Abstract
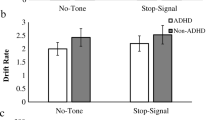
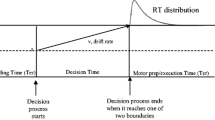
Using Ratcliff’s diffusion model and ex-Gaussian decomposition, we directly evaluate the role individual differences in reaction time (RT) distribution components play in the prediction of inhibitory control and working memory (WM) capacity in children with and without ADHD. Children with (n = 91, \( \overline{\mathrm{x}} \) age = 10.2 years, 67 % male) and without ADHD (n = 62, \( \overline{\mathrm{x}} \) age = 10.6 years, 46 % male) completed four tasks of WM and a stop signal reaction time (SSRT) task. Children with ADHD had smaller WM capacities and less efficient inhibitory control. Diffusion model analyses revealed that children with ADHD had slower drift rates (v) and faster non-decision times (Ter), but there were no group differences in boundary separations (a). Similarly, using an ex-Gaussian approach, children with ADHD had larger τ values than non-ADHD controls, but did not differ in μ or σ distribution components. Drift rate mediated the association between ADHD status and performance on both inhibitory control and WM capacity. τ also mediated the ADHD-executive function impairment associations; however, models were a poorer fit to the data. Impaired performance on RT and executive functioning tasks has long been associated with childhood ADHD. Both are believed to be important cognitive mechanisms to the disorder. We demonstrate here that drift rate, or the speed at which information accumulates towards a decision, is able to explain both.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alderson, R. M., Rapport, M. D., & Kofler, M. J. (2007). Attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder and behavioral inhibition: a meta-analytic review of the stop-signal paradigm. Journal of Abnormal Child Psychology, 35(5), 745–758.
Alderson, R. M., Rapport, M. D., Sarver, D. E., & Kofler, M. J. (2008). Adhd and behavioral inhibition: a re-examination of the stop-signal task. [Journal; Peer Reviewed Journal]. Journal of Abnormal Child Psychology: An official publication of the International Society for Research in Child and Adolescent Psychopathology, 36(7), 989–998.
Balota, D. A., & Yap, M. J. (2011). Moving beyond the mean in studies of mental chronometry: the power of response time distributional analyses. Current Directions in Psychological Science, 20(3), 160–166.
Banaschewski, T., Yordanova, J., Kolev, V., Heinrich, H., Albrecht, B., & Rothenberger, A. (2008). Stimulus context and motor preparation in attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder. Biological Psychology, 77(1), 53–62.
Beck, J. M., Ma, W. J., Kiani, R., Hanks, T., Churchland, A. K., Roitman, J., Shadlen, M. N., Latham, P. E., & Pouget, A. (2008). Probabilistic population codes for bayesian decision making. Neuron, 60(6), 1142–1152.
Biederman, J., Monuteaux, M. C., Doyle, A. E., Seidman, L. J., Wilens, T. E., Ferrero, F., Morgan, C. L., & Faraone, S. V. (2004). Impact of executive function deficits and attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder (adhd) on academic outcomes in children. Journal of Consulting and Clinical Psychology, 72(5), 757–766.
Blandon, A. Y., Calkins, S. D., Grimm, K. J., Keane, S. P., & O’Brien, M. (2010). Testing a developmental cascade model of emotional and social competence and early peer acceptance. Development and Psychopathology, 22, 737–748.
Bogacz, R., Brown, E., Moehlis, J., Holmes, P., & Cohen, J. D. (2006). The physics of optimal decision making: a formal analysis of models of performance in two-alternative forced-choice tasks. Psychological Review, 113(4), 700–765.
Broyd, S. J., Demanuele, C., Debener, S., Helps, S. K., James, C. J., & Sonuga-Barke, E. (2009). Default-mode brain dysfunction in mental disorders: a systematic review. Neuroscience and Biobehavioral Reviews, 33, 279–296.
