Abstract
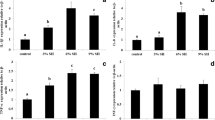
Seaweed in the diet has been widely reported to improve growth and immunity of fish. In China, a large bloom of Sargassum horneri occurred in 2017, which provided biomass for potential development and utilization in the aquaculture industry. The goal of this study was to evaluate the effects of S. horneri meal as a dietary supplement on the growth performance, body composition, and immune response of juvenile turbot (Scophthalmus maximus). A basal diet was supplemented with increasing amounts of S. horneri meal to formulate five groups of experimental diets containing 0, 2.5%, 5%, 7.5%, and 10% S. horneri meal (denoted as SH0, SH2.5, SH5, SH7.5, and SH10). Turbot juveniles (initial weight 66.45 ± 0.52 g) were fed experimental diets for 8 weeks. Final results showed similar growth performance and biometric indices among the diets. Fish fed with S. horneri meal had weight growth rates ranging from 85.03 to 88.12%, which were comparable to those of the SH0 group (90.50%). Crude protein content of whole fish increased linearly with increasing dietary S. horneri content, whereas crude fat content increased first and then decreased. The concentrations of serum cholesterol, high-density lipoprotein cholesterol (HDL-C), and low-density lipoprotein cholesterol (LDL-C) increased linearly with increasing amounts of dietary S. horneri, but the LDL-C/HDL-C ratio did not change significantly (P > 0.05). Activities of serum non-specific immune enzymes (acid phosphatase and catalase) gradually increased with increasing levels of dietary S. horneri. Challenge with the bacterium, Edwardsiella tarda revealed that fish fed the SH0 diet had lower disease resistance compared to those fed the diets containing S. horneri. Under the present experimental conditions, S. horneri meal could be used as an ingredient contributing up to 10% of the diet for juvenile turbot with no negative effects on growth performance. Inclusion of S. horneri in the diet enhanced the activity of non-specific immune enzymes and resistance to pathogenic bacteria. However, higher levels of S. horneri meal also inhibited intestinal lipase activity and reduced lipid deposition in the fish body.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
AOAC (2006) Official methods of analysis of AOAC International. AOAC International, Maryland
Araújo M, Rema P, Sousa-Pinto I, Cunha LM, Peixoto MJ, Pires MA, Seixas F, Brotas V, Beltrán C, Valente LMP (2016) Dietary inclusion of IMTA-cultivated Gracilaria vermiculophylla in rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss) diets: effects on growth, intestinal morphology, tissue pigmentation, and immunological response. J Appl Phycol 28:679–689
Azaza MS, Mensi F, Ksouri J, Dhraief MN, Brini B, Abdelmouleh A, Kraïem MM (2008) Growth of Nile tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus L.) fed with diets containing graded levels of green algae Ulva meal (Ulva rigida) reared in geothermal waters of southern Tunisia. J Appl Ichthyol 24:202–207
Bitou N, Ninomiya M, Tsujita T, Okuda H (1999) Screening of lipase inhibitors from marine algae. Lipids 34:441–445
Bradford MM (1976) A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem 72:248–254
Castro R, Zarra I, Lamas J (2004) Water-soluble seaweed extracts modulate the respiratory burst activity of turbot phagocytes. Aquaculture 229:67–78
Chen JY, Chen JJ, Wu JL (2003) Molecular cloning and functional analysis of zebrafish high-density lipoprotein-binding protein. Comp Biochem Phys B 136:117–130
Cheng W, Liu CH, Yeh ST, Chen JC (2004) The immune stimulatory effect of sodium alginate on the white shrimp Litopenaeus vannamei and its resistance against Vibrio alginolyticus. Fish Shellfish Immunol 17:41–51
Cheng AC, Tu CW, Chen YY, Nan FH, Chen JC (2007) The immunostimulatory effects of sodium alginate and iota-carrageenan on orange-spotted grouper Epinephelus coicoides and its resistance against Vibrio alginolyticus. Fish Shellfish Immunol 22:197–205
Cox S, Abu-Ghannam N, Gupta S (2010) An assessment of the antioxidant and antimicrobial activity of six species of edible Irish seaweeds. Int Food Res J 17:205–220
Dalmo RA, Seljelid R (2006) The immunomodulatory effect of LPS, laminaran and sulphated laminaran [ß(1,3)-D-glucan] on Atlantic salmon, Salmo salar L., macrophages in vitro. J Fish Dis 18:175–185
El-Tawil NE (2010) Effects of green seaweeds (Ulva sp.) as feed supplements in red tilapia (Oreochromis sp.) diet on growth performance, feed utilization and body composition. J Arabian Aquacult Soc 5:179–194
