Abstract
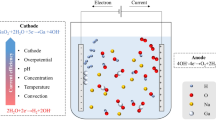
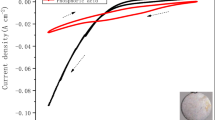
The electrochemical behaviour and recovery of rhodium in an acidic solution were investigated using a rotating disc electrode system and a modified electrochemical cyclone cell, respectively. The electrochemical polarization data indicated that the Rh3+ ions were reduced to metallic Rh below −0.1 V, and the limiting current density for rhodium deposition was observed at around −0.3 V (vs. SCE) with a diffusion coefficient of 6.3 × 10−6 cm2 s−1 using the Levich equation. The effects of the applied voltage and the initial concentration of rhodium were examined using the modified cyclone cell, and more than 91 % of the rhodium in solution was recovered within 2 h under the optimal conditions.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Reid FH (1963) Electrodeposition of the platinum-group metals. Met Rev 8:167–211
Tucker PM, Waite MJ, Hayden BE (2004) Electrocatalytic reduction of nitrate on activated rhodium electrode surfaces. J Appl Electrochem 34:781–796. doi:10.1023/B:JACH.000003510.607.19248.b6
Roth JF (1975) The production of acetic acid. Platinum Metals Rev 19:12–14
Heidingsfeldova M, Capka M (1985) Rhodium complexes as catalysts for hydrosilylation crosslinking of silicone rubber. J Appl Polym Sci 30:1837–1846. doi:10.1002/app.1985.070300505
Halligudi SB, Bajaj HC, Bhatt KN, Krishnaratnam M (1992) Hydrogenation of benzene to cyclohexane catalyzed by rhodium(I) complex supported on montmorillonite clay. React Kinet Catal Lett 48:547–552. doi:10.1007/BF02162706D
Akutagawa S (1995) Asymmetric synthesis by metal BINAP catalysts. Appl Catalysis A 128:171–207. doi:10.1016/0926-860X(95)00097-6
de Aberasturi DJ, Pinedo R, de Larramendi IR, de Larramendi JIR, Rojo T (2011) Recovery by hydrometallurgical extraction of the platinum-group metals from car catalytic converters. Min Eng 24:505–513. doi:10.1016/j.mineng.2010.12.009
Nowottny C, Halwachs W, Schurgerl K (1997) Recovery of platinum, palladium and rhodium from industrial process leaching solutions by reactive extraction. Sep Purif Technol 12:135–144. doi:10.1016/S1383-5866(97)00041-5
Kim CH, Woo SJ, Jeon SH (2000) Recovery of platinum-group metals from recycled automotive catalytic converters by carbochlorination. Ind Eng Chem Research 39:1185–1192. doi:10.1021/ie9905355
Fontas C, Salvado V, Hidalgo M (2002) Separation and concentration of Pd, Pt, and Rh from automotive catalytic converters by combining two hollow-fiber liquid membrane systems. Ind Eng Chem Research 41:1616–1620. doi:10.1021/ie010468q
Pletcher D, Urbina RI (1997) Electrodeposition of rhodium. Part 1. Chloride solutions. J Electroanal Chem 421:137–144. doi:10.1016/S0022-0728(96)04844-9
Pletcher D, Urbina RI (1997) Electrodeposition of rhodium. Part 2. Sulfate solutions. J Electroanal Chem 421:145–151. doi:10.1016/S0022-0728(96)04845-0
Oliveira RTS, Santos MC, Bulhoes LOS, Pereira EC (2004) Rh electrodeposition on Pt in acidic medium: a study using cyclic voltammetry and an electrochemical quartz crystal microbalance. J Electroanal Chem 569:233–240. doi:10.1016/j.jelechem.2004.03.006
Schulz EN, Salinas DR, Garcia SG (2010) Electrodeposition of rhodium onto a pre-treated glassy carbon surface. Electrochem Commun 12:583–586. doi:10.1016/j.elecom.2010.02.005
Park YJ, Fray DJ (2009) Recovery of high purity precious metals from printed circuit boards. J Hazard Mater 164:1152–1158. doi:10.1016/j.jhazmat.2008.09.043
Dhamo N (1994) An electrochemical hydrocyclone cell for the treatment of dilute solutions: approximate plug-flow model for electrodeposition kinetics. J Appl Electrochem 24:745–750. doi:10.1007/BF00578089
Dhamo N, Kammel R (1992) Electrochemical hydrocyclone-cell for metal recovery from dilute solutions. Metall 46:912–916
Kim YU, Cho HW, Lee HS, Lee CK, Lee JC, Rhee KI, Sohn HJ, Kang T (2002) Electrowinning of palladium using a modified cyclone reactor. J Appl Electrochem 32:1235–1239. doi:10.1023/A:1021667015212
Kim SK, Lee CK, Lee JC, Rhee KI, Sohn HJ, Kang T (2004) Electrowinning of platinum using a modified cyclone reactor. Resour Process 51:48–51. doi:10.4144/rpsj.51.4812
Wythers MC (2012) Advances in materials science research. Nova, New York, pp 257–274
Milazzon G (1963) Electrochemistry, theoretical principles and practical applications. Elsevier, Amsterdam, pp 160–172
Levich VJ (1962) Physicochemical hydrodynamics. Prentice-Hall, Englewood, p 69
Lin CS, Denton EB, Gaskill HS, Putnam GL (1951) Diffusion-controlled Electrode Reactions. Ind Eng Chem 43:2136–2143. doi:10.1021/ie5051a045
Chilton TH, Colburn AP (1934) Mass transfer (Absorption) coefficients prediction from data on heat transfer and fluid friction. Ind Eng Chem 26:1183–1187. doi:10.1021/ie50299a012
Ross TK, Wragg AA (1965) Electrochemical mass transfer studies in annuli. Electrochim Acta 10:1093–1106
Sonin AA (1983) Jet impingement systems for electroplating applications: mass transfer correlations. J Electrochem Soc 130:1501–1505. doi:10.1149/1.2120019
de Sa MS, Shemilt LW, Soegiarto IV (1991) Mass transfer in the entrance region for axial and swirling annular flow. Can J Chem Eng 69:294–299. doi:10.1002/cjce.5450690136
Acknowledgments
This research was supported by the Basic Research Project of the Korea Institute of Geoscience and Mineral Resources (KIGAM) funded by the Ministry of Science, ICT and Future Planning of Korea.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yu, BC., Kim, SK., Sohn, JS. et al. Electrochemical behaviour and electrowinning of rhodium in acidic chloride solution. J Appl Electrochem 44, 741–745 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10800-014-0683-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10800-014-0683-1