Buckholtz, J. W., & Meyer-Lindenberg, A. (2012). Psychopathology and the human connectome: toward a transdiagnostic model of risk for mental illness. Neuron, 74(6), 990–1004.
Buzy, W. M., Medoff, D. R., & Schweitzer, J. B. (2009). Intra-individual variability among children with adhd on a working memory task: an ex-gaussian approach. Child Neuropsychology, 15(5), 441–459.
Castellanos, F. X., & Tannock, R. (2002). Neuroscience of attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder: the search for endophenotypes. Nature Reviews Neuroscience, 3(8), 617–628.
Castellanos, F. X., Sonuga-Barke, E. J. S., Scheres, A., Di Martino, A., Hyde, C., & Walters, J. R. (2005). Varieties of attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder-related intra-individual variability. Biological Psychiatry, 57(11), 1416–1423.
Castellanos, F. X., Kelly, C., & Milham, M. P. (2009). The restless brain: attention-deficit hyperactivity disorder, resting-state functional connectivity, and intrasubject variability. Canadian Journal of Psychiatry-Revue Canadienne De Psychiatrie, 54(10), 665–672.
Conners, C. K. (2001). Conners’ rating scales—revised technical manual. North Tonawanda, NY: Multi-Health Systems Inc.
Conway, A., Kane, M. J., Bunting, M. F., Hambrick, D. Z., Wilhelm, O., & Engle, R. W. (2005). Working memory span tasks: a methodological review and user’s guide. Psychonomic Bulletin & Review, 12(5), 769–786.
Deco, G., Jirsa, V., McIntosh, A. R., Sporns, O., & Kotter, R. (2009). Key role of coupling, delay, and noise in resting brain fluctuations. PNAS Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 106(25), 10302–10307.
Douglas, V. I. (1999). Cognitive control processes in attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder. In H. C. Quay & A. E. Hogan (Eds.), Handbook of disruptive behavior disorders (Vol. xiii) (pp. 105–138). NY: Kluwer Academic Publishers.
Epstein, J. N., Langberg, J. M., Rosen, P. J., Graham, A., Narad, M. E., Antonini, T. N., Brinkman, W. B., Froehlich, T., Simon, J. O., & Altaye, M. (2011). Evidence for higher reaction time variability for children with adhd on a range of cognitive tasks including reward and event rate manipulations. Neuropsychology, 25(4), 427–441.
Fair, D. A., Posner, J., Nagel, B. J., Bathula, D., Costa Dias, T. G., Mills, K. L., Blythe, M. S., Giwa, A., Schmitt, C., & Nigg, J. T. (2010). Atypical defaultnetwork connectivity in youth with attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder. Biological Psychiatry, 68(12), 1084–1091.
Fair, D., Bathula, D., Nikolas, M., & Nigg, J. T. (2012). Distinct neuropsychological subgroups in typically developing youth inform heterogeneity in children with adhd. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America. doi:10.1073/pnas.1115365109.
Faraone, S. V., Perlis, R. H., Doyle, A., Smoller, J. W., Goralnick, J. J., Holmgren, M. A., & Sklar, P. (2005). Molecular genetics of attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder. Biological Psychiatry, 57(11), 1313–1323.
Fassbender, C., Zhang, H., Buzy, W. M., Cortese, C. R., Mizuiria, D., Beckett, L., & Schweitzer, J. B. (2009). A lack of default network suppression is linked to increased distractibility in adhd. Brain Research, 1273(1), 114–128.
Frazier, T. W., Demaree, H. A., & Youngstrom, E. A. (2004). Meta-analysis of intellectual and neuropsychological test performance in attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder. Neuropsychology, 18(3), 543–555.
Froehlich, T. E., Lanphear, B., Epstein, J. N., Barbaresi, W. J., Katusic, S. K., & Kahn, R. S. (2007). Prevalence, recognition, and treatment of attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder in a national sample of us children. Archives of Pediatrics & Adolescent Medicine, 161(9), 857–864.
