Abstract
Background
Diabetic neuropathy is one of the most common complications of diabetes. The synthetic drugs available in the market have side effects and limitations for diabetic patients, the vast majority of whom are in the upper age group. In this regard, based on Persian medicinal sources, Nigella sativa (N. sativa) has proved to have beneficial effects on neuropathic pain and neurological disorders. In this study, the effect of N. sativa is investigated topically in patients with diabetic neuropathy.
Methods
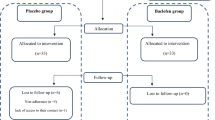
This study was performed as a double-blind clinical trial on 120 neuropathic patients. The patients were divided into three groups. The first group received a topical N. sativa product as an ointment, the second group was given a topical placebo, and the third received 300 mg gabapentin capsules. The blindness was done in first and second groups. Diabetic neuropathy was assessed before the study using the Michigan Neuropathy Screening Instrument (MNSI). In addition, neuropathy symptoms were evaluated after the trial using the MNSI questionnaire.
Results
The data were elicited from the patients’ answers to a number of questions in the Michigan questionnaire. There were statistically significant differences between the group that received the topical N. sativa product and the other two groups in terms of legs and feet numbness (p value = 0.001), burning pain in feet or legs (p value = 0.001), muscle cramps in feet or legs (p value = 0.001), prickling fleeing in feet or legs (p value = 0.001), hurting of the skin when the bed covers touch it (p value = 0.005), aggravated symptoms at night (p value = 0.001) and hurting feelings in the legs when walking (p value = 0.032). However, the three studied groups were not statistically different in distinguishing hot water from cold water.
Conclusion
According to the results of this study, the topical use of N. sativa, compared to the current drugs, has acceptable improving effects on diabetic neuropathic patients.

Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
Enquiries about data availability should be directed to the authors.
References
Booya F, Bandarian F, Larijani B, Pajouhi M, Nooraei M, Lotfi J (2005) Potential risk factors for diabetic neuropathy: a case control study. BMC Neurol 5:24
Callaghan BC, Cheng HT, Stables CL, Smith AL, Feldman EL (2012) Diabetic neuropathy: clinical manifestations and current treatments. The Lancet Neurology. 11(6):521–534
Celik F, Göçmez C, Karaman H, Kamaşak K, Kaplan I, Akıl E et al (2014) Therapeutic effects of thymoquinone in a model of neuropathic pain. Current Therapeutic Res, Clinical Exp. 76:11–16
Dalli M, Daoudi NE, Azizi S-e, Benouda H, Bnouham M, Gseyra N. (2021) Chemical composition analysis using HPLC-UV/GC-MS and inhibitory activity of different Nigella sativa fractions on Pancreatic α-Amylase and intestinal glucose absorption. BioMed research international
Dehghan F, Hajiaghaalipour F, Yusof A, Muniandy S, Hosseini SA, Heydari S et al (2016) Saffron with resistance exercise improves diabetic parameters through the GLUT4/AMPK pathway in-vitro and in-vivo. Sci Rep 6(1):25139
Dyck PJ, Kratz KM, Karnes JL, Litchy WJ, Klein R, Pach JM et al (1993) The prevalence by staged severity of various types of diabetic neuropathy, retinopathy, and nephropathy in a population-based cohort: the rochester diabetic neuropathy study. Neurology 43(4):817–824
Eftekharsadat B, Babaei-Ghazani A, Habibzadeh A (2015) The efficacy of 100 and 300 mg gabapentin in the treatment of carpal tunnel syndrome. Iranian J Pharmaceutical Res: IJPR. 14(4):1275
Elahi H, Masroorchehr MR, Nemati S, Kamalinejad M, Besharat M, Hajimehdipoor H, et al. (2014) Historical applications of Nigella sativa L.(Black cumin) in the treatment of Zokam and Nazleh in Persian medicine. Journal of Research on History of Medicine. 3(1).
