Abstract
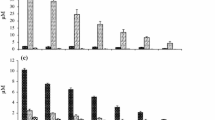
Effects of nitrogen to phosphorous (N/P) ratios of two nitrogen sources (nitrate and ammonium) on growth and toxin production of a tropical estuarine dinoflagellate, Alexandrium minutum Halim, were examined using a strain isolated from a bloom at Tumpat Estuary, Malaysia in September 2001. Experiments were carried out in batch cultures, using either nitrate (N-NO3) or ammonium (N-NH4) as the nitrogen source at a constant amount, and with initial N/P ratios ranging from 5 to 500. Cell density, residual N and P in the medium, cellular toxin quota (Q t), and toxin composition were analyzed throughout the growths. Our results showed that cell densities and growth rates of A. minutum were severely suppressed under high N/P ratios (>100) in both N-NO3 and N-NH4 treatments. Cells tended to be larger at lower growth rate and P-limited cultures. Toxin profile was relatively constant throughout the experiments, with GTX4/GTX1 as the dominant toxin congeners. Cellular toxin quota (Q t) increased with elevated N/P ratios in both N-NO3 and N-NH4 treatments. Toxin production rate, R tox, however was enhanced in N-NH4-grown cultures when P was limited, but showed no difference between N-NO3- and N-NH4-grown cultures when P was replete. Our results clearly showed that N/P ratios as well as the nitrogen compounds not only affected the growth of A. minutum, but also the cellular toxin quota and its toxin production rate.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Anderson DM, Kulis DM, Sullivan JJ, Hall S (1990a) Toxin composition variation in one isolate of the dinoflagellate Alexandrium fundyense. Toxicon 28:885–893. doi:10.1016/0041-0101(90)90018-3
Anderson DM, Kulis DM, Sullivan JJ, Hall S, Lee C (1990b) Dynamics and physiology of saxitoxin production by the dinoflagellates Alexandrium spp. Mar Biol (Berl) 104:511–524. doi:10.1007/BF01314358
Balode M, Purina I, Bechemin C-Y, Maestrini S (1998) Effects of nutrient enrichment on the growth rates and community structure of summer phytoplankton from the Gulf of Riga, Baltic Sea. J Plankton Res 20:2251–2272. doi:10.1093/plankt/20.12.2251
Bechemin C, Grzebyk D, Hachame F, Hummert C, Maestrini SY (1999) Effect of different nitrogen/phosphorus nutrient ratios on the toxin content in Alexandrium minutum. Aquat Microb Ecol 20:157–165. doi:10.3354/ame020157
Boyer GL, Sullivan JJ, Andersen RJ, Harrison PJ, Taylor FJR (1987) Effects of nutrient limitation on toxin production and composition in the marine dinolfagellate Protogonyaulax tamarensis. Mar Biol (Berl) 96:123–128. doi:10.1007/BF00394845
Carvalho AP, Meireles LA, Malcata FX (1998) Rapid spectrophotometric determination of nitrates and nitrites in marine aqueous culture media. Analusis 26:347–351. doi:10.1051/analusis:1998183
Cembella AD (1998) Ecophysiology and metabolism of paralytic shellfish toxins in marine microalgae. In: Anderson DM, Cembella AD, Hallegraeff GM (eds) Physiological ecology of harmful algal blooms. Springer, Berlin, pp 381–426
Cembella AD, Antia NJ, Harrison PJ (1984) The utilization of inorganic and organic phosphorus compounds as nutrients by eukariotic microalgae: a multidisciplinary perspective. Part 1. Crit Rev Microbiol 10(4):317–391
Collos Y, Mornet F, Sciandra A, Waser N, Larson A, Harrison PJ (1999) An optical method for the rapid measurement of micromolar concentrations of nitrate in marine phytoplankton cultures. J Appl Phycol 11:179–184. doi:10.1023/A:1008046023487
Delgado M, Estrada M, Camp J, Fernandez JJ, Santmarti M, Lleti C (1990) Development of a toxic Alexandrium minutum Halim (Dinophyceae) bloom in the harbour of Sant Charles de la Rapita (Ebro Delta, Northwestern Mediterranean). Sci Mar 54:1–7
Dixon GK, Syrett PJ (1988) The growth of dinoflagellates in laboratory cultures. New Phytol 109:297–302. doi:10.1111/j.1469-8137.1988.tb04198.x
Flynn K, Franco JM, Fernandez P, Reguera B, Zapata M, Wood G, Flynn KJ (1994) Change in toxin content, biomass and pigments of the dinoflagellate Alexandrium minutum during nitrogen refeeding and growth into nitrogen or phosphorus stress. Mar Ecol Prog Ser 111:99–109. doi:10.3354/meps111099
Frangópulos M, Guisande C, deBlas E, Maneiro I (2004) Toxin production and competitive abilities under phosphorus limitation of Alexandrium species. Harmful Algae 3:131–139
Giacobbe MG, Oliva FD, Maimone G (1996) Environmental factors and seasonal occurrence of the dinoflagellate Alexandrium minutum, a PSP potential producer, a Mediterranean lagoon. Estuar Coast Shelf Sci 42:539–549. doi:10.1006/ecss.1996.0035
Glibert PM, Magnien R, Lomas MW, Alexander J, Fan C, Haramoto E, Trice M, Kana TM (2001) Harmful algal blooms in the Chesapeake and coastal bays of Maryland, USA: comparison of 1997, 1998, and 1999 events. Estuaries 24:875–883. doi:10.2307/1353178
Guillard RRL (1973) Division rates. In: Sein JR (ed) Handbook of phycological methods. Culture methods and growth measurements. Cambridge University Press, London, pp 289–311
