Abstract
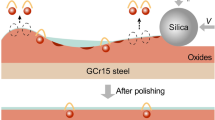
An ultra-smooth surface is required for mechanical components to improve the lubrication performance. In this study, the combination of 5-methyl-1H-benzotriazole (5-methyl-BTA) and thiazole (TA) was used as an effective composite corrosion inhibitor for chemical mechanical polishing of GCr15 bearing steel. The results reveal that, compared with the single corrosion inhibitor 5-methyl-BTA or TA, their combination results in lower surface roughness. By the synergistic corrosion inhibition effect of 5-methyl-BTA and TA, an ultra-smooth GCr15 steel surface with a sub-nanometer surface roughness Ra is achieved and the underneath substrate is free of damage. Specifically, 5-methyl-BTA can be first rapidly adsorbed on the GCr15 steel surface through the chemical and physical pathways. Then TA can be physically adsorbed on the GCr15 steel surface, and in addition, a part of TA may be further physically adsorbed on the outer layer of the surface film. As a result, the effective corrosion inhibition film is formed and cooperates with the oxide film to suppress the corrosive wear. Through our developed two-step polishing method, a rough GCr15 steel surface with the Ra of 263 nm can become ultra-smooth with the Ra of 0.8 nm in 21 min, providing a promising ultra-precision processing technique for industry.
Graphic abstract























Similar content being viewed by others
References
Beswick JM (ed) (2002) Bearing steel technology. ASTM International, Philadelphia
Ueda T, Mitamura N (2009) Mechanism of dent initiated flaking and bearing life enhancement technology under contaminated lubrication condition. Part II: Effect of rolling element surface roughness on flaking resulting from dents, and life enhancement technology of rolling bearings under contaminated lubrication condition. Tribol Int 42(11):1832–1837. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.triboint.2008.12.010
Komata H, Iwanaga Y, Ueda T, Ueda K, Mitamura N (2015) Enhanced performance of rolling bearings by improving the resistance of rolling elements to surface degradation. In: Beswick JM (ed) Bearing Steel technologies: 10th volume, advances in steel technologies for rolling bearings. ASTM International, West Conshohocken, pp 272–290. https://doi.org/10.1520/STP158020140085
Skurka JC (1970) Elastohydrodynamic lubrication of roller bearings. J Lubr Technol 92(2):281–288. https://doi.org/10.1115/1.3451388
Li Y (2007) Microelectronic applications of chemical mechanical planarization. Wiley, Hoboken
Kao MJ, Hsu FC, Peng DX (2014) Synthesis and characterization of SiO2 nanoparticles and their efficacy in chemical mechanical polishing steel substrate. Adv Mater Sci Eng 2014:1–8. https://doi.org/10.1155/2014/691967
Peng D-X (2014) Chemical mechanical polishing of steel substrate using aluminum nanoparticles abrasive slurry. Ind Lubr Tribol 66(1):124–130. https://doi.org/10.1108/ILT-10-2011-0078
Peng D-X (2014) Optimization of chemical mechanical polishing parameters on surface roughness of steel substrate with aluminum nanoparticles via Taguchi approach. Ind Lubr Tribol 66(6):685–690. https://doi.org/10.1108/ILT-07-2012-0063
Jiang L, He Y, Luo J (2015) Chemical mechanical polishing of steel substrate using colloidal silica-based slurries. Appl Surf Sci 330:487–495. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsusc.2015.01.016
Liu J, Jiang L, Wu H, Zhao T, Qian L (2020) 5-Methyl-1H-benzotriazole as an effective corrosion inhibitor for ultra-precision chemical mechanical polishing of bearing steel. J Electrochem Soc 167(13):131502. https://doi.org/10.1149/1945-7111/abb0d9
Wu H, Jiang L, Liu J, Deng C, Huang H, Qian L (2020) Efficient chemical mechanical polishing of AISI 52100 bearing steel with TiSol-NH4 dispersion-based slurries. Tribol Lett 68(1):34. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11249-020-1274-4
Wu H, Jiang L, Zhong X, Liu J, Qin N, Qian L (2021) Exploring the role of −NH2 functional groups of ethylenediamine in chemical mechanical polishing of GCr15 bearing steel. Friction 9(6):1673–1687. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40544-020-0460-6
Zhou J, Niu X, Cui Y, Wang Z, Wang J, Wang R (2020) Study on the film forming mechanism, corrosion inhibition effect and synergistic action of two different inhibitors on copper surface chemical mechanical polishing for GLSI. Appl Surf Sci 505:144507. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsusc.2019.144507
Hu L, Pan G, Wang H, Zhang X, Wang Z, Zhu T (2020) The synergy and DFT study of TT-LYK and potassium oleate on chemical mechanical polishing of cobalt in alkaline medium. Mater Chem Phys 256:123672. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matchemphys.2020.123672
Mehmeti VV, Berisha AR (2017) Corrosion study of mild steel in aqueous sulfuric acid solution using 4-methyl-4H-1,2,4-triazole-3-thiol and 2-mercaptonicotinic acid—an experimental and theoretical study. Front Chem. https://doi.org/10.3389/fchem.2017.00061