Feldman EL, Stevens MJ, Thomas PK, Brown MB, Canal N, Greene DA (1994) A practical two-step quantitative clinical and electrophysiological assessment for the diagnosis and staging of diabetic neuropathy. Diabetes Care 17(11):1281–1289
Feldman EL, Nave K-A, Jensen TS, Bennett DL (2017) New horizons in diabetic neuropathy: mechanisms, bioenergetics, and pain. Neuron 93(6):1296–1313
Hajhashemi V, Ghannadi A, Jafarabadi H (2004) Black cumin seed essential oil, as a potent analgesic and antiinflammatory drug. Phytotherapy Research : PTR. 18(3):195–199
Hamdan A, Haji Idrus R, Mokhtar MH (2019) Effects of Nigella sativa on type-2 diabetes mellitus: a systematic review. Inter J Environ Research Public Health. 16(24):4911
Hannan J, Ansari P, Haque A, Sanju A, Huzaifa A, Rahman A, et al. (2019) Nigella sativa stimulates insulin secretion from isolated rat islets and inhibits the digestion and absorption of (CH2O) n in the gut. Bioscience Reports 39(8)
Häuser W, Bartram-Wunn E, Bartram C, Reinecke H, Tölle T (2011) Systematic review: placebo response in drug trials of fibromyalgia syndrome and painful peripheral diabetic neuropathy-magnitude and patient-related predictors. Pain 152(8):1709–1717
Hershey DS (2017) Diabetic peripheral neuropathy: evaluation and management. J Nurse Practitioners 13(3):199–204
Heshmati J, Namazi N (2015) Effects of black seed (Nigella sativa) on metabolic parameters in diabetes mellitus: a systematic review. Complementary Therapies Med. 23(2):275–282
Holmes CJ, Hastings MK (2021) The application of exercise training for diabetic peripheral neuropathy. J Clinical Med. 10(21):5042
Hosseinzadeh H, Jafari MR, Khouei A, Rahmani M. (2006) Anti-ischemic effect of Nigella sativa L. seed in male rats
Ikhsan M, Hiedayati N, Maeyama K, Nurwidya F (2018) Nigella sativa as an anti-inflammatory agent in asthma. BMC Res Notes 11(1):1–5
Islam MH, Ahmad IZ, Salman MT (2015) Neuroprotective effects of Nigella sativa extracts during germination on central nervous system. Pharmacogn Mag 11(Suppl 1):S182–S189
Kanter M (2008) Effects of Nigella sativa and its major constituent, thymoquinone on sciatic nerves in experimental diabetic neuropathy. Neurochem Res 33(1):87–96
Khare CP (2004) Indian herbal remedies: rational Western therapy, ayurvedic, and other traditional usage. Springer science and business media, Botany
Khodaie SA, Emadi F, Naseri M, Kamalinejad M, Riahi SM, Alijaniha F et al (2021) The effect of myrtus communis aqueous extract-containing gel on wound healing in streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats. Curr Drug Discov Technol 18(4):542–547
Kioskli K, Scott W, Winkley K, Kylakos S, McCracken LM (2019) Psychosocial factors in painful diabetic neuropathy: a systematic review of treatment trials and survey studies. Pain Medicine (malden, Mass). 20(9):1756–1773
Mahboubi M, Mohammad Taghizadeh Kashani L, Mahboubi M. (2018) Nigella sativa fixed oil as alternative treatment in management of pain in arthritis rheumatoid. Phytomedicine : international journal of phytotherapy and phytopharmacology.46:69–77.
Maher RL, Hanlon J, Hajjar ER (2014) Clinical consequences of polypharmacy in elderly. Expert Opinion Drug Safety. 13(1):57–65
Majdinasab N, Kaveyani H, Azizi M (2019) A comparative double-blind randomized study on the effectiveness of duloxetine and gabapentin on painful diabetic peripheral polyneuropathy. Drug Design, Devel Therapy. 13:1985
Mathur ML, Gaur J, Sharma R, Haldiya KR (2011) Antidiabetic properties of a spice plant Nigella sativa. J Endocrino Metabolism. 1(1):1–8
Mohebbati R, Abbasnezhad A (2020) Effects of Nigella sativa on endothelial dysfunction in diabetes mellitus: a review. J Ethnopharmacol 252:112585
Namazi N, Larijani B, Ayati MH, Abdollahi M (2018) The effects of Nigella sativa L. on obesity: a systematic review and meta-analysis. J Ethnopharmacol 219:173–181
Nasser M, Tibi A, Savage-Smith E (2009) Ibn Sina’s canon of medicine: 11th century rules for assessing the effects of drugs. J Royal Soc Med. 102(2):78–80
Nazarbaghi S, Amiri-Nikpour MR, Eghbal AF, Valizadeh R (2017) Comparison of the effect of topiramate versus gabapentin on neuropathic pain in patients with polyneuropathy: a randomized clinical trial. Electron Physician 9(10):5617