Fevolden SE, Røed K, Gjerde B (1994) Genetic components of post-stress cortisol and lysozyme activity in Atlantic salmon; correlations to disease resistance. Fish Shellfish Immunol 4:507–519
Francis G, Makkar HPS, Becker K (2001) Antinutritional factors present in plant-derived alternate fish feed ingredients and their effects in fish. Aquaculture 199:197–227
Fujiki K, Yano T (1997) Effects of sodium alginate on the non-specific defence system of the common carp (Cyprinus carpio L.). Fish Shellfish Immunol 7:417–427
Fujiki K, Matsuyama H, Yano T (1994) Protective effect of sodium alginates against bacterial infection in common carp, Cyprinus carpio L. J Fish Dis 17:349–355
Gabrielsen BO, Austreng E (1998) Growth, product quality and immune status of Atlantic salmon, Salmo salar L., fed wet feed with alginate. Aquac Res 29:397–401
Gordon T, Castelli WP, Hjortland MC, Kannel WB, Dawber TR (1977) High density lipoprotein as a protective factor against coronary heart disease: the Framingham study. Am J Med 62:707–714
Guo Z, Yang N, Wang Z, Lu Q, Wang R, Lin Y (2015) Optimal dietary Enteromorpha prolifera in turbot (Scophthalmus maximus). Fish Sci 34:423–427 (in Chinese)
Hemmingson JA, Falshaw R, Furneaux RH, Thompson K (2006) Structure and antiviral activity of the galactofucan sulfates extracted from Undaria pinnatifida (Phaeophyta). J Appl Phycol 18:185–193
Jiménez-Escrig A, Gómez-Ordóñez E, Rupérez P (2011) Seaweed as a source of novel nutraceuticals: sulfated polysaccharides and peptides. In: Kim S-K (ed) Advances in food and nutrition research, vol 64. Academic Press, New York, pp 325–337
Kanimozhi S, Krishnaveni M, Deivasigmani B, Rajasekar T, Priyadarshni P (2013) Immunomo-stimulation effects of Sargassum Whitti on Mugil Cephalus against Pseudomonas fluorescence. Int J Curr Microbiol App Sci 2:93–103
Kanjana K, Radtanatip T, Asuvapongpatana S, Withyachumnarnkul B, Wongprasert K (2011) Solvent extracts of the red seaweed Gracilaria fisheri prevent Vibrio harveyi infections in the black tiger shrimp Penaeus monodon. Fish Shellfish Immunol 30:389–396
Kim SS, Lee KJ (2008) Effects of dietary kelp (Ecklonia cava) on growth and innate immunity in juvenile olive flounder Paralichthys olivaceus (Temminck et Schlegel). Aquac Res 39:1687–1690
Kim KW, Kim SS, Khosravi S, Rahimnejad S, Lee KJ (2014) Evaluation of Sargassum fusiforme and Ecklonia cava as dietary additives for olive flounder (Paralichthys olivaceus). Turk J Fish Aquat Sc 14:321–330
Leonard SG, Sweeney T, Bahar B, Lynch BP, O’Doherty JV (2011a) Effect of dietary seaweed extracts and fish oil supplementation in sows on performance, intestinal microflora, intestinal morphology, volatile fatty acid concentrations and immune status of weaned pigs. Br J Nutr 105:549–560
Leonard SG, Sweeney T, Bahar B, Lynch BP, O’Doherty JV (2011b) Effects of dietary seaweed extract supplementation in sows and post-weaned pigs on performance, intestinal morphology, intestinal microflora and immune status. Br J Nutr 106:688–699
Li J, Mo Z, Mao Y, Xiao P (2008) Isolation and classification of two pathogenic bacteria associated with hamorrhages of Scophthalmus maximus. Mar Sci 32:1–5 (in Chinese)
Li H, Liu T, Wang X, Wu Z, Li X, Sun Y, Wang Y (2016) Effect of dietary green alga Enteromorpha prolifera in different formulations on growth of turbot Scophthalmus maximus. Fish Sci 35:334–339 (in Chinese)
Linares F, Peleteiro JB, Álvarez-Blázquez B, Pazos G, Valente LMP, Rodriguez JL (2014) Dietary inclusion of 10% seaweeds in Senegalese sole (Solea senegalensis) juveniles. Paper presented at the Aquaculture Europe, San Sebastián, 14–17 Oct, 2014
Lu Q, Yang N, Wang Z, Guo Z (2015) The effects of dietary Enteromorpha prolifera on the growth and non-specific immunity of juvenile turbot (Scophthalmus maximus). J Qingdao Agri Univ (Nat Sci) 32:62–66 (in Chinese)
Manilal A, Selvin J, George S (2012) In vivo therapeutic potentiality of red seaweed, Asparagopsis (Bonnemaisoniales, Rhodophyta) in the treatment of Vibriosis in Penaeus monodon Fabricius. Saudi J Biol Sci 19:165–175
Mustafa G, Wakamatsu S, Takeda TA, Umino T, Nakagawa H (1995) Effects of algae meal as feed additive on growth, feed efficiency, and body composition in red sea bream. Fish Sci 61:25–28
Narasimhan MK, Pavithra SK, Krishnan V, Chandrasekaran M (2013) In vitro analysis of antioxidant, antimicrobial and antiproliferative activity of Enteromorpha antenna, Enteromorpha linza and Gracilaria corticata extracts. Jundishapur J Nat Pharm Prod 8:151–159