Ramya K, Mohan R, Joseph A (2014) Interaction of benzimidazoles and benzotriazole: its corrosion protection properties on mild steel in hydrochloric acid. J Mater Eng Perform 23(11):4089–4101. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11665-014-1183-5
Li J, Liu Y, Wang T, Lu X, Luo J (2013) Electrochemical investigation of copper passivation kinetics and its application to low-pressure CMP modeling. Appl Surf Sci 265:764–770. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsusc.2012.11.106
Kim YJ, Kwon OJ, Kang MC, Kim JJ (2011) Effects of the functional groups of complexing agents and Cu oxide formation on Cu dissolution behaviors in Cu CMP process. J Electrochem Soc 158(2):H190–H196. https://doi.org/10.1149/1.3522811
Cao P, Yao J, Zheng J, Gu R, Tian ZQ (2002) Comparative study of inhibition effects of benzotriazole for metals in neutral solutions as observed with surface-enhanced Raman spectroscopy. Langmuir 18(1):100–104
Yao JL, Ren B, Huang ZF, Cao PG, Gu RA, Tian Z-Q (2003) Extending surface Raman spectroscopy to transition metals for practical applications IV. A study on corrosion inhibition of benzotriazole on bare Fe electrodes. Electrochim Acta 48(9):1263–1271. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0013-4686(02)00834-4
Bhargava G, Gouzman I, Chun CM, Ramanarayanan TA, Bernasek SL (2007) Characterization of the “native” surface thin film on pure polycrystalline iron: A high resolution XPS and TEM study. Appl Surf Sci 253(9):4322–4329. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsusc.2006.09.047
Joong Kim K, Moon DW, Lee SK, Jung K-H (2000) Formation of a highly oriented FeO thin film by phase transition of Fe3O4 and Fe nanocrystallines. Thin Solid Films 360:118–121. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0040-6090(99)00562-3
Mullet M, Khare V, Ruby C (2008) XPS study of Fe(II)-Fe(III) (oxy)hydroxycarbonate green rust compounds. Surf Interface Anal 40(3–4):323–328. https://doi.org/10.1002/sia.2758
Dong J, Dong J, Han E, Liu C, Ke W (2009) Rusting evolvement of mild steel under wet/dry cyclic condition with pH 4.00 NaHSO3 solution. Corros Sci Prot Technol 21(1):1–4 (in Chinese)
Cao P, Gu R, Tian Z (2002) Electrochemical and surface-enhanced Raman spectroscopy studies on inhibition of iron corrosion by benzotriazole. Langmuir 18(20):7609–7615
Guo L, Ren X, Zhou Y, Xu S, Gong Y, Zhang S (2017) Theoretical evaluation of the corrosion inhibition performance of 1,3-thiazole and its amino derivatives. Arab J Chem 10(1):121–130. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.arabjc.2015.01.005
Mao J, He X, Tang Y (2019) Role of heteroatoms in the adsorption of thiazole on Cu (1 1 1) surface: first principles study. Corros Sci 148:171–177. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.corsci.2018.12.014
Meighan M, MacNeil J, Falconer R (2008) Determining the solubility product of Fe(OH)3: an equilibrium study with environmental significance. J Chem Educ 85(2):254. https://doi.org/10.1021/ed085p254
Cao C (2008) Principles of electrochemistry of corrosion (in Chinese). Chemical Industry Press, Beijing (in Chinese)
Chu L, Wang J, Dong J, Liu H, Sun X (2012) Treatment of coking wastewater by an advanced Fenton oxidation process using iron powder and hydrogen peroxide. Chemosphere 86(4):409–414. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2011.09.007
Hart DS, Davis LC, Erickson LE, Callender TM (2004) Sorption and partitioning parameters of benzotriazole compounds. Microchem J 77(1):9–17. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.microc.2003.08.005
University W (2016) Analytical chemistry. Higher Education Press, Beijing (in Chinese)
Israelachvili JN (2010) Intermolecular and surface forces, 3rd edn. Academic Press, Cambridge
Ji Ram V, Sethi A, Nath M, Pratap R (2019) Five-membered heterocycles. In: Ji Ram V, Sethi A, Nath M, Pratap R (eds) The chemistry of heterocycles. Elsevier, Amsterdam, pp 149–478. https://doi.org/10.1016/B978-0-08-101033-4.00005-X
Xing C, Yu Y (2001) Organic chemistry. Shandong University Press, Jinan (in Chinese)
Hong Y, Devarapalli V, Roy D, Babu S (2007) Synergistic roles of dodecyl sulfate and benzotriazole in enhancing the efficiency of CMP of copper. J Electrochem Soc 154(6):H444–H453
Acknowledgements
The authors are grateful for the financial support by the National Key R&D Program of China (2020YFA0711001), National Natural Science Foundation of China (51975488 and 51991373), National Key R&D Program of China (2018YFB2000400), and Beijing Key Laboratory of Long-life Technology of Precise Rotation and Transmission Mechanisms (BZ0388201902).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, J., Jiang, L. & Qian, L. Achievement of sub-nanometer surface roughness of bearing steel via chemical mechanical polishing with the synergistic effect of heterocyclic compounds containing N and S. J Appl Electrochem 52, 357–373 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10800-021-01625-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10800-021-01625-2