Hillebrand H, Durselen C-D, Kirschtel D, Pollingher U, Zohary T (1999) Biovolume calculation for pelagic and benthic microalgae. J Phycol 35:403–424. doi:10.1046/j.1529-8817.1999.3520403.x
Hodgkiss IJ, Ho KC (1997) Are changes in N:P ratios in coastal waters the key to increased red tide blooms. Hydrobiologia 352:141–147. doi:10.1023/A:1003046516964
Hwang DF, Lu YH (2000) Influence of environmental and nutritional factors on growth, toxicity, and toxin profile of dinoflagellate Alexandrium minutum. Toxicon 38:1491–1503. doi:10.1016/S0041-0101(00)00080-5
Ignatiades L, Gotsis-Skretas O, Metaxatos A (2007) Field and culture studies on the ecophysiology of the toxic dinoflagellate Alexandrium minutum (Halim) present in Greek coastal waters. Harmful Algae 6:153–165. doi:10.1016/j.hal.2006.04.002
John EH, Flynn KJ (2000) Growth dynamics and toxicity of Alexandrium fundyense (Dinophyceae): the effect of changing N:P supply ratios on internal toxin and nutrient levels. Eur J Phycol 35:11–23
Kokinos JP, Anderson DM (1995) Morphological development of resting cysts in cultures of the marine dinoflagellate Lingulodinium polyedrum (= L. machaerophorum). Palynology 19:143–166
Koroleff I (1970) Direct determination of ammonia in natural waters as indophenol blue. Information on techniques and methods for seawater analysis. Interlab Rep Cons Perm Int Explor Mer 3:19–22
Latasa M, Berdalet E (1994) Effect of nitrogen and phosphorus starvation on pigment composition of cultured Heterocapsa sp. J Plankton Res 16:83–94. doi:10.1093/plankt/16.1.83
Lim P-T, Ogata T (2005) Salinity effect on growth and toxin production of four tropical Alexandrium species (Dinophyceae). Toxicon 45:699–710. doi:10.1016/j.toxicon.2005.01.007
Lim P-T, Leaw C-P, Usup G (2004) First incidence of paralytic shellfish poisoning on the east coast of Peninsular Malaysia. In: Phang SM, Chong VC, Ho SS, Mokhtar N, Ooi JLS (eds) Marine science into the new millennium: new perspectives and challenges. University of Malaya Maritime Research Centre, Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia, pp 661–667
Lim P-T, Leaw C-P, Usup G, Kobiyama A, Koike K, Ogata T (2006) Effects of light and temperature on growth, nitrate uptake, and toxin production of two tropical dinoflagellates: Alexandrium tamiyavanichii and Alexandrium minutum (Dinophyceae). J Phycol 42:786–799. doi:10.1111/j.1529-8817.2006.00249.x
Lippemeier S, Frampton DMF, Blackburn SI, Geier SC, Negri AP (2003) Influence of phosphorus limitation on toxicity and photosynthesis of Alexandrium minutum (Dinophyceae) monitored by in-line detection of variable chlorophyll fluorescence. J Phycol 38:320–331
Maguer JF, Wafar M, Madec C, Morin P, Erard-Le Denn E (2004) Nitrogen and phophorous requirements of an Alexandrium minutum bloom in the Penzi estuary, France. Limnol Oceanogr 49:1108–1114
Oshima Y (1995) Postcolumn derivatization liquid chromatography method for paralytic shellfish toxins. J AOAC Int 78:528–532
Siu GKY, Young MLC, Chan DKO (1997) Environmental and nutritional factors which regulate population dynamics and toxin production in the dinoflagellate Alexandrium catenella. Hydrobiologia 352:117–140. doi:10.1023/A:1003042431985
Strickland JDH, Parsons TR (1968) A practical handbook of the sea water analysis. Bull Fish Res Board Canada 167:310
Tanaka K, Choo P-S (2000) Influences of nutrient outwelling from the mangrove swamp on the distribution of phytoplankton in the Matang Mangrove Estuary, Malaysia. J Oceanogr 56:69–78. doi:10.1023/A:1011114608536
Turpin DH (1988) Physiological mechanisms in phytoplankton resource competition. In: Sandren C (ed) Growth and reproduction strategies of freshwater microalgae. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, pp 316–368
Vaulot D, Lebot N, Marie D, Fukai E (1996) Effect of phophorous on the Synechococcus cell cycle in surface Mediterranean waters during summer. Appl Environ Microbiol 62:2527–2533
Wood G, Flynn KJ (1995) Growth of Heterosigma carterae (Raphidophyceae) on nitrate and ammonium at three photon flux densities: evidence for N-stress in nitrate-growing cells. J Phycol 31:859–867. doi:10.1111/j.0022-3646.1995.00859.x
Yamamoto T, Tarutani K (1999) Growth and phosphate uptake kinetics of the toxic dinoflagellate Alexandrium tamrense from Hiroshima Bay in the Seto Inland Sea, Japan. Phycol Res 47:27–32. doi:10.1111/j.1440-1835.1999.tb00280.x
Acknowledgments
This study was financially supported by Grant-in-Aid for Scientific Research from the Ministry of Education, Science and Cultures, Japan to T. Ogata and UNIMAS short-term research grant to P.-T. Lim.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lim, PT., Leaw, CP., Kobiyama, A. et al. Growth and toxin production of tropical Alexandrium minutum Halim (Dinophyceae) under various nitrogen to phosphorus ratios. J Appl Phycol 22, 203–210 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10811-009-9443-8
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10811-009-9443-8