Fry, A. F., & Hale, S. (2000). Relationships among processing speed, working memory, and fluid intelligence in children. Biological Psychology, 54(1–3), 1–34.
Geurts, H. M., Grasman, R. P. P. P., Verté, S., Oosterlaan, J., Roeyers, H., van Kammen, S. M., & Sergeant, J. A. (2008). Intra-individual variability in adhd, autism spectrum disorders and tourette’s syndrome. Neuropsychologia, 46(13), 3030–3041.
Grudnik, J. L., & Kranzler, J. H. (2001). Meta-analysis of the relationship between intelligence and inspection time. Intelligence, 29(6), 523–535.
Halperin, J. M., & Schulz, K. P. (2006). Revisiting the role of the prefrontal cortex in the pathophysiology of attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder. Psychological Bulletin, 132(4), 560–581.
Heekeren, H. R., Marrett, S., & Ungerleider, L. G. (2008). The neural systems that mediate human perceptual decision making. Nature Reviews Neuroscience, 9(6), 467–479.
Hervey, A. S., Epstein, J. N., Curry, J. F., Tonev, S., Arnold, L. E., Conners, C. K., Hinshaw, S. P., Swanson, J. M., & Hechtman, L. (2006). Reaction time distribution analysis of neuropsychological performance in an adhd sample. Child Neuropsychology, 12(2), 125–140.
Huang-Pollock, C. L., & Karalunas, S. L. (2010). Working memory demands impair skill acquisition in children with adhd. Journal of Abnormal Psychology, 119(1), 174–185.
Huang-Pollock, C. L., Karalunas, S. L., Moore, A., & Tam, H. (2011). Working memory subsystems and their contribution to working memory deficits in children with adhd. Poster presented at the biennial meeting of the International Society for Research in Child and Adolescent Psychopathology, Chicago, IL.
Huang-Pollock, C. L., Karalunas, S. L., Tam, H., & Moore, A. N. (2012). Evaluating vigilance deficits in adhd: a meta-analysis of cpt performance. Journal of Abnormal Psychology, 121(2), 360–371.
Hurks, P. P. M., Adam, J. J., Hendriksen, J. G. M., Vles, J. S. H., Feron, F. J. M., Kalff, A. C., Kroes, M., Steyaert, J., Crolla, I. F. A. M., van Zeben, T. M. C. B., & Jolles, J. (2005). Controlled visuomotor preparation deficits in attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder. Neuropsychology, 19(1), 66–76.
Insel, T., Cuthbert, B., Garvey, M., Heinssen, R., Pine, D. S., Quinn, K., Sanislow, C., & Wang, P. (2010). Research domain criteria (rdoc): toward a new classification framework for research on mental disorders. The American Journal of Psychiatry, 167(7), 748–751.
Kail, R. (2007). Longitudinal evidence that increases in processing speed and working memory enhance children’s reasoning. Psychological Science, 18(4), 312–313.
Karalunas, S. L., Huang-Pollock, C. L., & Nigg, J. T. (2012). Decomposing adhd-related effects in response speed and variability. Neuropsychology, 26(6), 684–694.
Klimkeit, E. I., Mattingley, J. B., Sheppard, D. M., Lee, P., & Bradshaw, J. L. (2005). Motor preparation, motor execution, attention, and executive functions in attention deficit/hyperactivity disorder (adhd). Child Neuropsychology, 11(2), 153–173.
Kühn, S., Schmiedek, F., Schott, B., Ratcliff, R., Heinze, H.-J., Düzel, E., Lindenberger, U., & Lövden, M. (2011). Brain areas consistently linked to individual differences in perceptual decision-making in younger as well as older adults before and after training. Journal of Cognitive Neuroscience, 23(9), 2147–2158.
Kuntsi, J., & Stevenson, J. (2001). Psychological mechanisms in hyperactivity: Ii the role of genetic factors. Journal of Child Psychology and Psychiatry, 42(2), 211–219.
