive of implantation and live birth rates. J Assist Reprod Genet. 2006;23:171–5.
Lee MJ, Lee RKK, Lin MH, Hwu YM. Cleavage speed and implantation potential of early-cleavage embryos in IVF or ICSI cycles. J Assist Reprod Genet. 2012;29:745–50.
Conaghan J, Chen AA, Willman SP, Ivani K, Chenette PE, Boostanfar R, et al. Improving embryo selection using a computer-automated time-lapse image analysis test plus day 3 morphology: results from a prospective multicenter trial. Fertil Steril. 2013;100:412–9.
Lemmen JG, Agerholm I, Ziebe S. Kinetic markers of human embryo quality using time-lapse recordings of IVF/ICSI-fertilized oocytes. Reprod BioMed Online. 2008;17:385–91.
Meseguer M, Herrero J, Tejera A, Hilligsøe KM, Ramsing NB, Remoh J. The use of morphokinetics as a predictor of embryo implantation. Hum Reprod. 2011;26:2658–71.
Hashimoto S, Kato N, Saeki K, Morimoto Y. Selection of high-potential embryos by culture in poly(dimethylsiloxane) microwells and time-lapse imaging. Fertil Steril. 2012;97:332–7.
Cruz M, Garrido N, Herrero J, Pérez-Cano I, Muñoz M, Meseguer M. Timing of cell division in human cleavage-stage embryos is linked with blastocyst formation and quality. Reprod BioMed Online. 2012;25:371–81.
Kirkegaard K, Sundvall L, Erlandsen M, Hindkjær JJ, Knudsen UB, Ingerslev HJ. Timing of human preimplantation embryonic development is confounded by embryo origin. Hum Reprod. 2016;31:324–31.
Shoukir Y, Campana A, Farley T, Sakkas D. Early cleavage of in-vitro fertilized human embryos to the 2-cell stage: a novel indicator of embryo quality and viability. Hum Reprod. 1997;12:1531–6.
Sakkas D, Shoukir Y, Chardonnens D, Bianchi PG, Campana A. Early cleavage of human embryos to the two-cell stage after intracytoplasmic sperm injection as an indicator of embryo viability. Hum Reprod. 1998;13:182–7.
Fenwick J, Platteau P, Murdoch AP, Herbert M. Time from insemination to first cleavage predicts developmental competence of human preimplantation embryos in vitro. Hum Reprod. 2002;17:407–12.
Salumets A, Hydén-Granskog C, Mäkinen S, Suikkari AM, Tiitinen A, Tuuri T. Early cleavage predicts the viability of human embryos in elective single embryo transfer procedures. Hum Reprod. 2003;18:821–5.
Giorgetti C, Hans E, Terriou P, Salzmann J, Barry B, Chabert-Orsini V, et al. Early cleavage: an additional predictor of high implantation rate following elective single embryo transfer. Reprod BioMed Online. 2007;14:85–91.
Emiliani S, Fasano G, Vandamme B, Vannin AS, Verdoodt M, Biramane J, et al. Impact of the assessment of early cleavage in a single embryo transfer policy. Reprod BioMed Online. 2006;13:255–60.
Desai N, Ploskonka S, Goodman LR, Austin C, Goldberg J, Falcone T. Analysis of embryo morphokinetics, multinucleation and cleavage anomalies using continuous time-lapse monitoring in blastocyst transfer cycles. Reprod Biol Endocrinol. 2014;12:54.
Goldman RH, Kaser DJ, Missmer SA, Srouji SS, Farland LV, Racowsky C. Building a model to increase live birth rate through patient-specific optimization of embryo transfer day. J Assist Reprod Genet. 2016;33:1525–32.
Mizobe Y, Oya N, Iwakiri R, Yoshida N, Sato Y, Miyoshi K, et al. Effects of early cleavage patterns of human embryos on subsequent in vitro development and implantation. Fertil Steril. 2016;106:348–53.
Kuwayama M, Vajta G, Kato O, Leibo SP. Highly efficient vitrification method for cryopreservation of human oocytes. Reprod BioMed Online. 2005;11:300–8.
Kuwayama M. Highly efficient vitrification for cryopreservation of human oocytes and embryos: the Cryotop method. Theriogenology. 2007;67:73–80.
Gardner DK, Lane M, Stevens J, Schlenker T, Schoolcraft WB. Blastocyst score affects implantation and pregnancy outcome: towards a single blastocyst transfer. Fertil Steril. 2000;73:1155–8.
Nikas G, Ao A, Winston RM, Handyside AH. Compaction and surface polarity in the human embryo in vitro. Biol Reprod. 1996;55:32–7.
Fleming TP, Sheth B, Fesenko I. Cell adhesion in the preimplantation mammalian embryo and its role in trophectoderm differentiation and blastocyst morphogenesis. Front Biosci. 2001;6:D1000–7.
Larue L, Ohsugi M, Hirchenhain J, Kemler R. E-cadherin null mutant embryos fail to form a trophectoderm epithelium. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1994;91:8263–7.
Bell CE, Calder MD, Watson AJ. Genomic RNA profiling and the programme controlling preimplantation mammalian development. Mol Hum Reprod. 2008;14:691–701.
Alikani M. Epithelial cadherin distribution in abnormal human pre-implantation embryos. Hum Reprod. 2005;20:3369–75.
Iwata K, Yumoto K, Sugishima M, Mizoguchi C, Kai Y, Iba Y, et al. Analysis of compaction initiation in human embryos by using time-lapse cinematography. J Assist Reprod Genet. 2014;31:421–6.
Ivec M, Kovacic B, Vlaisavljevic V. Prediction of human blastocyst development from morulas with delayed and/or incomplete compaction. Fertil Steril. 2011;96:1473–8.
Tao J, Tamis R, Fink K, Williams B, Nelson-White T, Craig R. The neglected morula/compact stage embryo transfer. Hum Reprod. 2002;17:1513–8.
Skiadas CC, Jackson KV, Racowsky C. Early compaction on day 3 may be associated with increased implantation potential. Fertil Steril. 2006;86:1386–91.
Chamayou S, Patrizio P, Storaci G, Tomaselli V, Alecci C, Ragolia C, et al. The use of morphokinetic parameters to select all embryos with full capacity to implant. J Assist Reprod Genet. 2013;30:703–10.
Kirkegaard K, Kesmodel US, Hindkjær JJ, Ingerslev HJ. Time-lapse parameters as preductors of blastocyst development and pregnancy outcome in embryos from good prognosis patients: a prospective cohort study. Hum Reprod. 2013;28:2643–51.
Acknowledgements
The authors thank their fellow embryologist’s doctors and nursing staff at Aiiku Ladies Clinic (Kagoshima, Japan) for their technical assistance and support.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Funding declaration
The studied received no external funding.
Conflicts of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Research involving human participants
This study was approved by the Institutional Review Board of AIIKUKAI Medical Corporation.
Informed consent
Written informed consent for their treatment and for their outcomes to be described was obtained from all patients.
Ethical approval
All procedures performed in studies involving human participants were in accordance with the ethical standards of the Institutional and National Research Committee and the 1964 Helsinki Declaration and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards.
Ethical considerations
All study participants provided informed consent, and the study design was approved by the appropriate ethics review boards. Written informed consent for their treatment and outcomes to be described was obtained from all patients.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mizobe, Y., Ezono, Y., Tokunaga, M. et al. Selection of human blastocysts with a high implantation potential based on timely compaction. J Assist Reprod Genet 34, 991–997 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10815-017-0962-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10815-017-0962-y