Nukada H (2014) Ischemia and diabetic neuropathy. Handbook Clin Neurokl. 126:469–487
Petramfar P, Moein M, Samani SM, Tabatabaei SH, Zarshenas MM (2016) Trachyspermum ammi 10 % topical cream versus placebo on neuropathic pain, a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. Neurol Sci : off J Italian Neurol Soc Italian Society Clinical Neurophysiol. 37(9):1449–1455
Pop-Busui R, Boulton AJ, Feldman EL, Bril V, Freeman R, Malik RA et al (2017) Diabetic neuropathy: a position statement by the American diabetes association. Diabetes Care 40(1):136–154
Qureshi MS, Iqbal M, Zahoor S, Ali J, Javed MU (2017) Ambulatory screening of diabetic neuropathy and predictors of its severity in outpatient settings. J Endocrinol Invest 40(4):425–430
Raza AKMM (2016) Peripheral neuropathies associated with diabetes mellitus: a review. J Neurol Res. 6(5–6):91–94
Safi S, Razmpoosh E, Fallahzadeh H, Mazaheri M, Abdollahi N, Nazari M et al (2021) The effect of Nigella sativa on appetite, anthropometric and body composition indices among overweight and obese women: a crossover, double-blind, placebo-controlled, randomized clinical trial. Complementary Therapies Med. 57:102653
Salehi OR, Hosseini SA, Farkhaie F, Farzanegi P, Zar A (2019) The effect of moderate intensity endurance training with Genistein on brain-derived neurotrophic factor and tumor necrosis Factor-αin diabetic rats. J Nutrition, Fasting Health. 7(1):44–51
Salehi OR, Hosseini SA, Farkhaie F, Farzanegi P, Zar A (2019) The effect of moderate intensity endurance training with genistein on brain-derived neurotrophic factor and tumor necrosis factor-α in diabetic rats. J Nutrition, Fasting Health. 7(1):44–51
Seidavi A, Laudadio V, Khazaei R, Puvača N, Selvaggi M, Tufarelli V (2020) Feeding of black cumin (Nigella sativa L.) and its effects on poultry production and health. World’s Poultry Sci J 76(2):346–357
Setayesh M, Zargaran A, Sadeghifar AR, Salehi M, Rezaeizadeh H (2018) New candidates for treatment and management of carpal tunnel syndrome based on the Persian canon of medicine. Integrative Medicine Research. 7(2):126–135
Shamsinejad S, Davati A, Roughani M, Ghasemlouie A, Afshinmajd S. (2018) Evaluation of topiramate efficacy on neuropathic pain in patients with diabetic polyneuropathy. Acta Medica Iranica.:764–8.
Soleimani-Dodran M, Alipanah-Moghadam R, Jeddi F, Babaei M, Salimnejad R, Bahreini E (2022) Effect of hydroalcoholic seed extract of Nigella sativa on hepatic and pancreatic factors of Nrf2 and FGF21 in the regulation of insulin transcription factors of MafA and PDX-1 in streptozotocin-treated diabetic rats. Nutri Metabolism. 19(1):1–12
Timar B, Timar R, Gaiță L, Oancea C, Levai C, Lungeanu D (2016) The Impact of diabetic neuropathy on balance and on the risk of falls in patients with Type 2 diabetes mellitus: a cross-sectional study. PLoS ONE 11(4):e0154654
Vakilinia SR, Vaghasloo MA, Aliasl F, Mohammadbeigi A, Bitarafan B, Etripoor G et al (2020) Evaluation of the efficacy of warm salt water foot-bath on patients with painful diabetic peripheral neuropathy: a randomized clinical trial. Complementary Therapies Med. 49:102325
Vase L, Wartolowska K (2019) Pain, placebo, and test of treatment efficacy: a narrative review. British J Anaesthesia. 123(2):e254–e262
Vase L, Petersen GL, Lund K (2014) Placebo effects in idiopathic and neuropathic pain conditions. Handbook Exp Pharmacol. 225:121–136
Veves A, Backonja M, Malik RA (2008) Painful diabetic neuropathy: epidemiology, natural history, early diagnosis, and treatment options. Pain Med 9(6):660–674
Zakaria A, Jais MR, Ishak R (2018) Analgesic properties of Nigella sativa and Eucheuma cottonii extracts. J Natural Sci, Bio, Med. 9(1):23–26
Funding
The authors have not disclosed any funding.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors have not disclosed any competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Khodaie, SA., Nikkhah, H., Namiranian, N. et al. Topical Nigella sativa L. product: a new candidate for the management of diabetic peripheral neuropathy. Inflammopharmacol 32, 551–559 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10787-023-01338-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10787-023-01338-2