Kuntsi, J., Rogers, H., Swinard, G., Borger, N., van der Meere, J., Rijsdijk, F., & Asherson, P. (2006). Reaction time inhibition, working memory and ‘delay aversion’ performance: genetic influences and their interpretation. Psychological Medicine, 36(11), 1613–1624.
Lacouture, Y., & Cousineau, D. (2008). How to use matlab to fit the ex-gaussian and other probability functions to a distribution of response times. Tutorials in Quantitative Methods for Psychology, 4(1), 35–45.
Lahey, B. B., Applegate, B., McBurnett, K., Biederman, J., Greenhill, L., Hynd, G. W., Barkley, R. A., Newcorn, J., Jensen, P., Richters, J., Garfinkel, B., Kerdyk, L., Frick, P. J., Ollendick, T., Perez, D., Hart, E. L., Waldman, I., & Shaffer, D. (1994). Dsm-iv field trials for attention-deficit hyperactivity disorder in children and adolescents. The American Journal of Psychiatry, 151(11), 1673–1685.
Lajoie, G., Anderson, V., Anderson, P., Tucker, A. R., Robertson, I. H., & Manly, T. (2005). Effects of methylphenidate on attention skills in children with attention deficit/hyperactivity disorder. Brain Impairment, 6(1), 21–32.
Leth-Steensen, C., Elbaz, Z. K., & Douglas, V. I. (2000). Mean response times, variability and skew in the responding of adhd children: a response time distributional approach. Acta Psychologica, 104(2), 167–190.
Lijffijt, M., Bekker, E. M., Quik, E. H., Bakker, J., Kenemans, J. L., & Verbaten, M. N. (2004). Differences between low and high trait impulsivity are not associated with differences in inhibitory motor control. Journal of Attention Disorders, 8(1), 25–32.
Lijffijt, M., Kenemans, J. L., Verbaten, M. N., & van Engeland, H. (2005). A meta-analytic review of stopping performance in attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder: deficient inhibitory motor control? Journal of Abnormal Psychology, 114(2), 216–222.
MacDonald, S. W. S., Li, S.-C., & Bäckman, L. (2009). Neural underpinnings of within-person variability in cognitive functioning. Psychology and Aging, 24(4), 792–808.
Martinussen, R., Hayden, J., Hogg-Johnson, S., & Tannock, R. (2005). A meta-analysis of working memory impairments in children with attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder. Journal of the American Academy of Child and Adolescent Psychiatry, 44(4), 377–384.
Matzke, D., & Wagenmakers, E.-J. (2009). Psychological interpretation of the ex-gaussian and shifted wald parameters: a diffusion model analysis. Psychonomic Bulletin & Review, 16(5), 798–817.
Miyake, A., Friedman, N. P., Emerson, M. J., Witzki, A. H., Howerter, A., & Wager, T. D. (2000). The unity and diversity of executive functions and their contributions to complex “frontal lobe” tasks: a latent variable analysis. Cognitive Psychology, 41(1), 49–100.
Mulder, M. J., Bos, D., Weusten, J. M. H., van Belle, J., van Dijk, S. C., Simen, P., van Engeland, H., & Durston, S. (2010). Basic impairments in regulating the speed-accuracy tradeoff predict symptoms of attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder. Biological Psychiatry, 68(12), 1114–1119.
Newman, M. E. J. (2006). Modularity and community structure in networks. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 103(23), 8577–8582.
Nigg, J. T., Willcutt, E. G., Doyle, A., & Sonuga-Barke, E. J. S. (2005). Causal heterogeneity in attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder: do we need neuropsychologically impaired subtypes? Biological Psychiatry, 57(11), 1224–1230.
Philiastides, M. G., & Sajda, P. (2006). Temporal characterization of the neural correlates of perceptual decision making in the human brain. Cerebral Cortex, 16(4), 509–518.
