Abstract
Purpose
To evaluate the effect of a new nutritional supplement based on melatonin on the intraocular pressure (IOP) in normotensive subjects.
Patients and methods
A short-term prospective study was designed. Sixty-seven normotensive subjects were recruited. Patients were divided into two groups. The daily group (DG) (n = 18) was instructed to take the supplement between 22:00 and 23:00 (before sleeping) for 3 consecutive days. IOP was measured from 10.00 to 11.00 am the day before treatment and during the 3 days of experiment. The acute group (AG) (n = 49) was instructed to take the supplement after the second measure (11.00) of the second day. IOP was measured 1 h and just before the intake of the supplement and 1 and 2 h after. All measurements in this group were taken 1 day before without any supplement (control) and the day of experiment.
Results
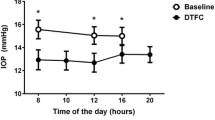
The DG group showed a significant decrease in IOP after supplement intake in all days of experiment, from 14.9 ± 3.4 mm Hg to 13.8 ± 2.9 mm Hg after 3 days of experiment (p value < 0.001). For AG, IOP did not change during the control day; however, a reduction of 1 mm Hg was found 2 and 3 h after supplement intake, from 15.7 ± 2.5 mm Hg to 14.7 ± 2.5 mm Hg and 15.1 ± 2.7 mm Hg, respectively, being statistically significant (p value < 0.001).
Conclusion
The supplement based on melatonin was able to reduce the IOP in normotensive subjects after 2 h of intake. Moreover, the daily intake showed a reduction in IOP during the 3 days of experiment.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Casson RJ, Chidlow G, Wood JP, Crowston JG, Goldberg I (2012) Definition of glaucoma: clinical and experimental concepts. Clin Exp Ophthalmol 40(4):341–349
Alarma-Estrany P, Pintor J (2007) Melatonin receptors in the eye: location, second messengers and role in ocular physiology. Pharmacol Ther 113(3):507–522
Osborne NN (1994) Serotonin and melatonin in the iris/ciliary processes and their involvement in intraocular pressure. Acta Neurobiol Exp (Wars) 54(Suppl):57–64
Martinez-Aguila A, Fonseca B, Bergua A, Pintor J (2013) Melatonin analogue agomelatine reduces rabbit’s intraocular pressure in normotensive and hypertensive conditions. Eur J Pharmacol 701(1–3):213–217
Mediero A, Alarma-Estrany P, Pintor J (2009) New treatments for ocular hypertension. Auton Neurosci 147(1–2):14–19
Pescosolido N, Gatto V, Stefanucci A, Rusciano D (2015) Oral treatment with the melatonin agonist agomelatine lowers the intraocular pressure of glaucoma patients. Ophthalmic Physiol Opt 35(2):201–205
Ismail SA, Mowafi HA (2009) Melatonin provides anxiolysis, enhances analgesia, decreases intraocular pressure, and promotes better operating conditions during cataract surgery under topical anesthesia. Anesth Analg 108(4):1146–1151
Samples JR, Krause G, Lewy AJ (1988) Effect of melatonin on intraocular pressure. Curr Eye Res 7(7):649–653
Majsterek I, Malinowska K, Stanczyk M, Kowalski M, Blaszczyk J, Kurowska AK, Kaminska A, Szaflik J, Szaflik JP (2011) Evaluation of oxidative stress markers in pathogenesis of primary open-angle glaucoma. Exp Mol Pathol 90(2):231–237
Tan DX, Manchester LC, Hardeland R, Lopez-Burillo S, Mayo JC, Sainz RM, Reiter RJ (2003) Melatonin: a hormone, a tissue factor, an autocoid, a paracoid, and an antioxidant vitamin. J Pineal Res 34(1):75–78
World Medical Association (2013) World Medical Association Declaration of Helsinki: ethical principles for medical research involving human subjects. JAMA 310(20):2191–2194
Hellmann H, Mooney S (2010) Vitamin B6: a molecule for human health? Molecules 15(1):442–459
Ohguro H, Ohguro I, Yagi S (2013) Effects of black currant anthocyanins on intraocular pressure in healthy volunteers and patients with glaucoma. J Ocul Pharmacol Ther 29(1):61–67
Sudesh S, Moseley MJ, Thompson JR (1993) Accuracy of Goldmann tonometry in clinical practice. Acta Ophthalmol 71(2):185–188
Ogbuehi KC, Almubrad TM (2008) Accuracy and reliability of the Keeler Pulsair EasyEye non-contact tonometer. Optom Vis Sci 85(1):61–66
Funding
The authors do not have any financial interest on the materials and instruments used in this study, and this study was not funded by third parties.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
All procedures performed in studies involving human participants were in accordance with the ethical standards of the institutional and/or national research committee and with the 1964 Helsinki Declaration and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Carracedo-Rodríguez, G., Martínez-Águila, A., Rodriguez-Pomar, C. et al. Effect of nutritional supplement based on melatonin on the intraocular pressure in normotensive subjects. Int Ophthalmol 40, 419–422 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10792-019-01199-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10792-019-01199-1