Peixoto MJ, Salas-Leitón E, Pereira LF, Queiroz A, Magalhães F, Rui P, Abreu H, Reis PA (2016) Role of dietary seaweed supplementation on growth performance, digestive capacity and immune and stress responsiveness in European seabass (Dicentrarchus labrax). Aquacult Rep 3:189–197
Qi L, Hu C, Wang M, Shang S, Wilson C (2017) Floating algae blooms in the East China Sea. Geophys Res Lett 44:11501–11509
Queiroz ACdS, Pereira R, Domingues AF, Peixoto MJoD, Goncalves JFMe, Ozorio ROA (2014) Effect of seaweed supplementation on growth performance, immune and oxidative stress responses in gilthead seabream (Sparus aurata). Paper presented at the International Meeting on Marine Research, Peniche, 10–11 Jul, 2014
Reilly P, O’Doherty JV, Pierce KM, Callan JJ, O’Sullivan JT, Sweeney T (2008) The effects of seaweed extract inclusion on gut morphology, selected intestinal microbiota, nutrient digestibility, volatile fatty acid concentrations and the immune status of the weaned pig. Animal 2:1465–1473
Ribeiro AR, Gonçalves A, Barbeiro M, Bandarra N, Nunes ML, Carvalho ML, Silva J, Navalho J, Dinis MT, Silva T, Dias J (2017) Phaeodactylum tricornutum in finishing diets for gilthead seabream: effects on skin pigmentation, sensory properties and nutritional value. J Appl Phycol 29:1945–1956
Rudtanatip T, Withyachumnarnkul B, Wongprasert K (2015) Sulfated galactans from Gracilaria fisheri bind to shrimp haemocyte membrane proteins and stimulate the expression of immune genes. Fish Shellfish Immunol 47:231–238
Skjermo J, Defoort T, Dehasque M, Espevik T, Olsen Y, Skjak-Braek G, Sorgeloos P, Vadstein O (1995) Immunostimulation of juvenile turbot (Scophthalmus maximus L.) using an alginate with high mannuronic acid content administered via the live food organism Artemia. Fish Shellfish Immunol 5:531–534
Solervila A, Coughlan S, Guiry MD, Kraan S, Beardall J, Belay A, Kraan S (2009) The red alga Porphyra dioica as a fish-feed ingredient for rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss): effects on growth, feed efficiency, and carcass composition. J Appl Phycol 21:617–624
Thanigaivel S, Chandrasekaran N, Mukherjee A, Thomas J (2015a) Investigation of seaweed extracts as a source of treatment against bacterial fish pathogen. Aquaculture 448:82–86
Thanigaivel S, Vidhya Hindu S, Vijayakumar S, Mukherjee A, Chandrasekaran N, Thomas J (2015b) Differential solvent extraction of two seaweeds and their efficacy in controlling Aeromonas salmonicida infection in Oreochromis mossambicus: a novel therapeutic approach. Aquaculture 443:56–64
Uribe C, Folch H, Enriquez R, Moran G (2011) Innate and adaptive immunity inteleost fish: a review. Vet Med 56:486–503
Valente LMP, Gouveia A, Rema P, Matos J, Gomes EF, Pinto IS (2006) Evaluation of three seaweeds Gracilaria bursa-pastoris, Ulva rigida and Gracilaria cornea as dietary ingredients in European sea bass (Dicentrarchus labrax) juveniles. Aquaculture 252:85–91
Vizcaíno AJ, Mendes SI, Varela JL, Ruiz-Jarabo I, Rico R, Figueroa FL, Abdala R, Moriñigo MÁ, Mancera JM, Alarcón FJ (2016) Growth, tissue metabolites and digestive functionality in Sparus aurata juveniles fed different levels of macroalgae, Gracilaria cornea and Ulva rigida. Aquac Res 47:3224–3238
Wongprasert K, Rudtanatip T, Praiboon J (2014) Immunostimulatory activity of sulfated galactans isolated from the red seaweed Gracilaria fisheri and development of resistance against white spot syndrome virus (WSSV) in shrimp. Fish Shellfish Immunol 36:52–60
Yeh ST, Lee CS, Chen JC (2006) Administration of hot-water extract of brown seaweed Sargassum duplicatum via immersion and injection enhances the immune resistance of white shrimp Litopenaeus vannamei. Fish Shellfish Immunol 20:332–345
Acknowledgements
We thank International Science Editing (http://www.internationalscienceediting.com) for editing this manuscript.
Funding
This work was supported by the Key Research and Development Program of Yantai City (grant number 2017ZH066), the Modern Agricultural Industry System of Shandong Province of China: Industrial Innovation Team of Algae (grant number SDAIT-26-05), and the Shandong Provincial Natural Science Foundation, China (ZR2017QD007).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, C., Hu, W., Wang, L. et al. Effects of dietary supplementation with Sargassum horneri meal on growth performance, body composition, and immune response of juvenile turbot. J Appl Phycol 31, 771–778 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10811-018-1590-3
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10811-018-1590-3