Philiastides, M. G., Ratcliff, R., & Sajda, P. (2006). Neural representation of task difficulty and decision making during perceptual categorization: a timing diagram. The Journal of Neuroscience, 26(35), 8965–8975.
Preacher, K. J., & Hayes, A. F. (2008). Asymptotic and resampling strategies for assessing and comparing indirect effects in multiple mediator models. Behavior Research Methods, 40, 879–891.
Ratcliff, R. (2002). A diffusion model account of response time and accuracy in a brightness discrimination task: fitting real data and failing to fit fake but plausible data. Psychonomic Bulletin & Review, 9(2), 278–291.
Ratcliff, R., & McKoon, G. (2008). The diffusion decision model: theory and data for two-choice decision tasks. Neural Computation, 20(4), 873–922.
Ratcliff, R., & Rouder, J. N. (1998). Modeling response times for two-choice decisions. Psychological Science, 9(5), 347–356.
Ratcliff, R., Cherian, A., & Segraves, M. (2003). A comparison of macaque behavior and superior colliculus neuronal activity to predictions from models of two-choice decisions. Journal of Neurophysiology, 90(3), 1392–1407.
Ratcliff, R., Thapar, A., Gomez, P., & McKoon, G. (2004). A diffusion model analysis of the effects of aging in the lexical-decision task. Psychology and Aging, 19(2), 278–289.
Ratcliff, R., Philiastides, M. G., & Sajda, P. (2009). Quality of evidence for perceptual decision making is indexed by trial-to-trial variability of the eeg. PNAS Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 106(16), 6539–6544.
Reynolds, C., & Kamphaus, R. (2004). Behavioral assessment system for children, 2nd ed. Manual. Circle Pines, MN: AGS Publishing.
Rommelse, N. N., Altink, M. E., Oosterlaan, J., Beem, L., Buschgens, C. J. M., Buitelaar, J. K., & Sergeant, J. A. (2008). Speed, variability, and timing of motor output in adhd: which measures are useful for endophenotypic research. Behavior Genetics, 38(2), 121–132.
Salthouse, T. A., McGuthry, K. E., & Hambrick, D. Z. (1999). A framework for analyzing and interpreting differential aging patterns: application to three measures of implicit learning. [Article]. Aging Neuropsychology and Cognition, 6(1), 1–18.
Sattler, J. (2008). Resource guide to accompany assessment of children: Cognitive foundations (5th ed.). San Diego: Jerome Sattler Publisher, Inc.
Schachar, R., Chen, S., Logan, G., Ornstein, T. J., Crosbie, J., Ickowicz, A., & Pakulak, A. (2004). Evidence for an error monitoring deficit in attention deficit hyperactivity disorder. Journal of Abnormal Child Psychology, 32(3), 285–293.
Schmiedek, F., Oberauer, K., Wilhelm, O., Süß, H.-M., & Wittmann, W. W. (2007). Individual differences in components of reaction time distributions and their relations to working memory and intelligence. Journal of Experimental Psychology. General, 136(3), 414–429.
Schmiedek, F., Lövdén, M., & Lindenberger, U. (2009). On the relation of mean reaction time and intraindividual reaction time variability. Psychology and Aging, 24(4), 841–857.
Sergeant, J. (2000). The cognitive-energetic model: an empirical approach to attention-deficit hyperactivity disorder. Neuroscience and Biobehavioral Reviews, 24(1), 7–12.
Sergeant, J. A., & Scholten, C. A. (1985). On data limitations in hyperactivity. Journal of Child Psychology and Psychiatry, 26(1), 111–124.
Sergeant, J., Oosterlaan, J., & van der Meere, J. (1999). Information processing and energetic factors in attention deficit/hyperactivity disorder. In H. Quay & A. Hogan (Eds.), Handbook of disruptive behavior disorders. NY: Kluwer Academic Publishers.
Sheslow, D., & Adams, W. (2003). Wide range assessment of memory and learning, 2nd ed (wraml-2): Administration and technical manual. Wilmington, DE: Wide Range.
Sonuga-Barke, E., & Castellanos, F. X. (2007). Spontaneous attentional fluctuations in impaired states and pathological conditions: a neurobiological hypothesis. Neuroscience and Biobehavioral Reviews, 31(7), 977–986.
Spaniol, J., & Bayen, U. J. (2005). Aging and conditional probability judgments: a global matching approach. Psychology and Aging, 20(1), 165–181.
Steger, J., Imhof, K., Coutts, E., Gundelfinger, R., Steinhausen, H. C., & Brandeis, D. (2001). Attentional and neuromotor deficits in adhd. Developmental Medicine and Child Neurology, 43(3), 172–179.
Suskauer, S. J., Simmonds, D. J., Caffo, B. S., Denckla, M. B., Pekar, J. J., & Mostofsky, S. H. (2008). Fmri of intrasubject variability in adhd: anomalous premotor activity with prefrontal compensation. Journal of the American Academy of Child and Adolescent Psychiatry, 47(10), 1141–1150.
Thapar, A., Ratcliff, R., & McKoon, G. (2003). A diffusion model analysis of the effects of aging on letter discrimination. Psychology and Aging, 18(3), 415–429.
Verbruggen, F., & Logan, G. D. (2009). Proactive adjustments of response strategies in the stop-signal paradigm. Journal of Experimental Psychology. Human Perception and Performance, 35(3), 835–854.
Verbruggen, F., Logan, G., Liefooghe, B., & Vandierendonck, A. (2008). Short-term aftereffects of response inhibition: repetition priming or between-trial control adjustments. Journal of Experimental Psychology of Human Performance, 34(2), 413–426.
Voss, A., & Voss, J. (2007). Fast-dm: a free program for efficient diffusion model analysis. Behavior Research Methods, 39(4), 767–775.
Voss, A., Rothermund, K., & Voss, J. (2004). Interpreting the parameters of the diffusion model: an empirical validation. Memory & Cognition, 32(7), 1206–1220.
Wagenmakers, E.-J., Grasman, R. P. P. P., & Molenaar, P. C. M. (2005). On the relation between the mean and the variance of a diffusion model response time distribution. Journal of Mathematical Psychology, 49, 195–204.
Wechsler, D. (2003). Wechsler intelligence scale for children, 4th ed (wisc-iv) technical and interpretive manual. San Antonio: Harcourt Brace.
Weissman, D. H., Roberts, K. C., Visscher, K. M., & Woldorff, M. G. (2006). The neural bases of momentary lapses in attention. Nature Neuroscience, 9, 971–978.
Widaman, K. F. (2006). Best practices in quantitative methods for developmentalists: Iii. Missing data: what to do with or without them. Monographs of the Society for Research in Child Development, 71(3), 42–64.
Willcutt, E. G., Doyle, A., Nigg, J. T., Faraone, S. V., & Pennington, B. F. (2005). Validity of the executive function theory of attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder: a meta-analytic review. Biological Psychiatry, 57(11), 1336–1346.
Winstanley, C. A., Eagle, D. M., & Robbins, T. W. (2006). Behavioral models of impulsivity in relation to adhd: translation between clinical and preclinical studies. Clinical Psychology Review, 26(4), 379–395.
Acknowledgments
The project described was supported in part by R01MH084947 to Cynthia Huang-Pollock and F32MH098632 to Sarah Karalunas from the National Institutes of Mental Health. The content is solely the responsibility of the authors and does not necessarily represent the official views of the National Institute of Mental Health or the National Institutes of Health.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Karalunas, S.L., Huang-Pollock, C.L. Integrating Impairments in Reaction Time and Executive Function Using a Diffusion Model Framework. J Abnorm Child Psychol 41, 837–850 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10802-013-9715-2
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10802-013-9715-2